The “golden rules of anesthesia” are a set of principles and practices designed to ensure patient safety during anesthesia administration. These rules emphasize careful pre-operative preparation, vigilant intraoperative monitoring, and prompt management of potential emergencies. Mnemonic: ANESTHESIA
Tag: Anesthesia
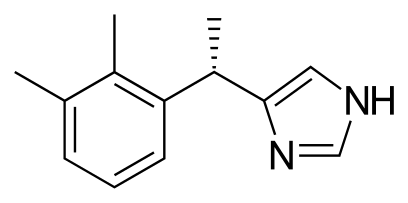
Dexmedetomidine – Mnemonic
Mnemonic: BARASH Uses of Dexmedetomidine: This mnemonic, BARASH, is dedicated to Dr. Paul G. Barash, whose work in anesthesiology has profoundly shaped medical education and clinical practice. Just as his textbook has guided countless practitioners, may this mnemonic serve as a concise tool for remembering key concepts with clarity and…
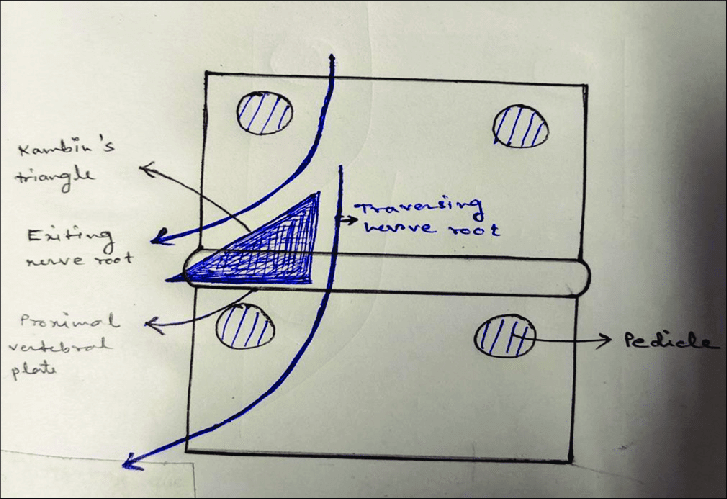
Kambin’s Triangle or Prism
There is confusion regarding the borders of Kambin’s triangle across the literature. Kambin originally described the borders of this triangular working zone as: Though it was named as a “triangle” it was described with 4 borders with 2 triangles (in AP view and Lateral view) which gives a 3D structure…
Understanding Chronic Pain: Answers to Common Questions
Pain is an undeniable reality that each of us encounters at some point in life. While most pains are fleeting, vanishing once the underlying cause is addressed, there exists a tormenting kind that persists and takes a toll on every aspect of life. Chronic pain, the elusive agony that defies…
