When an older loved one begins forgetting things, it’s natural to wonder if it’s just part of aging, or something more serious like dementia. The two lines can feel blurry, especially in the early stages. Families often struggle with knowing when to be concerned, what to expect, or how to…
Tag: Nervous system
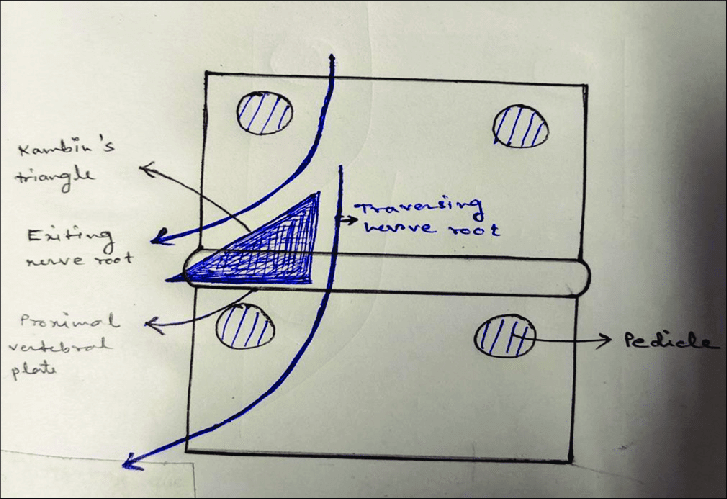
Kambin’s Triangle or Prism
There is confusion regarding the borders of Kambin’s triangle across the literature. Kambin originally described the borders of this triangular working zone as: Though it was named as a “triangle” it was described with 4 borders with 2 triangles (in AP view and Lateral view) which gives a 3D structure…
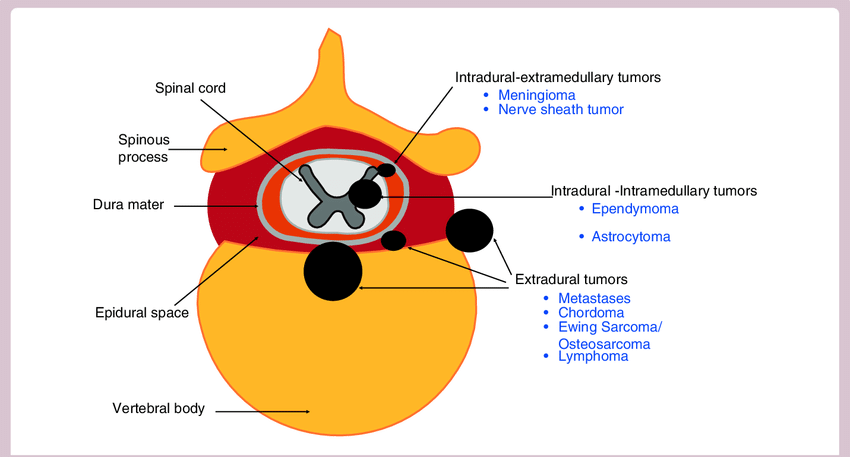
Spinal Tumors Localization : Mnemonics
Intradural Intramedullary Spinal Tumors Mnemonic: I HEAL Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumors Mnemonic: MNM Extradural Spinal Tumors Lesions outside the thecal sac are categorized as extradural lesions. Remember that everything that isn’t in the thecal sac is extradural, including discs, bones, nerves, and blood vessels.
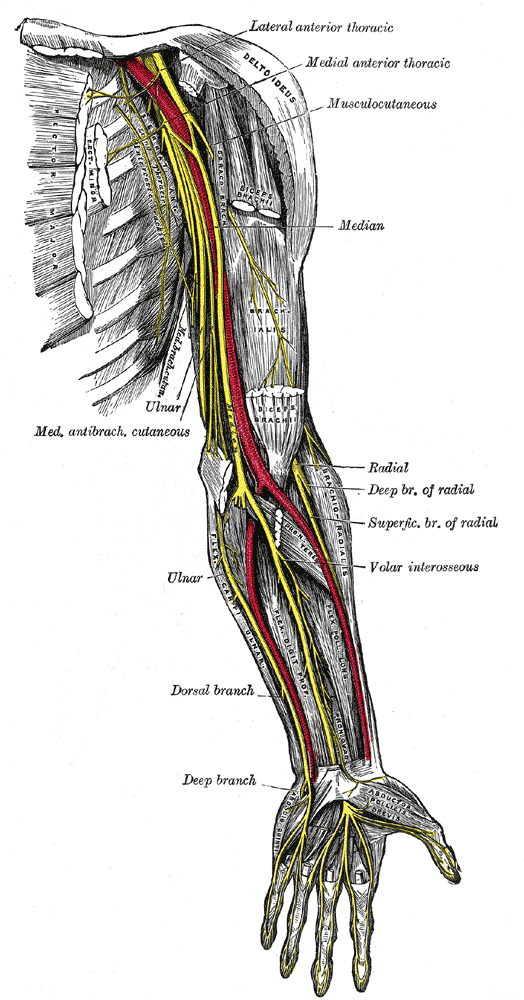
Lateral and Medial Pectoral Nerve : Mnemonic
Mnemonics a. Lateral is Less and Medial is More. b. Major receives 2 innervations and Minor receives 1 innervation. Hence, Lateral pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major. Medial pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major and minor. The lateral pectoral nerve and the medial pectoral nerve form…
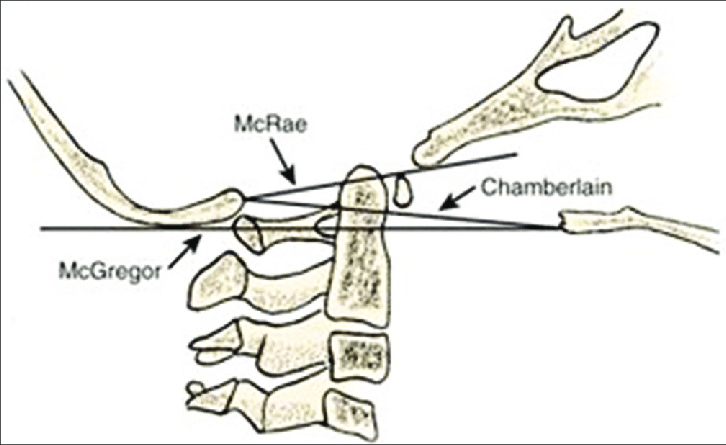
