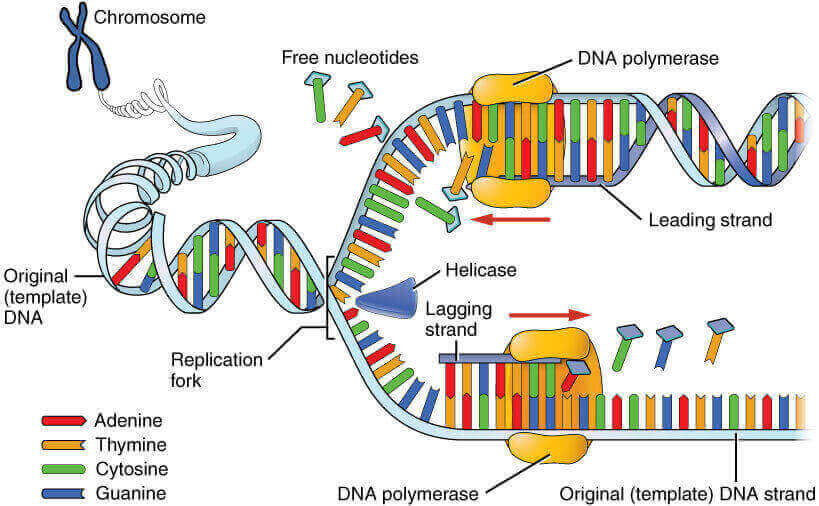
Imagine DNA as a zipper Prokaryotic DNA as a zipper with single slider (single origin of replication) and Eukaryotic DNA as a zipper with two sliders (multiple origin of replication). Zipper teeth: Purines and pyrimidine bases Complementary teeth pair: Complementary base pairs attached by hydrogen bonds Top stops: Origin of…
Tag: General concepts
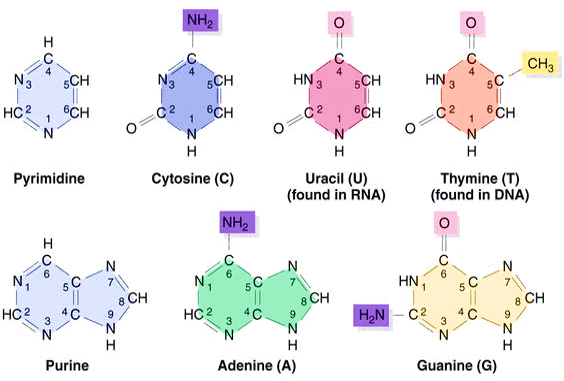
Purine and Pyrimidines : Structure, Synthesis and Metabolism
Purines and Pyrimidines Bases Purines = 2 rings Adenine Guanine Hypoxanthine (Deaminated Adenine) Adenine to Hypoxanthine deamination is mediated by Adenosine deaminase which is decreased in Autosomal recessive SCID. Accumulated dATP inhibit ribonucleotide reductase leading to deficient synthesis of other deoxyribonulceotide precursors for DNA synthesis. Xanthine (Deaminated Guanine) Mnemonics: Pure…
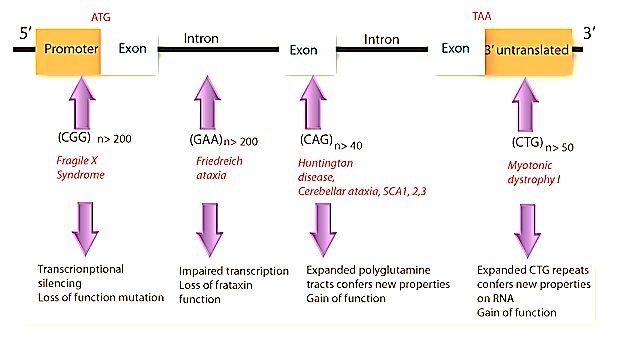
Trinucleotide Repeat Disorders and Anticipation Mnemonics
Anticipation in genetics refers to an increase in severity and decrease in age of onset in successive generations, most likely due to increased size of trinucleotide repeats. Paternal anticipation: Huntington’s disease, Friedreich’s Ataxia Maternal anticipation: Myotonic dystrophy, Fragile X syndrome Diseases Trinucleotide Repeat Affected gene Chromosome Fragile X syndrome CGG…
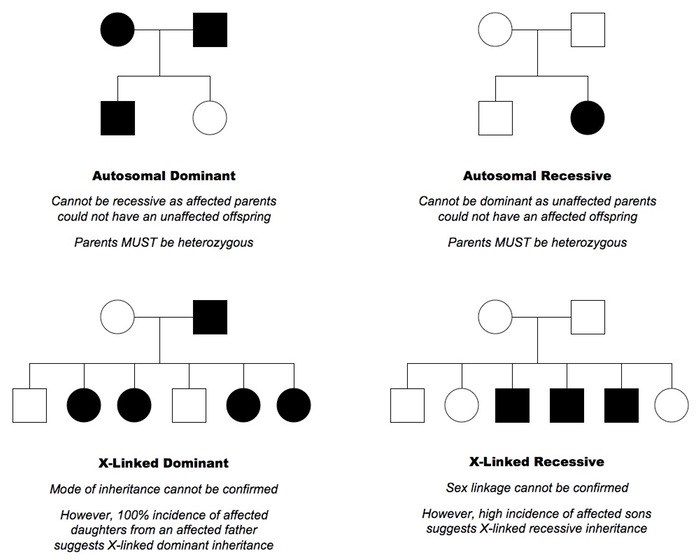
Solving Pedigree Analysis in 3 steps
First: Look for Mitochondrial Inheritance Female transmits disease to all the offsprings (both males and females). Male doesn’t transmit the disease and only the females transmit the disease. If Mitochondrial inheritance is absent, go to second step. Second: Look if the gene is Dominant, Recessive Dominant: Atleast one member in…
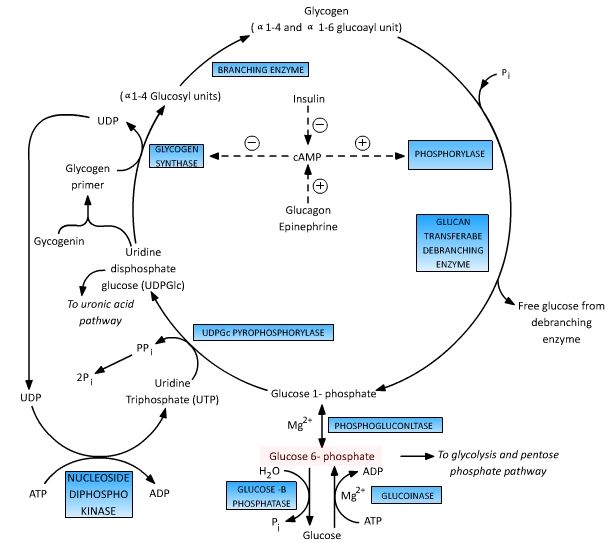
