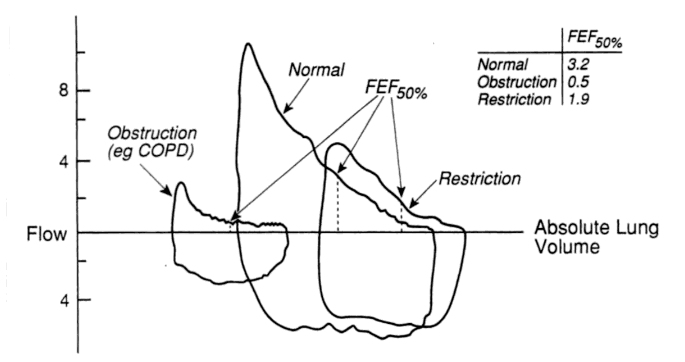
The flow-volume loop is a plot of inspiratory and expiratory flow (on the Y-axis) against volume (on the X-axis) during the performance of maximally forced inspiratory and expiratory maneuvers. Condition Mnemonic Flow-volume loop Features Obstructive lung disease (small airways) Shift to leftConcave/Scooped out expiratory flow (↓FEV 25-75%) ↑TLC and RV↓FEV1…
Tag: Physiology
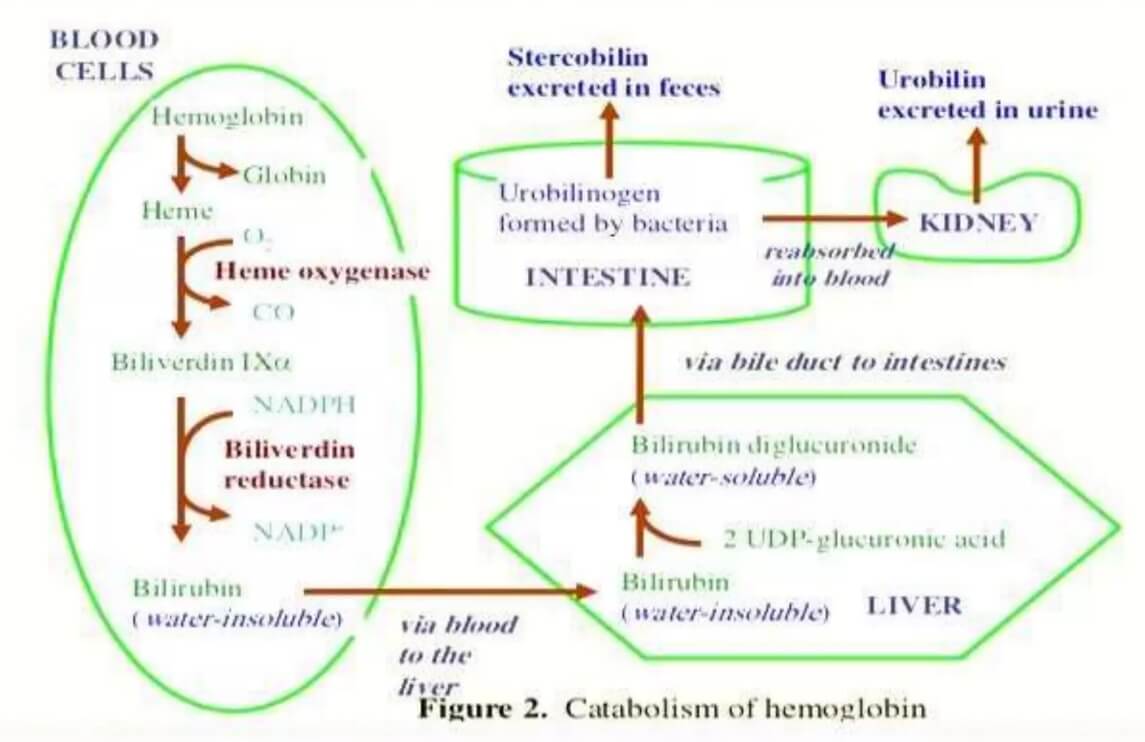
Bilirubin Metabolism and Disorders
Bilirubin Metabolism Mnemonic: ABCDE 1. Aged RBCs (80-85%) 2. Breakdown to Biliverdin and Bilirubin (in reticuloendothelial system) 3. Circulation 4. Delivery to liver (Conjugation) 5. Excretion and Enterohepatic circulation Unconjugated Vs Conjugated Bilirubin Unconjugated bilirubin Conjugated bilirubin Van den Bergh reaction Indirect Direct Solubility Water insoluble; Lipid soluble Water soluble;…
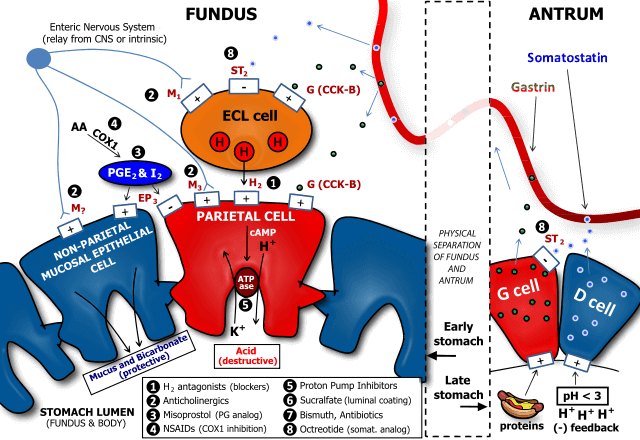
Gastric Acid Secretion Made Easy