Radiological Lines for assessing Basilar Invagination : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: Imagine a letter “Z“. a. McRae’s line has “R” and is at Roof. b. Chamberlain’s line starts with “C” and is at Center. c. McGregor’s line has “G” and is at Ground. a. McRae’s line (foramen magnum line): drawn from anterior margin of foramen (basion) to posterior margin of…
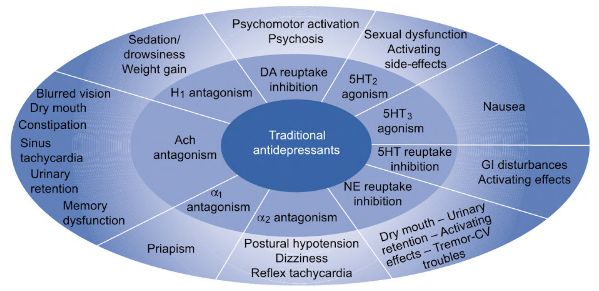
Antidepressants : Mnemonics
Classification and Mechanism of Action Acronyms: Mnemonic: TRIM 3N 3S Class Mechanism Drugs Side effects TCA Blocks reuptake of 5-HT, NA & other receptors (H1, ACh, α1, Voltage sensitive Na+ channel) Mnemonic: ANTI-DeP-C1. Amitryptiline, Amoxapine2. Nortryptiline3. Trimipramine4. Imipramine5. Doxepin, Desipramine, Dothiepin6. Protryptiline7. Clomipramine M1 blockade: Muscarinic anticholinergic side-effects α1 blockade:…

Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome : Mnemonic
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is the most serious form of thiamine deficiency in patients diagnosed with alcohol use disorder. Thiamine deficiency in alcoholics (Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome) results in degeneration of the medial-dorsal nucleus of thalamus, mamillary bodies, hippocampus and vermis of cerebellum. Mnemonic: COAT RACK Wernicke’s Encephalopathy (Acute phase) Korsakoff’s Psychosis (Chronic phase)
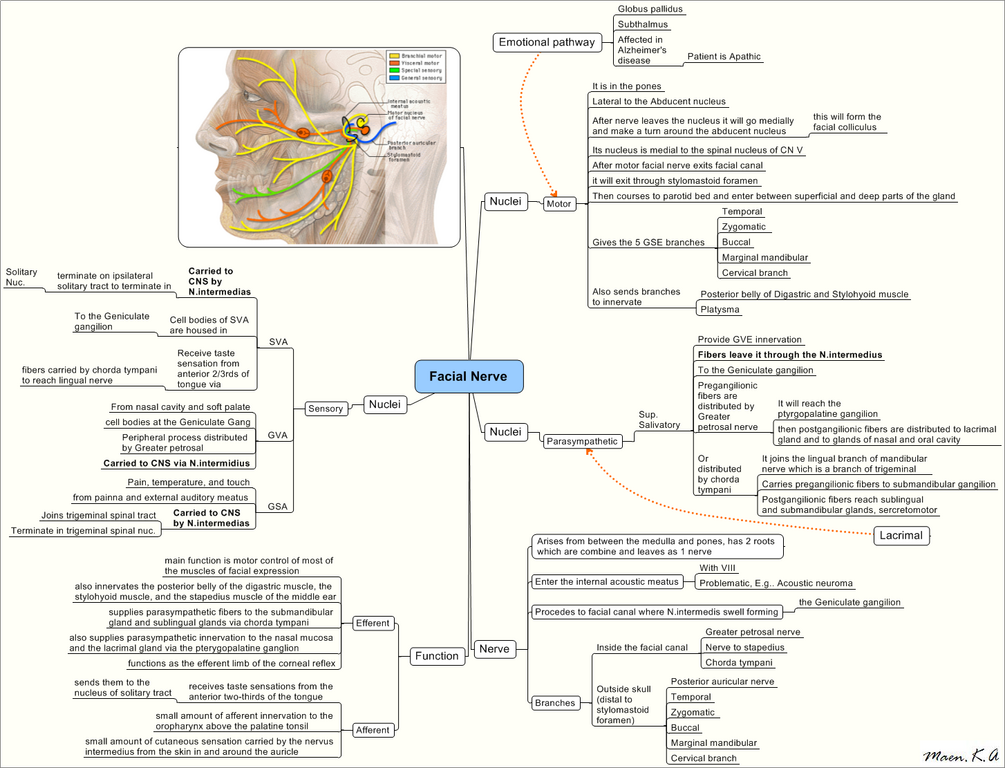
Facial Nerve : Mnemonics
Course Origin: Ponto-medullary junction (Nucleus solitarius, Facial nucleus and Superior salivatory nucleus) Internal acoustic meatus: 7 up, Coke down Facial canal: After exiting skull from stylomastoid foramen: Further reading: Facial nerve lesions 1. Supranuclear lesion: Contralateral lower 1/2 face paralyzed; forehead wrinkling spared (Bilateral cortical innervation) 2. Infranuclear lesion: Entire…
