Necrotizing fasciitis can be misdiagnosed in about 75% of the cases in the intial stage of the disease. The most consistent feature of early necrotizing fasciitis is the pain out of proportion to swelling or erythema. Other features helping to differentiate from other soft tissue infections are:
- Tenderness extending beyond the apparent involved area (due to toxins and enzymes spreading along the fascia below the skin)
- Indistinct margins of involvement
- Lymhangitis is often absent (infection is in deep fascia rather than skin)
- Rapidly progressive despite use of antibiotics
Fever may be present in only 40% of the cases due to masking effect of NSAIDs, steroids and antibiotics. Clinicians should have a higher index of suspicion when patients with diabetes or liver cirrhosis present with cutaneous infection.
Necrotizing fasciitis can be differentiated from cellulitis using ABCDEFG mnemonic.
Adenitis (also lymphangitis) often absent
Bullae (Serous – intermediate stage; Hemorrhagic – late stage)
Crepitus (Late stage)
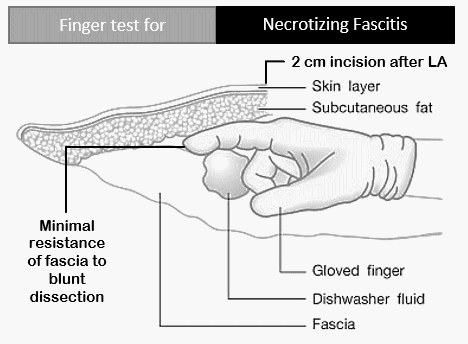
Dishwater-colored fluid discharge
Extension of tenderness beyond area of involvement and Expanding despite antibiotic use
Finger test
Greater pain than swelling and erythema
Another ABCDE mnemonic for summarizing the relevant clinical features and diagnostic criteria.
- A – Anaerobic, Aerobic, Adult, Antibiotics refractory
- B – Bacterial synergistic gangrene, group B streptococcus, and Blood count higher than normal
- C – Cellulitis, Crepitus, and Coagulopathy
- D—Dermal gangrene, Delay in presentation almost fatal
- E – Erythema with spreading Edema
Stages of Necrotizing Fasciitis
| Early | Intermediate | Late |
| Warm to palpation | Blister or Bullae (serous) | Hemorrhagic bullae |
| Erythema | Skin fluctuance | Skin anesthesia |
| Tenderness to palpation (extending beyond apparent areas of skin involvement) | Skin induration | Crepitus |
| Swelling | Skin necrosis with dusky discoloration progressing to frank gangrene |
STAFF mnemonic for USG diagnosis to diagnose necrotizing fasciitis
- Subcutaneous Thickening
- Air [hyperechoic (white) patches, with indistinct, “dirty” shadows]
- Fascial Fluid
LRINEC score mnemonic for necrotizing fasciitis
Reference:
- Asif Zubair Bhatti, MD, FRCS, FCPS, James Mcdiarmid, FRCS, FRCS (PLAST), MSc, Necrotizing Fasciitis: An Aid to Prompt Diagnosis, Aesthetic Surgery Journal, Volume 26, Issue 1, January 2006, Page 54, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2005.11.005
- Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg. 2014 Jan;101(1):e119-25. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9371. Epub 2013 Nov 29. PMID: 24338771.
- https://med.emory.edu/departments/emergency-medicine/sections/ultrasound/image-of-the-fortnight/miscellaneous/necfasc.html

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.