Steps for gastric acid secretion by parietal cells 1. H+ and HCO3- are produced from CO2 and H2O. 2. H+ is secreted into the lumen by H+/K+ ATPase pump. 3. HCO3- moves out of the cell, across the basolateral membrane via antiport with Cl-. 4. Cl- diffuses passively into the…
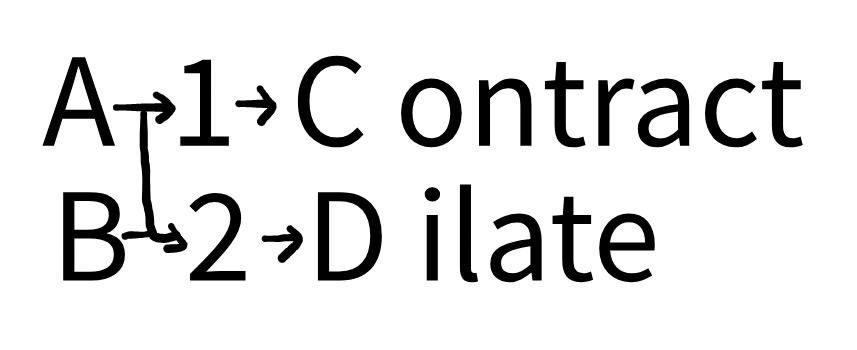
Alpha and Beta Adrenergic Receptors : Mnemonics
Location Alpha = Arteries and smooth muscles Beta = Beats or Breaths Types and Action 1 = Contract 2 = Dilate Receptors Alpha 1: Alpha 2: Beta 1: Mnemonic: We have 1 HEART Beta 2: Mnemonic: We have 2 LUNGS Beta 3: Mnemonic: 3 = Triglyceride
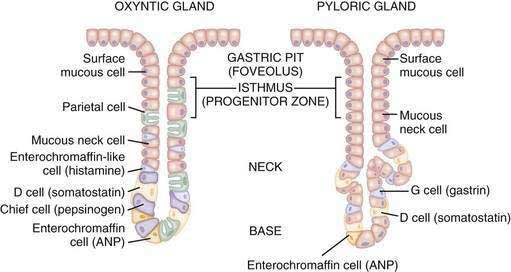
Gastric Acid Secretion in Parietal cells: Mechanism
Key player: H+/K+ ATPase or “proton pump” (in canalicular membrane of parietal cells) a. Hydrogen ions are generated within the parietal cell from dissociation of water. The hydroxyl ions formed in this process rapidly combine with carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate ion, a reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase. b. Bicarbonate…
