(Article for Nepalese/ Indian and South Asian students) Postgraduate entrance exam for MD/MS is one of the toughest examinations in Nepal. The cut throat competition, the dilemma between studying or earning, and the pressure to perform against the toppers and best minds in the country make it one of the…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
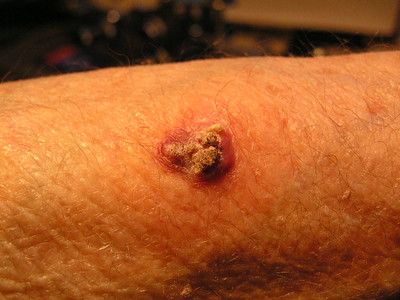
Skin Malignancies : Mnemonics
Malignant Melanoma Diagnosis or Clinical features: Mnemonic: ABCDE Risk factors: Mnemonic: MM RISK Pathologic Types: Mnemonic: Melanoma Always Spreads to Nodes (in order of worsening prognosis) Mnemonic Type Incidence Site Growth pattern Melanoma Maligna – lentiginous 10-15% Face (Precursor – Hutchison’s freckles/lentigo maligna) long in-situ stage before vertical growth Always…
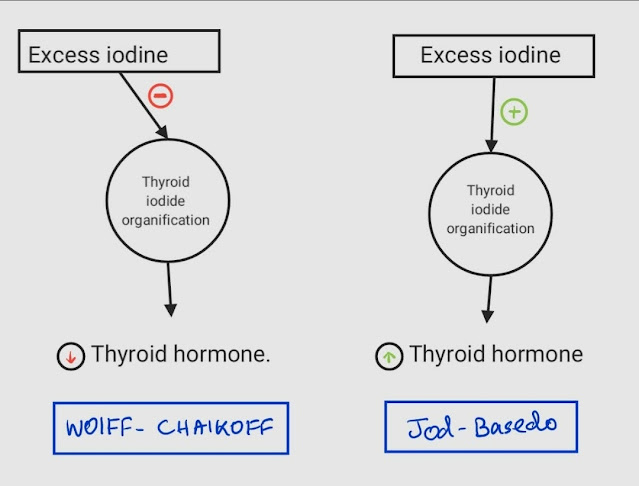
Jod-Basedow Phenomenon vs Wolff-Chaikoff Effect : Mnemonic
Jod = Addition in Hindi or Nepali = Iodine induced Hyperthyroidisim ChaikOFF = Thyroid hormone synthesis is switched OFF = Iodine induced Hypothyroidisim Mechanism Jod-Basedow Wolff-Chaikoff Pre-requisite Abnormal