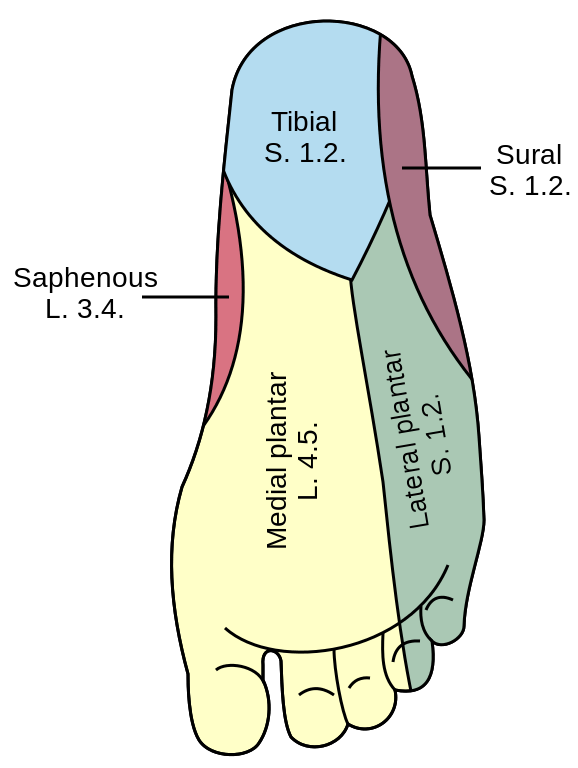
Origin: Tibial nerve (both medial and lateral plantar nerve)
Similar to:
- Medial plantar nerve: similar to median nerve in upper limb
- Lateral plantar nerve: similar to ulnar nerve in upper limb
Course and innervation:
| Medial plantar nerve | Lateral plantar nerve | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Larger branch of tibial nerve | Smaller branch of tibial nerve |
| Course | Deep to abductor hallucis muscle Between 1st and 2nd plantar layers | Deep to abductor hallucis muscle Between 1st and 2nd plantar layers |
| Motor innervation | Mnemonic: LAFF muscles 1. 1st Lumbrical 2. Abductor hallucis 3. Flexor digitorum brevis 4. Flexor hallucis brevis | All other intrinsic plantar muscles |
| Sensory innervation | Anterior 2/3 of medial sole and medial 3 and 1/2 toes including nail beds on dorsum | Anterior 1/3 of lateral sole and lateral 1 and 1/2 toes |
Baxter’s nerve:
- Also known as inferior calcaneal nerve
- 1st branch of the lateral plantar nerve arising within the tarsal tunnel
- Courses vertically between abductor hallucis and quadratus plantae, then makes a 90 degree horizontal turn, coursing laterally beneath the calcaneus to innervate abductor digiti minimi muscle.
- Can be entrapped as it passes:
- through the fascia of the abductor hallucis
- in close proximity to a plantar spur or the medial calcaneal tuberosity
- gets enmeshed in scar tissue from prior surgery
- Entrapment can be misdiagnosed as plantar fasciitis
- Plantar fascia pain is predominantly felt under the heel itself, whereas Baxter’s nerve entrapment is felt more on the heel and the medial arch of the foot and can also include a sensation of numbness or pins and needles.