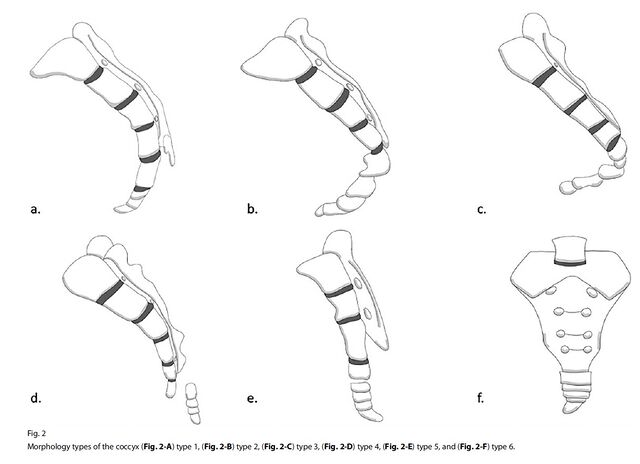
Postacchini and Massobrio Classification (Nathan Modification) Can be classified into 6 types: Type I (slight curve): Curved slightly forward with apex pointing caudally (>50% incidence) Type II (forward curve): More prominent ventral curvature with coccyx apex pointing anteriorly (8-32% incidence) Type III (sharp angle): Acute anterior angulation of coccyx but…
Tag: Radiology
Ivory Vertebra : Mnemonic
Ivory vertebra refers to diffuse and homogenous increase in opacity of a vertebral body that retains size and contour with no change is size and opacity of adjacent intervertebral discs. Mnemonic: PH FILMS 1. Paget disease of bone 2. Hemangioma 3. Fluorosis 4. Infection (tubercular spondylitis) 5. Lymphoma (usually Hodgkin’s…
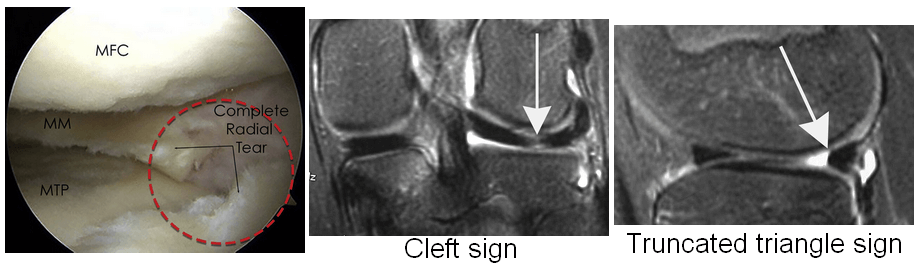
Meniscal Tears on MRI
Meniscal tears are best seen on T1-weighted, gradient-echo and proton-density images. The menisci are low intensity on all sequences. Morphologies Meniscal tear morphology Description MRI appearance Horizontal Separates meniscus into superior (femoral) & inferior (tibial) fragments Primarily horizontal signal on sagittal images Vertical radial Splits central margin of meniscus Vertical…
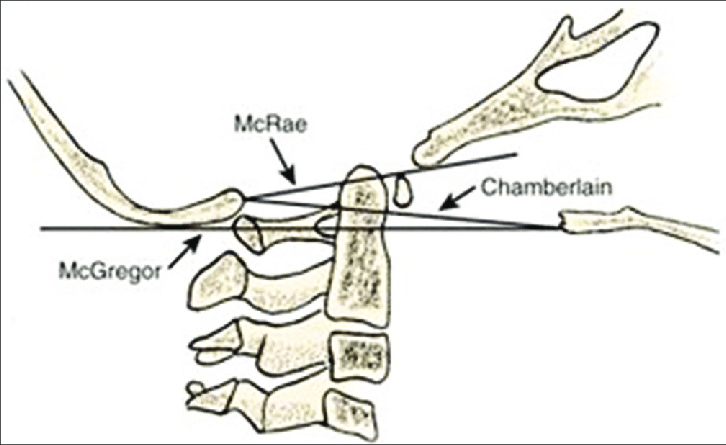
Radiological Lines for assessing Basilar Invagination : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: Imagine a letter “Z“. a. McRae’s line has “R” and is at Roof. b. Chamberlain’s line starts with “C” and is at Center. c. McGregor’s line has “G” and is at Ground. a. McRae’s line (foramen magnum line): drawn from anterior margin of foramen (basion) to posterior margin of…