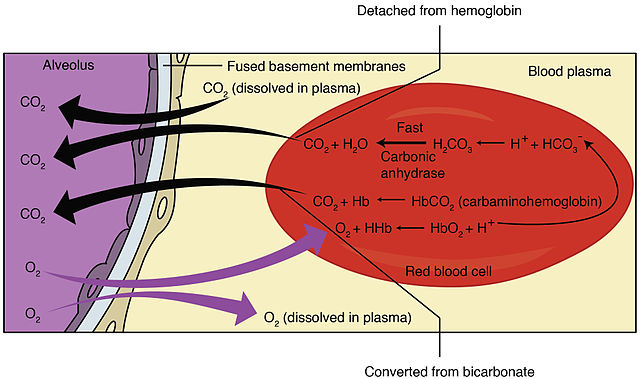
Bohr and Haldane Effect : Mnemonics
Haldane effect Mnemonic: HALD Bohr Effect Mnemonic: BOHR
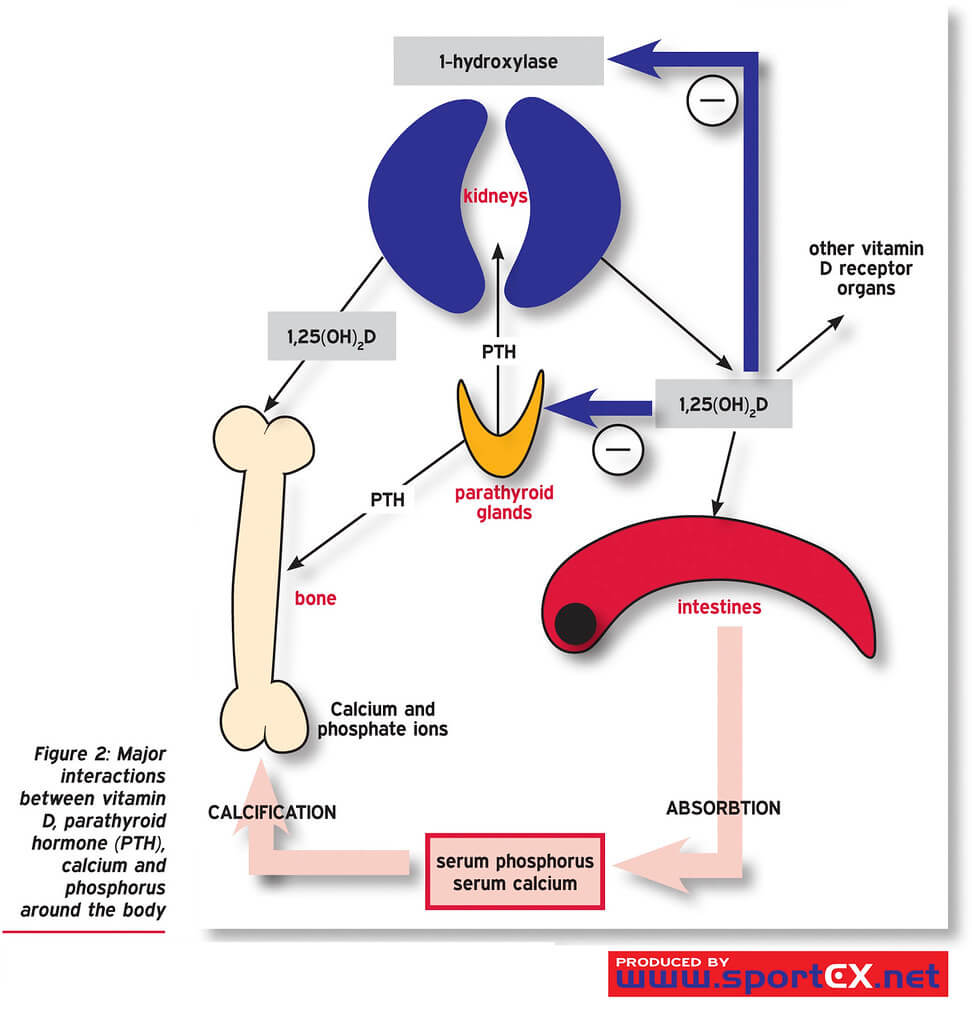
Calcium Metabolism
Functions Mnemonic: Six ‘C’s Contraction of muscles (Coupling of excitation-contraction) Conduction in nerves Cardiac function Coagulation in blood (Co-factor) Communication (intracellular messengers) for hormones, autacoids and transmitters Cementing (mineralization) of bone – Compressive strength Distribution Average young adult = 1200 gm calcium 99% in bone as calcium hydroxyapatite 1% in…
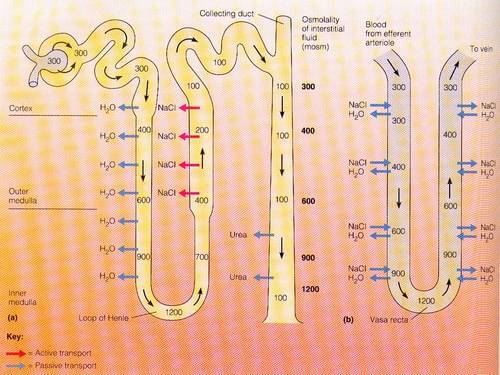
Renal Counter-Current Mechanism Made Easy
The term counter-current means flow in opposite direction. The renal counter-current mechanism comprises of: Flow of filtrate in opposite direction in nephron loop (down the descending limb and up the ascending limb of LOH or Loop of Henle) – that functions as a counter-current multiplier Flow of blood in opposite…