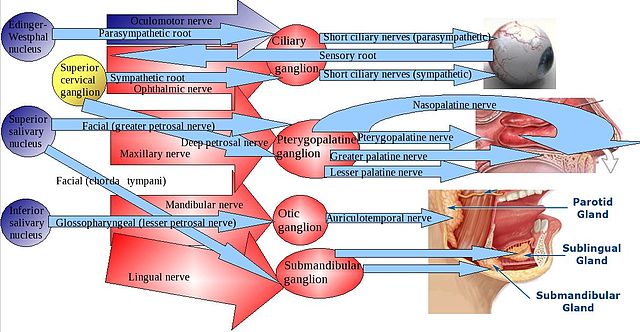
Important points:
- Preganglionic fibers travel with cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X, then meet cranial nerve V in ganglion and post-ganglionic fibers are carried by branch of cranial nerve V.
- Parasympathetic ganglia also have sympathetic components.
- Each PSNS ganglion has three roots: a motor root, a sympathetic root, and a sensory root, as well as a number of exiting branches.
Mnemonics:
1. COPS 3977
2. C is 3rd letter hence related to cranial nerve III
3. S for Sphenopalatine and Submandibular and S for Seven and is related to Superior Salivatory nucleus
4. All postganglionic fibers are carried by trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve V)
| Ganglion | Nucleus | Pre-ganglionic | Post-ganglionic | Sympathetic root | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciliary | Edinger-Westphal | CN III | CN V1 – short ciliary nerve | Nasociliary nerve (internal carotid plexus) | Sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles |
| Otic | Inferior salivatory | CN IX (lesser petrosal nerve) | CN V3 – auriculo-temporal nerve | Plexus around medial meningeal artery | Parotid gland |
| Pterygopalatine/ Sphenopalatine | Superior salivatory | CN VII (greater petrosal nerve) | CN V1/V2 | Deep petrosal nerve (internal carotid plexus) | Lacrimal, nasal, palatine, pharyngeal glands |
| Submandibular | Superior salivatory | CN VII (chorda tympani) | CN V3 – lingual branch | Plexus around facial nerve | Sublingual, submandibular glands |
Petrosal nerves:
- Greater petrosal nerve = Parasympathetic CN VII (facial nerve)
- Lesser petrosal nerve = Parasympathetic CN IX (glossopharyngeal nerve)
- Deep petrosal nerve = Sympathetic (internal carotid plexus)
- Nerve of pterygoid canal = Greater petrosal nerve + Deep petrosal nerve