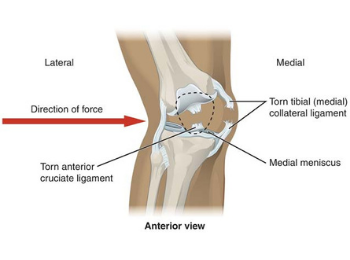
Unhappy Triad of O’Donoghue : Mnemonic
O’Donoghue unhappy triad is occurrence of 3 different soft tissue injuries of knee simultaneously. It includes: Mnemonic: MAM Mechanism: valgus stress with rotation of the knee Later on, more studies emerged showing that injuries in the lateral meniscus were more prevalent than injuries in the medial meniscus. The unhappy triad…
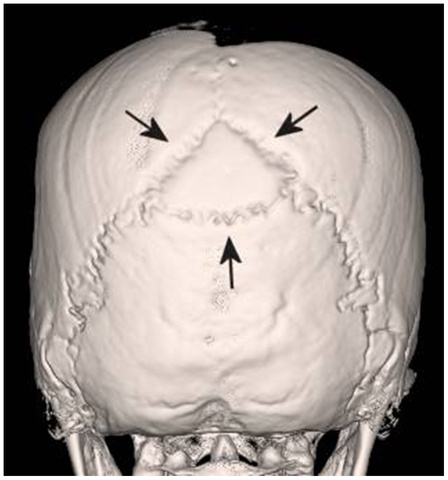
Wormian Bones
Wormian bones are abnormal ossicles that develop from extra ossification centers within the cranium. They are most frequently located in the lambdoid suture or the coronal suture, and have been seen in the fontanelles, particularly the posterior fontanelle. Commonest Cause Idiopathic (Anatomic variant) Other Causes Mnemonic: PORK CHOPS 1. Pyknodyostosis…
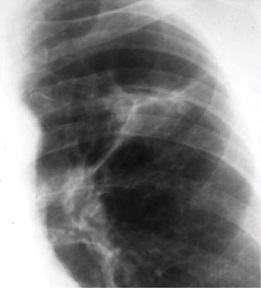
Eponyms in Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a multi-systemic, granulomatous disease caused by the bacilli Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is also known as Koch’s bacillus. Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis 1. Ghon focus or lesion: Subpleural fibro-caseous lesion of lung parenchyma (common site is upper part of lower lobe or lower part of upper lobe) 2. Ghon’s…
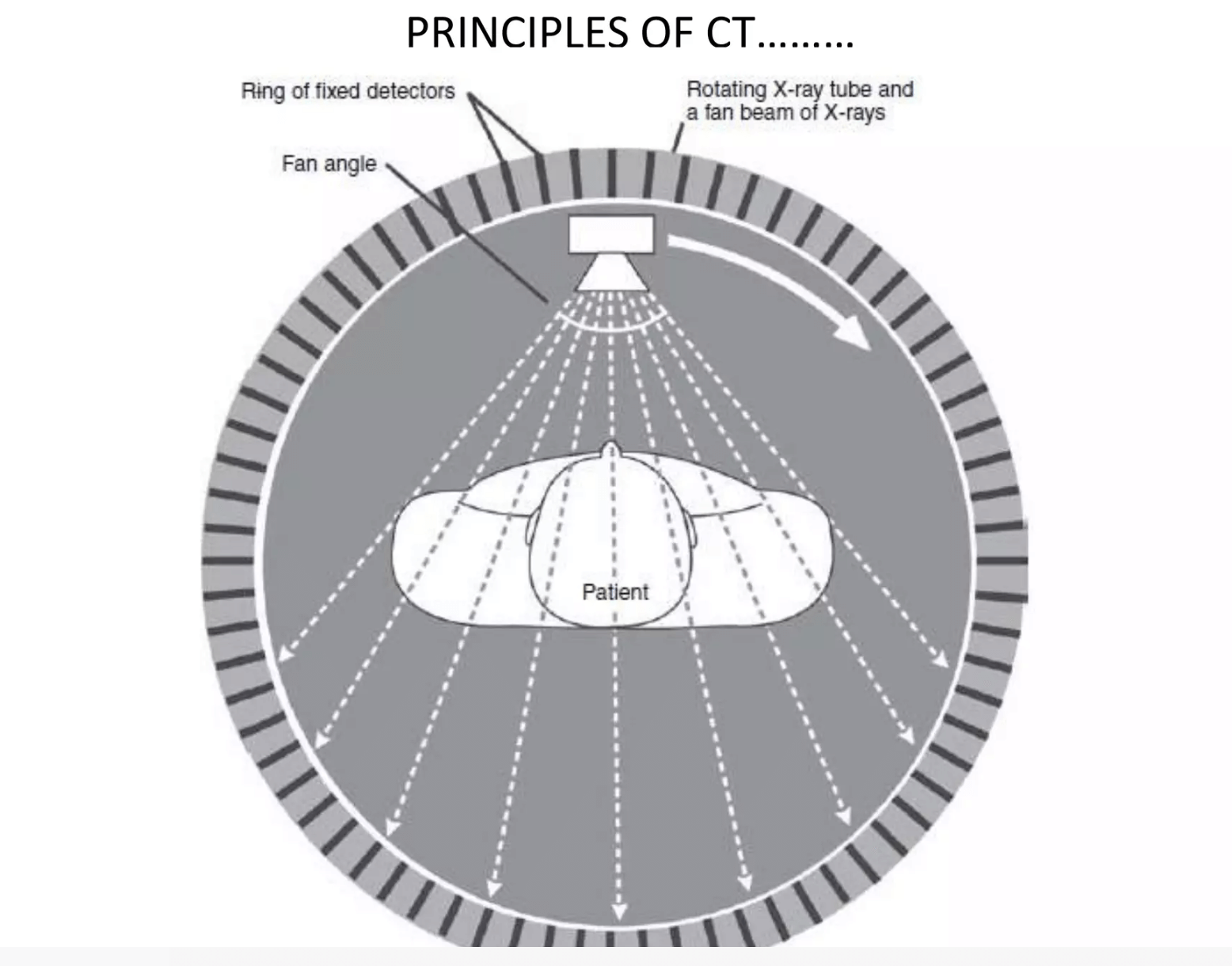
Interpretation of NCCT head: Normal findings
History: In 1972, Sir Godfrey Hounsfield developed CT scan for which he was awarded Nobel prize in 1979. Through these years CT has come from one rotation in 6 minutes to one in 0.33 seconds. Principle: X rays are produced by CT machine, which are absorbed by different tissues in…