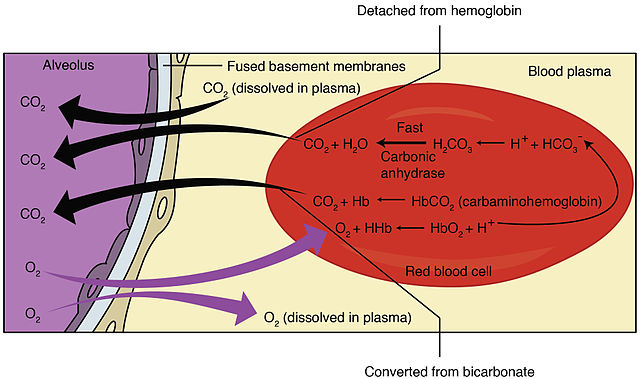
Haldane effect Mnemonic: HALD Bohr Effect Mnemonic: BOHR
Tag: Anesthesia
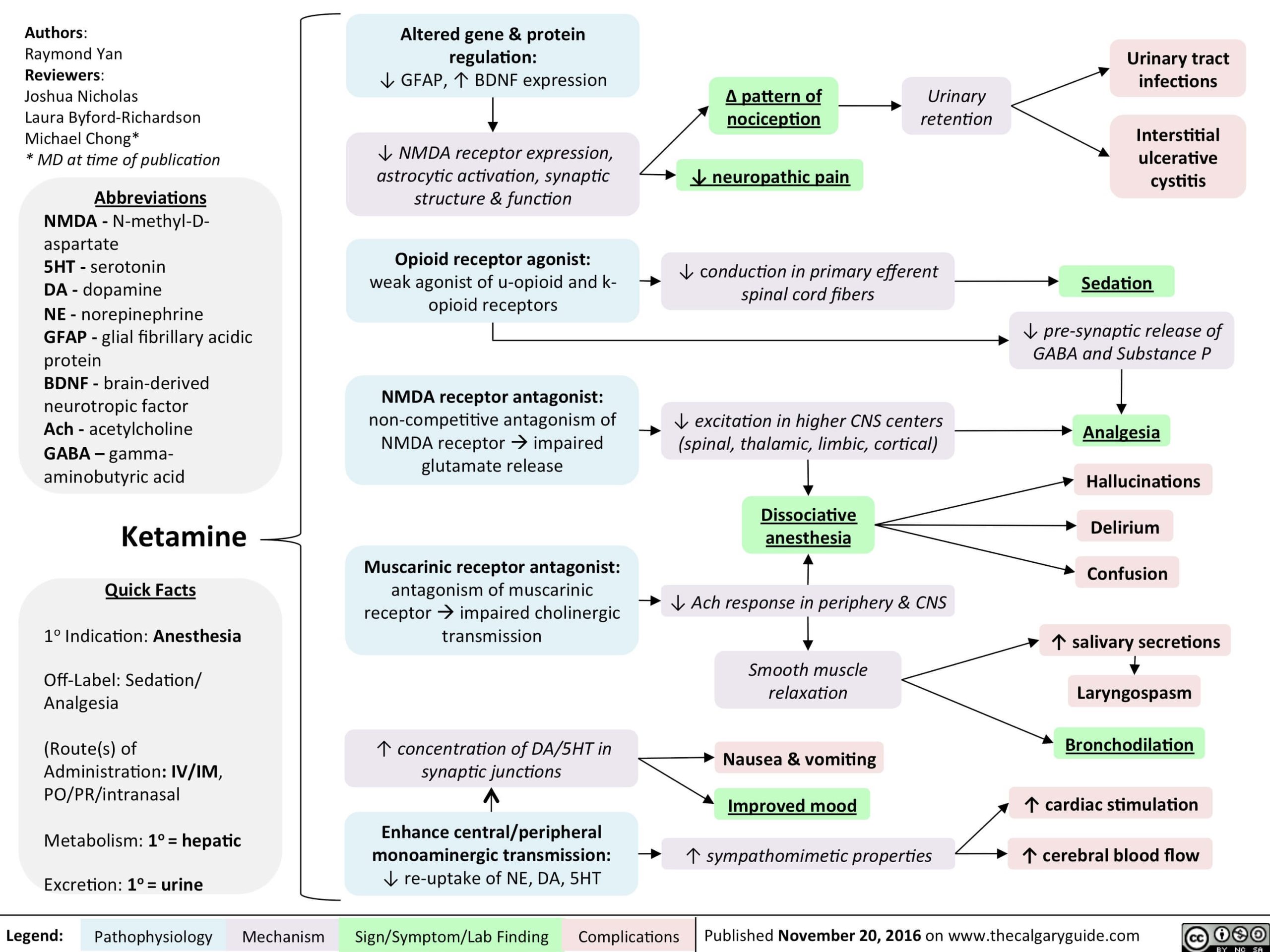
Ketamine : Mnemonic
K: Kids (Induction agent of choice in children) E: Emergence reaction (floating sensations, vivid dreams and hallucination; reduced using benzodiazepines), Enantiomers (S-Ketamine and R-Ketamine) T: Thalamo-cortical dissociation with limbic system causing dissociative anesthesia A: Analgesic, Amnesic, Antidepressant, All routes (IV, IM, PO, Intranasal, Epidural, Intrathecal) M: Meals – can be…
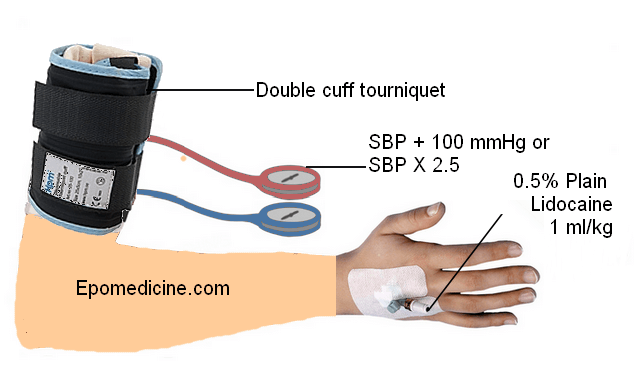
Bier Block
Named after: German Surgeon August Bier (first introduced the block in 1908) Definition: It is a peripheral intravenous local anesthetic block (IVRA; Intravenous Regional Anesthesia) of the upper limb using a pneumatic cuff technique Mechanism of action: Local anesthesia diffuses into the small veins surrounding the nerves and then into…
Atropine Induced Paradoxical Bradycardia
Atropine induced paradoxical bradycardia is the sinus bradyarrhythmia following low-dose atropine resulting from the paradoxical slowing in the sinoatrial (SA) node discharge rate. Mechanism of Atropine Induced Paradoxical Bradycardia Central vagotonic effect (blocking M1 acetylcholine receptors in parasympathetic ganglion controlling SA node) of atropine which, at higher doses, is masked…
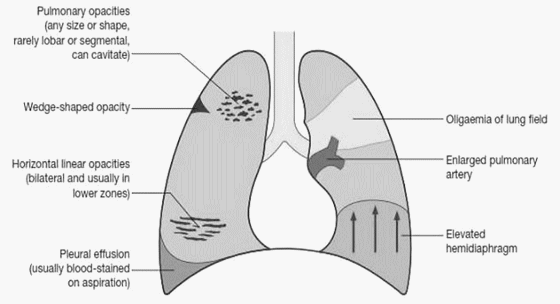