ABG Interpretation Made Easy
Normal values Step 1: pH Step 2: pCO2 Step 3: HCO3- Step 4: Determine compensation If there is metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, determine if there is appropriate respiratory compensation: No respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 = Measured pCO2 Respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 ≠ Measure pCO2 Step 5: Delta ratio ΔAG /…
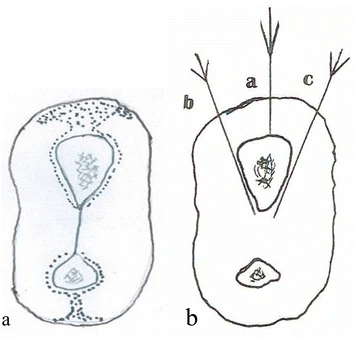
Circumferential Periosteal Block (CPB)
Use: Alternative to hematoma block in reduction of distal radius and ulna fractures Advantage: Providing distance from the fracture hematoma (no theoretical risk of converting closed fracture into open fracture) Disadvantage: Risk of neurovascular injury on volar surface of forearm Local anesthetic and volume: 10–15 ml of 1 % plain lidocaine…
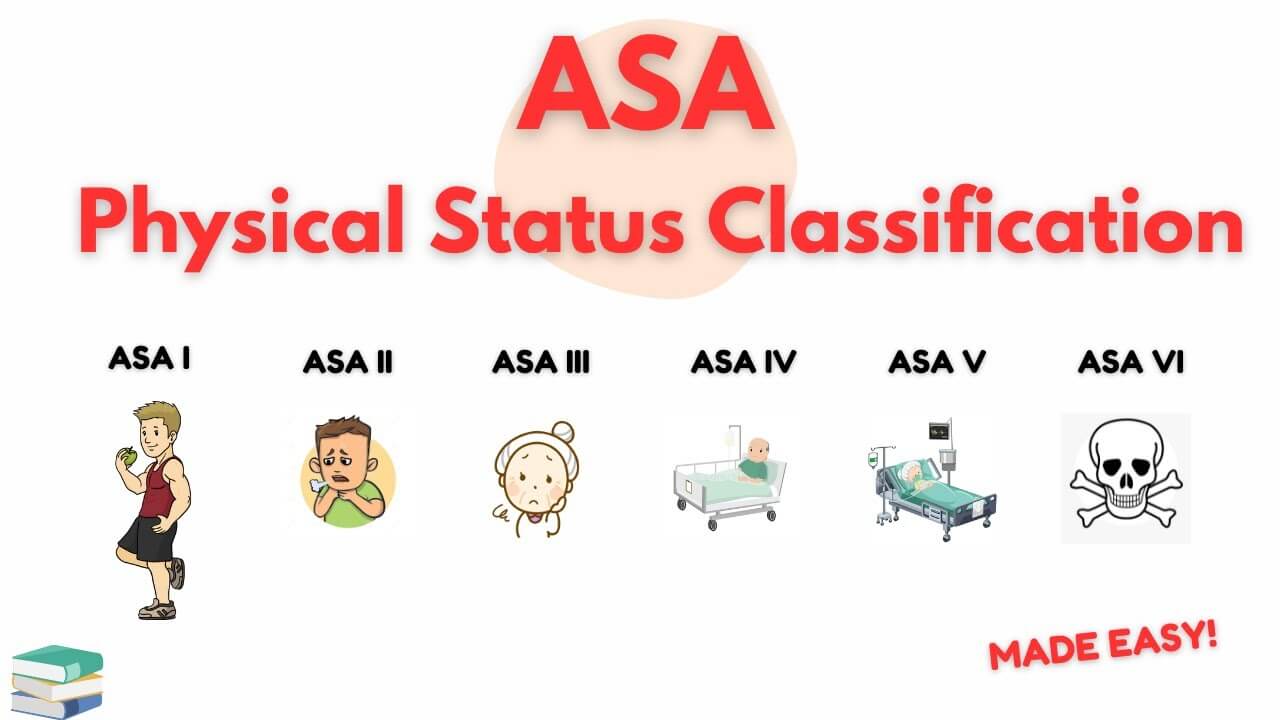
ASA Classification: Made Easy
The purpose of the system is to assess and communicate a patient’s pre-anesthesia medical co-morbidities. The classification system alone does not predict the perioperative risks, but used with other factors (e.g., type of surgery, frailty, level of deconditioning), it can be helpful in predicting perioperative risks. ASA grade Definition Mortality…
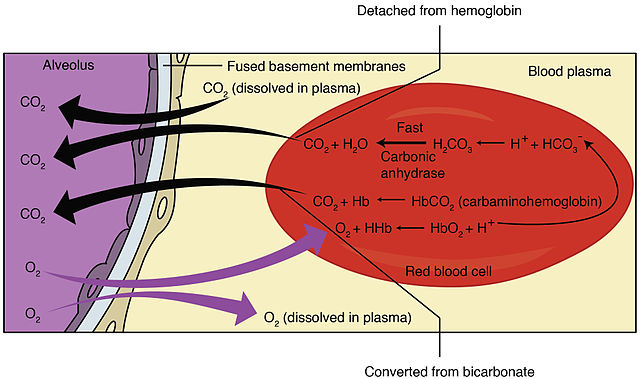
Bohr and Haldane Effect : Mnemonics
Haldane effect Mnemonic: HALD Bohr Effect Mnemonic: BOHR
