Diaphragm is a thoracoabdominal organ which is musculotendinous. It is the primary muscle of respiration.
Extension:
- Sternal – xiphoid process and transverse abdominis aponeurosis
- Costal – lower 6 ribs and costal cartilage
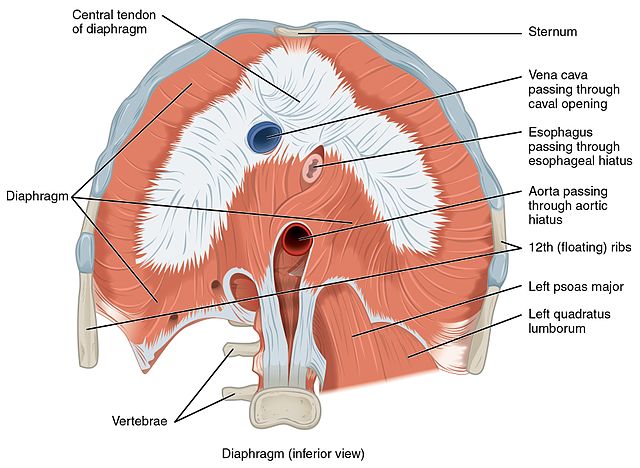
There are 2 crura of diaphragm:
- Right crus – L1 to L4
- Left crus – L1 to L3
3 ligaments:
- Lateral arcuate ligament
- Medial arcuate ligament
- Median arcuate ligament
Quadratus lumborum muscle is related to lateral arcuate whereas psoas muscle is related to medial arcuate ligament.
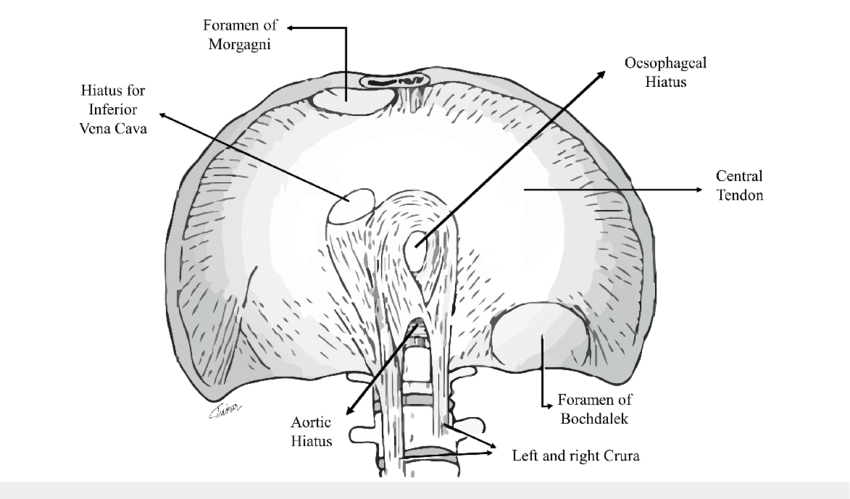
The foramen of Morgagni shown in the above picture (anteromedially) should obliterate normally. If it does not do so it results in congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
3 openings:
- IVC at T8 level
- Esophageal hiatus at T10 level
- Aortic opening at T12 level
Other structures passing through different openings in diaphragm:
- Caval hiatus: IVC and branches of right phrenic nerve
- Esophageal hiatus: esophagus, vagal trunks, esophageal branch of left gastric artery and left gastric vein
- Aortic hiatus: aorta, thoracic duct, azygous and hemiazygos vein
- Minor apertures (through crura): greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves
Arterial supply:
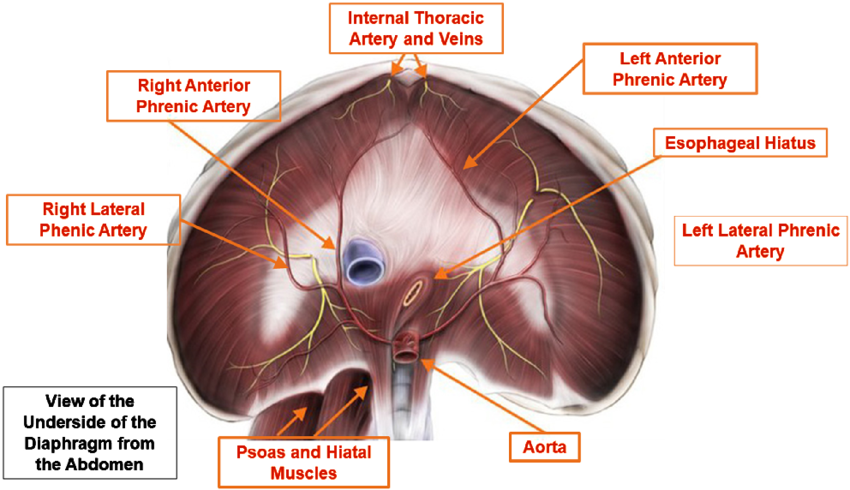
- Major supply by right and left inferior phrenic artery (either as direct branch of aorta in 40% or from celiac trunk in 47%)
- Superior phrenic artery supplies posterior part of diaphragm
- Pericardiophrenic arteries- central area of diaphragm
- Others: musculophrenic and lower intercostal arteries
Venous drainage:
- Right inferior phrenic vein (IPV) directly drains into IVC
- Left IPV either drains directly to IVC or can drain to left suprarenal vein which in turn drains into left renal vein then to IVC
Nerve supply:
- Motor supply – right and left phrenic nerve which are divided as sternal, anterolateral and posterolateral branch
- Sensory supply:
- Central portion: phrenic nerve
- Peripheral: lower 5 intercostal and subcostal nerve
Embryological structures and their adult derivatives:
| Embryonic structures | Adult derivatives |
| Septum transversum | Central tendon of diaphragm |
| Pleuroperitoneal membrane | Small peripheral part of diaphragm |
| Dorsal mesentery of esophagus | Crura of diaphragm |
| Mesoderm of body wall | Large peripheral part of diaphragm external to parts derived from pleuroperitoneal membrane |
Reference: Fischer’s mastery of surgery 8th edition

He is an avid reader, guitar player, melodious singer and old songs lover. He has a passion for making medical knowledge accessible and comprehensive.