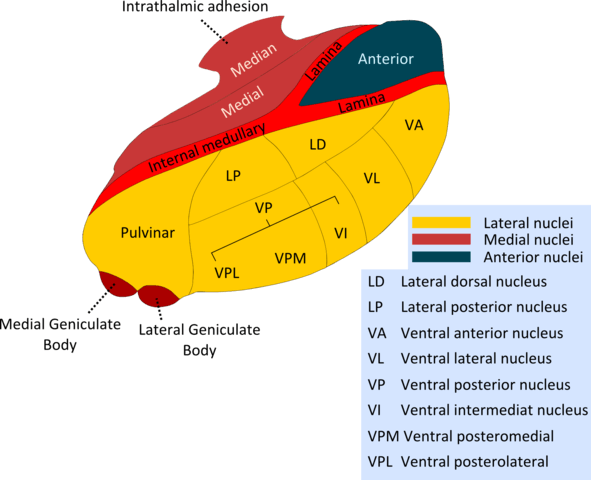
Structure of Thalamus
A vertical “Y” shaped white mater – internal medullary lamina divides thalamus into:
- Anterior nuclear groups
- Medial nuclear groups
- Lateral nuclear groups
In anatomical position:
- Dorsal surface of brain: faces towards sky
- Ventral surface of brain: faces towards floor
Pulvinar = Posterior end or posterior pole of thalamus
Thalamic Connections
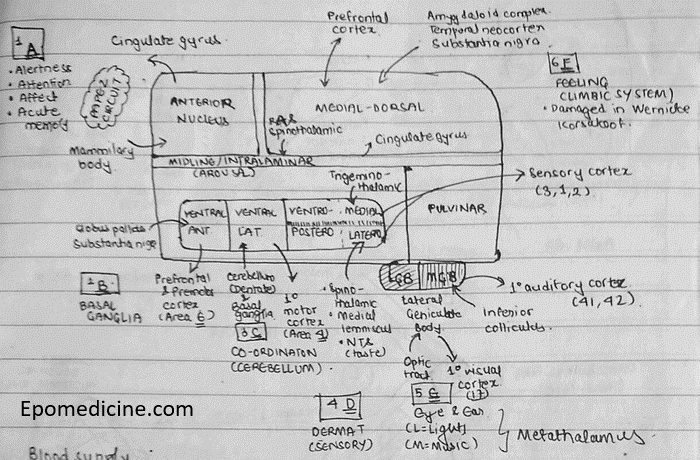
Picture mnemonic
Remember the schematic diagram drawn below showing important parts of thalamus in an anticlockwise fashion:
- Anterior nucleus
- Ventral nuclear group:
- Anterior
- Lateral
- Posterior
- Medial
- Lateral
- Lateral and Medial geniculate body
- Medial-Dorsal nucleus
Now, we assign alphabets “A, B, C, D, E, F” sequentially to these important structures in anticlockwise fashion starting from anterior nucleus.
“A” for Anterior nucleus
A for:
- Alertness
- Attention
- Affect
- Acute memory
These are the functions of limbic system – Papez circuit:
- Afferent: Mamillary body
- Efferent: Cingulate gyrus
“B” for Ventral-anterior nucleus
B for: Basal ganglia
- Afferent: Globus pallidus and Substantia nigra
- Efferent: Brodmann Area 6 (Prefrontal and premotor cortex)
“C” for Ventral-lateral nucleus
C for: Co-ordination and Cerebellum
- Afferent: Cerebellum (Dentate nucleus) and Basal ganglia
- Efferent: Brodmann Area 4 (Primary motor cortex)
“D” for Ventral-Posterior nucleus
D for: Dermatome (Sensory)
- Afferent:
- Ventro-postero-medial (VPM) nucleus: Trigemino-thalamic tract, Solitario-thalamic tract
- Medial = Mask (face)
- Taste (Nucleus tractus solitarius)
- Ventro-postero-lateral (VPL) nucleus:
- Lateral = Limbs
- Spinothalamic tract
- Medial lemniscus
- Ventro-postero-medial (VPM) nucleus: Trigemino-thalamic tract, Solitario-thalamic tract
- Efferent:
- Brodmann Area 3, 1, 2 (Sensory cortex)
Thalamic pain syndrome: Involvement of primary somatosensory thalamic nucleus (ventral posterior lateral [VPL]/ventral posterior medial thalamus [VPM]) and the anterior pulvinar, a major spinothalamic target gives rise to thalamic pain syndrome. Approximately 25% of patients with a sensory stroke due to a thalamic lesion will develop central post-stroke pain. Thalamic pain is a severe, treatment-resistant pain syndrome. The pain is often described as burning or constrictive and is frequently accompanied by evoked pain (allodynia/hyperalgesia), paresthesias, or summation hyperpathia. 1
“E” for Geniculate Bodies
E for: Eyes and Ears
- Lateral geniculate body = Light (Eyes)
- Afferent: Optic tract
- Efferent: Primary visual cortex (Area 17)
- Medial geniculate body = Music (Ears)
- Afferent: Inferior colliculus
- Efferent: Primary auditory cortex (Area 41, 42)
“F” for Medial-Dorsal Nucleus
F for: Feelings (Limbic system)
- Afferent:
- Amygdala
- Olfactory cortex
- Efferent:
- Prefrontal cortex
- Limbic system
Thiamine deficiency in alcoholics (Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome) results in degeneration of the medial-dorsal nucleus of thalamus, mamillary bodies, hippocampus and vermis of cerebellum.
Other mnemonics:
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) = Light (Visual pathway)
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) = Music (Auditory pathway)
- Ventral postero-lateral nucleus (VPL) = Very Painful Limbs (Spinothalamic tract and Dorsal column)
- Ventral postero-medial nucleus (VPM) = Very Painful Mouth (Trigeminal and Gustatory pathway)
- Ventrolateral nucleus (VL) = Victory Lap (Motor)
- Dorsomedial nucleus (DMN) = Dog’s Memory and Nose (Memory, smell and emotions)

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.

Sir, Isn’t solitariothalamic tract reaching the VPL nucleus?
Hello Renjini,
Solitario-thalamic tract reaches VPM nucleus where the trigemino-thalamic tract reaches. Remember the tongue lies inside head and all the sensation from head are carried into VPM nucleus.
There had been a mistake initially, it has been corrected. Thank you.
Sir I appreciate and respect your beautiful efforts !!
This topic is so tough to understand and memorize but you reduced it to “a piece of cake”.
I am indebted to you Sir…
God Bless You!
Found this very helpful,thank you.
Hello sir,
Sorry,i framed my question in a wrong way! Saw the correction ,got it now,
Thank you.
tnx much. it help me
So much helpful
made it really simple, thank you
Good one sir
Thank you sir a beautiful representation and a beautiful way to remember thanks a lot
This is very helpful to all medcal students! Thankyou very much for the contribution in making studying easier for us 🙂
This was a great topic. Keep up the good work!
I have used your mneumonic for my students.. thank you so much
Found this really helpful prepping for Usmle….thank you!
Its really helpful thank you
Excellent stuff, was really struggling to memorise the thalamic nuclei before I saw this.
Sir.. It was very useful.. Hope u come up with these kind of usefull tips..
U r now the god of thalamus
WHre are rhe connection of dorso lateral and postero lateral parts
This is what I need most for these exams. Thanks
thank you sooooo much sir. you are a savior.
Hypothalamic Nuclear organisation in quadrepeds (Cows) may have a evolutionary base in bipeds (Humans)…