Perioperative Management of Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Recommended duration of anticoagulant prophylaxis The recommendations are as follows: 1. Provoked DVT (with reversible surgical or nonsurgical provoking factor): 3 months 2. Unprovoked isolated distal DVT (has low risk of recurrence): 3 months 3. Unprovoked proximal DVT or PE: Indefinite therapy if D-dimer positive after 1 month after 3 months of therapy or second VTE…
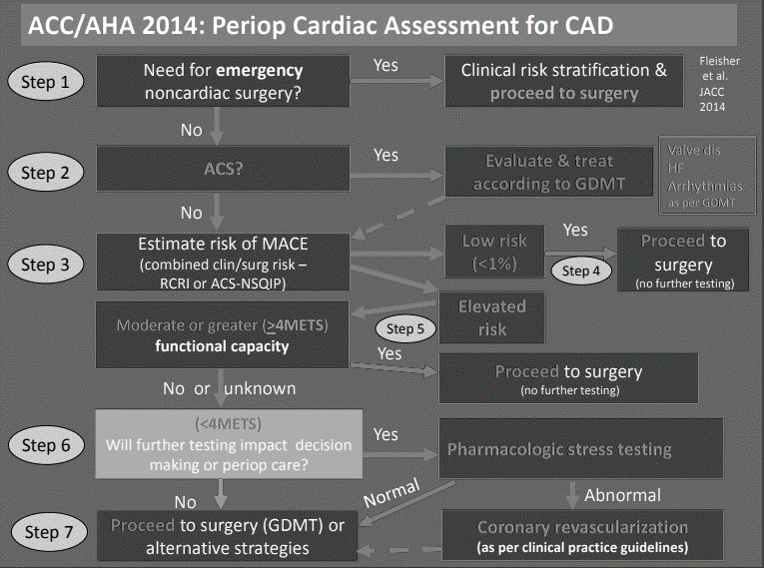
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation in Non-cardiac Surgery : Mnemonic
Besides, for the emergency/urgent surgeries, one needs to evaluate 4 variables in the preoperative cardiac evaluation of the patient for the non-cardiac surgery. We have elaborated the mnemonics used by CasesBlog. These variables can be remembered by the mnemonic PAST. Patient risk Activity level (METs) Surgical risk Test (Stress test)…
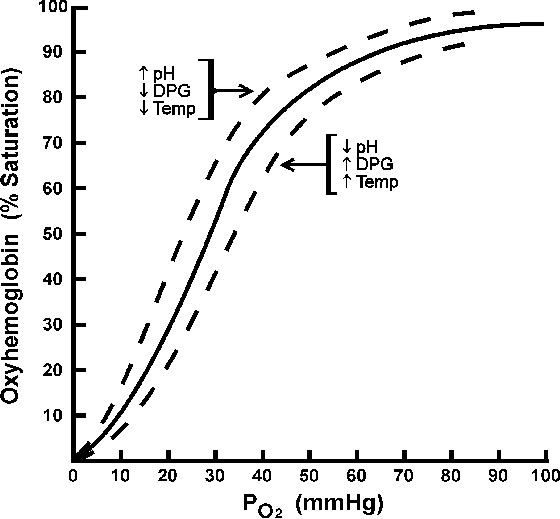
Oxygen Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve : Mnemonic
The oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve is sigmoidal in shape because the binding of 1st oxygen molecule is difficult, however once bound, they facilitate the binding of subsequent molecules until the saturation is reached (plateau). This is called the allosteric interaction (cooperativity). Lets come to the mnemonics now. The curve can…
Opioid Adverse Effects – Mnemonic
Mnemonic: MORPHINES 1. Miosis Mechanism: Stimulation of Edinger-Westphal nucleus of Cranial nerve III 2. Orthostatic hypotension Mechanism: Vasodilation due to – Direct action decreasing tone of blood vessels Histamine release Depression of vasomotor center 3. Respiratory depression Mechanism: Inhibits respiratory center in a dose-dependent manner (neurogenic, hypercapneic and hypoxic drives…