Glucose 6 Phosphate : Central to Glucose Metabolism
Glucose-6-Phosphate central to the 4 major metabolic pathways of glucose, i.e. glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis and HMP shunt (Pentose phosphate pathway). Glucose is immediately phosphorylated inside the cells to Glucose-6-Phsophate to trap them inside cell and prevent diffusion out of the cell. Glucose-6-Phosphate is the key intermediate to understand the…
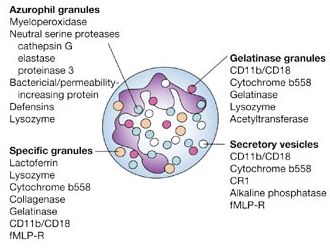
Granular contents of Neutrophils and Platelets
Neutrophil Granules Azurophilic (Primary) Granules These are lysosomes that occur in all granulocytes, as well as in lymphocytes and monocytes. In addition to expected lysosomal hydrolases, they also contain peroxidases (used to demonstrate azurophilic granules chemically). Develop earlier than specific granules. Stains blue/purple by Romanowsky stain. Mnemonic: ABCDE MnOP Acid hydrolase…
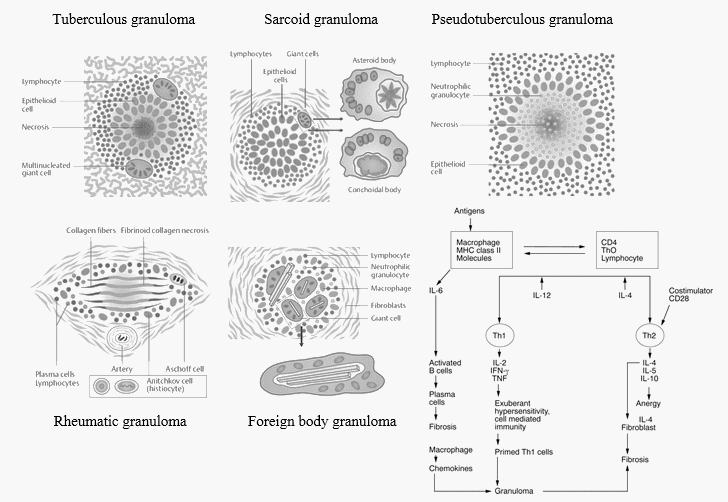
Morphology of Granuloma
Concentric layers of Granuloma There are 4 concentric layers in a granuloma, however the clear distinction is difficult in reality due to overlapping. From inside to out: 1. Necrosis Caseating necrosis: Tuberculosis, Leprosy Coagulative necrosis: Buruli ulcer (M.ulcerans), Gumma containing central blood vessels (Syphilis) Fibrinoid necrosis: Aschoff bodies (Rheumatic granuloma),…
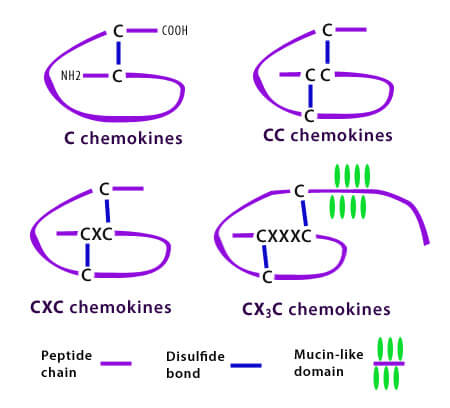
Chemokines Mnemonics
Difference between cytokines and chemokines Cytokines are small proteins released by cells, the function of which is “cell-signaling“. Chemokines are small cytokines, which functions as a “chemo-attractant“. Types of Chemokines When you go through the structural classification of chemokines, you come accross various arrangements of letter: C: denotes cysteine X:…