Mnemonic: BRAIN ATTACK a. Blood pressure: Antihypertensives are recommended only in following conditions: SBP >220 mmHg, DBP >120 mmHg or MAP >130 mmHg (Target SBP reduction by 15% in 1st 24 hours) End organ damage: Acute MI, Aortic dissection, Hypertensive encephalopathy, Severe left ventricular failure Candidates for thrombolysis: SBP >185…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
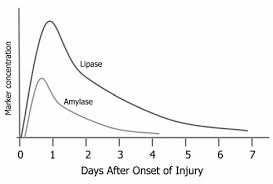
Amylase and Lipase in Acute Pancreatitis
Test Rise Peak Return to baseline Lipase 4-6 hours 48 8-14 days Amylase 2-4 hours 24-48 5-7 days Serum lipase elevation has a better diagnostic value as compared to serum amylase due to its superior specificity. Amylase has a low molecular weight and as a result can easily pass through…
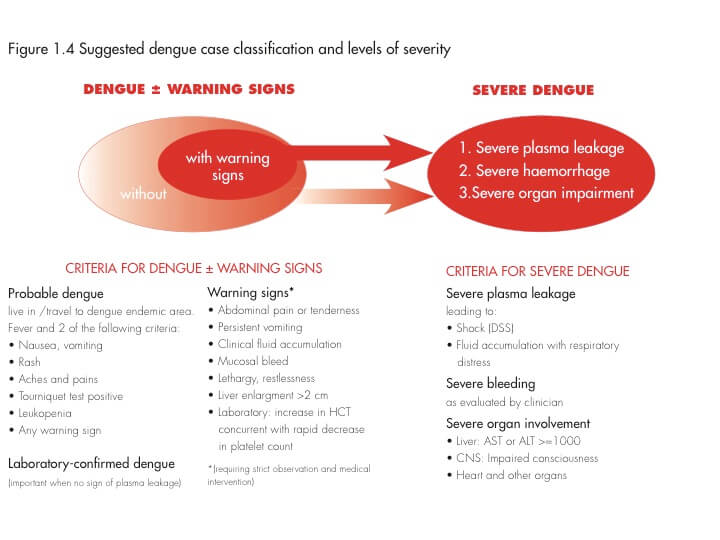
Dengue Classification : Mnemonic
Probable Dengue Mnemonic: FEVeR TLC (Send Total Leukocyte Count in Fever) a. Feverb. Endemic area (living or travel)and 2 of –c. Vomiting and nausead. Rashe. Tourniquet test positivef. Leukopenia (EARLIEST sign)g. Cramps and cries (Aches and pains) Tourniquet test: Inflate the BP cuff between SBP and DBP and keep it…

Simplified Guide to Statin Therapy
Statins Equivalent Dose Mnemonic: PRASLPF 2-5-10-20-40-40-80 Pituvastatin 2 mg Rosuvastatin 5 mg Atorvastatin 10 mg Simvastatin 20 mg Lovastatin 40 mg Pravastatin 40 mg Fluvastatin 80 mg Intensity of Statins a. High intensity (LDL lowering >/= 50%) Atorvastatin 40-80 mg Rosuvastatin 20-40 mg b. Moderate intenstity (LDL lowering 30-49%) Atorvastatin…
Beta-Blockers : Mnemonics
We have 1 heart and 2 lungs. a. B1 – heartb. B2 – bronchial wall Cardioselective (B1) vs Non-selective (B1 and B2) beta blockers Beta blockers with 1st letter from A to N are Cardioselective: Acebutolol Atenolol Bispoprolol Betaxolol Celiprolol Esmolol Metoprolol Nebivolol Nebivolol = NO donor Beta blockers with…
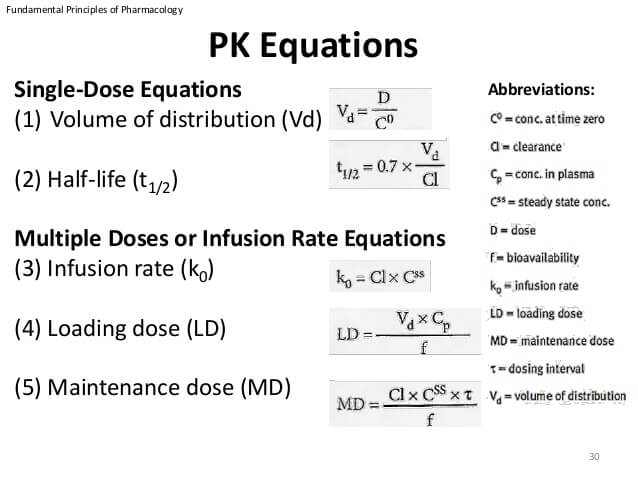
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics
ADME is the 4-letter acronym used to describe pharmacokinetics: ABCD is another 4-letter acronym used to describe pharmacokinetics: The most important pharmacokinetic parameters from a dosing point of view are: Vd = Volume of distributionD = DoseCo = Concentration in plasmaCL = ClearancekE = Elimination constantt1/2 = Half life In…
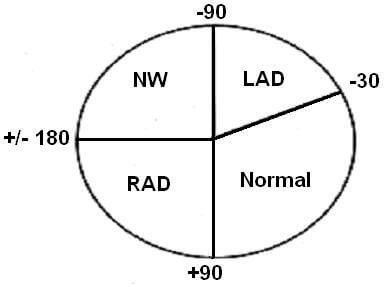
ECG Axis Determination : Mnemonic
Lead I = left (0 degrees)Lead aVF = floor (90 degrees) Lead I +ve and Lead aVF +ve = Between 0-90 degrees (Normal axis) Lead I -ve and Lead aVF +ve = Between 90-180 degrees (Right axis deviation) Lead I +ve and Lead aVF -ve = Between 0 to -90…
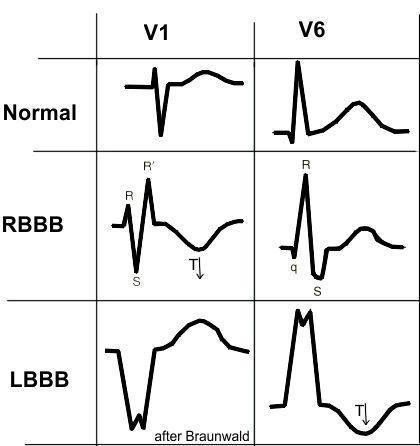
Bundle Branch Block : Mnemonic
If the QRS complex is wide (>0.12 s/>3 small squares), the ventricular activity may be arising from the ventricle conducting system. caused by a ‘bundle branch block’. WiLLiaM MaRRoW (classic mnemonic) Wi – V1LL – LBBBM – V6 M – V1RR – RBBBW – V6 ViLLheiM MaRRooN (more accurate) V…
