Anticipation in genetics refers to an increase in severity and decrease in age of onset in successive generations, most likely due to increased size of trinucleotide repeats.
- Paternal anticipation: Huntington’s disease, Friedreich’s Ataxia
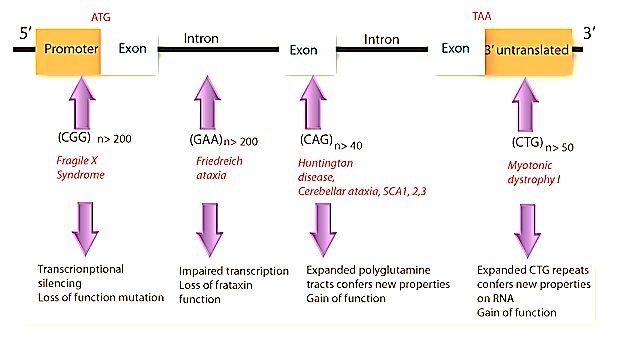
- Maternal anticipation: Myotonic dystrophy, Fragile X syndrome
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Friedrich’s ataxia
- Trinucleotide repeat: GAA (Out of the four, only one to start with letter G).
- Chromosomal mapping of affected gene: Chromosome 9 (Mnemonic: FRIEDRICH has 9 letters).
- Clinical features: Mnemonic – FRIEDREICH’S Ataxia
- Foot – Pes cavus
- Reflexes (Knee and Ankle jerks) – Absent
- Intention tremors
- Extensor plantar response, Eye – Optic atrophy
- Diabetes mellitus, Dorsal column degeneration
- Recessive Inheritance
- Cerebellar signs, Cranial nerve 7, 10 and 12 involvement
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Scoliosis
- Ataxia, Axonal neuropathy
Trinucleotide repeat of the other 3 disorders, starts with C and ends with G, i.e. C_G.
Huntington’s disease
Mnemonic: Hunter’s CAGe
- Trinucleotide repeat: CAG
- Chromosomal mapping of affected gene: Chromosome 4 (Cage has 4 letters).
- Clinical features and Pathophysiology: Mnemonic – CAGED
- Caudate and putamen atrophy and Choreiform movements
- Agression/psychosis, depression and dementia
- Glutamate excitotoxicity mediated death
- Ex-vacuo hydrocephalus
- Dopamine increased; GABA and ACh decreased
- Deacetylation of histone increased – Deacetylation makes DNA-histone bond strong and genomes unavailable for transcription (transcriptional repression or silencing)
Myotonic dystrophy
Mnemonic: See the 4th letter. dysTrophia myoTonica
- Trinucleotide repeat: CTG
- Chromosomal mapping of affected gene: Chromosome 19 (dystrophia myotonica has 19 letters)
- Clinical features: Mnemonic – DySTROPHIC
- Distal muscles weakness and wasting, Dysmotility of GI muscles and biliary tree, Dementia
- Swan-like neck
- Testicular atrophy
- Reflexes depressed or absent
- Ocular cataract and ptosis
- Pilomatrixomas (skin), Pulmonary infections, Pseudodrop attack due to quadriceps weakness
- Haggard or Hatchet facies, Hair loss (frontal balding)
- Intrinsic muscles of hand wasting, IQ low, Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias
Fragile X syndrome
Mnemonic: See the 4th letter. fraGile
- Trinucleotide repeat: CGG
- Chromosomal mapping of affected gene: X chromosome (fragile X)
- Clinical features and Pathophysiology: Everything is big
- Thick brain: Mental retardation (2nd most common genetic cause of mental retardation after Down’s syndome), ADHD (female), Autism
- Long face
- Large jaw
- Large ears
- Large testicles (macro-orchidism)
- Increased methylation (Hypermethylation of FMR gene due to >200 CGG repeats) leading to inactivation and prevention of transcription.
I love the the way you simplify the subject especially the mnemonics and but could you add the age of onset and death, cause of death and images if available thanks