thyroid gland free from pituitary control Thyroid gland under pituitary control Conditions Endemic goitre, Grave’s disease, Toxic multinodular goitre, Thyroid adenoma Normal…
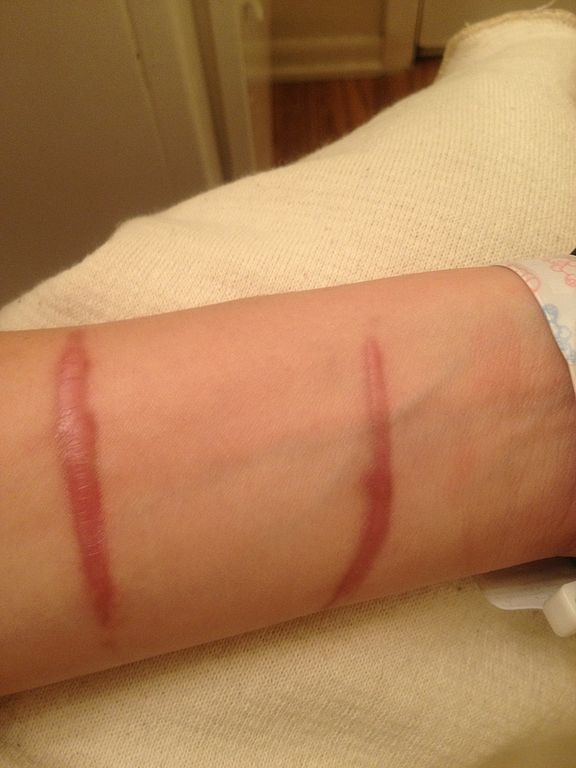
Hypertrophic Scar vs Keloid
Hypertrophic scars and keloids are both raised, firm scars formed from excess fibrinogen production and collagen during healing. Mnemonic: BAD SCARS Mnemonic Basis Hypertrophic scar Keloid B Behavior Natural regression No spontaneous regressio A Acuteness Appears in weeks Appears over months to years D Demographic All races affected More prevalent…
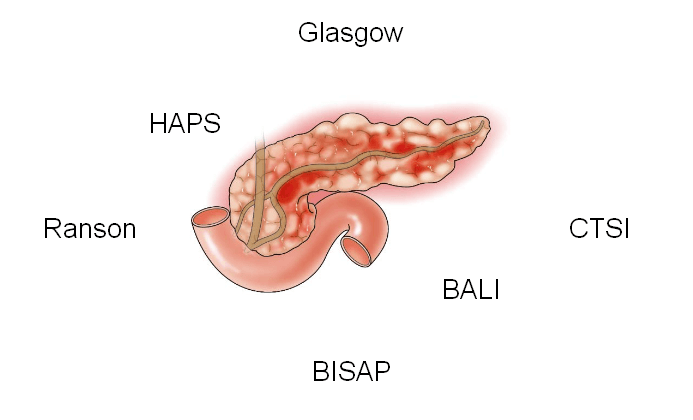
Severity Scores for Acute Pancreatitis : Mnemonics
Modified Glasgow-Imrie Score Severe pancreatitis likely: 3 or more of the following within 48 hours of symptom onset Mnemonic: PANCREAS Mnemonic Criteria Positive when P PaO2 <60 mmHg A Age >55 years N Neutrophils (WBC) >15,000/cu.mm C Calcium <2 mmol/l R RFT (Urea) >16 mmol/l E Enzyme (LDH/AST) LDH >600…
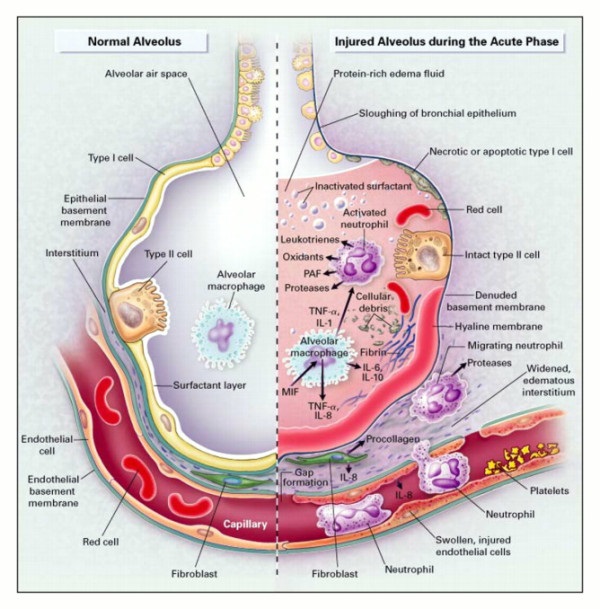
ALI and ARDS : Mnemonics
Diagnosis (Berlin Criteria) Mnemonic A R D S Acute Lung Injury (ALI) Acute onset (<7 days) Ratio PaO2/FiO2 ≤300 mmHg or 40 kPa Diffuse bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on CXR Swan-Ganz pulmonary wedge pressure ≤18 mmHg or No evidence of Left atrial hypertension Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Acute onset (<7…
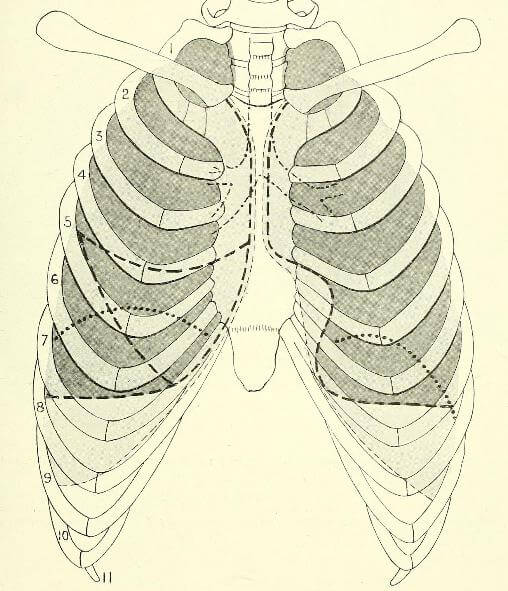
Surface Anatomy of Pleura and Lung
Surface Anatomy of Pleura Mnemonic: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 rule 1. Starts about 2 cm above the midpoint of medial 1/3 of clavicle. 2. Meet in the midline at rib 2. 3. Left side reaches sternal line at rib 4 (to make room for heart). 4. Right side…
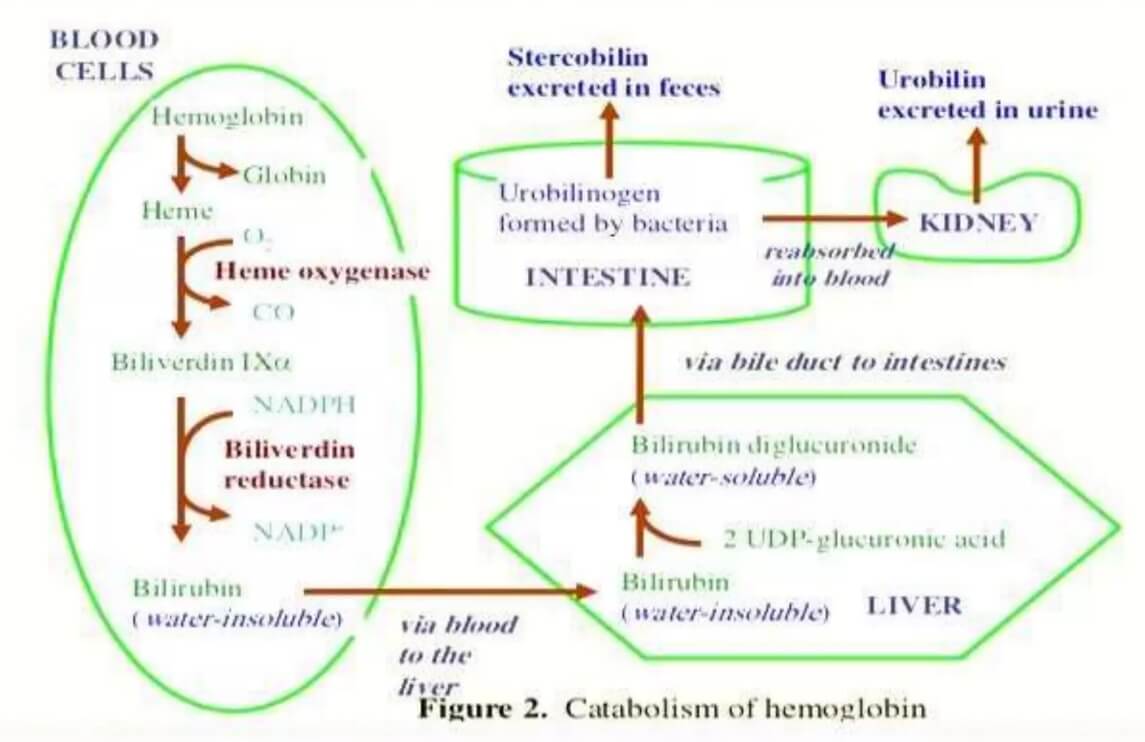
Bilirubin Metabolism and Disorders
Bilirubin Metabolism Mnemonic: ABCDE 1. Aged RBCs (80-85%) 2. Breakdown to Biliverdin and Bilirubin (in reticuloendothelial system) 3. Circulation 4. Delivery to liver (Conjugation) 5. Excretion and Enterohepatic circulation Unconjugated Vs Conjugated Bilirubin Unconjugated bilirubin Conjugated bilirubin Van den Bergh reaction Indirect Direct Solubility Water insoluble; Lipid soluble Water soluble;…
