Boundaries
- Anteriorly: Clivus (Basiocciput + Basisphenoid)
- Laterally: Petrous temporal bone + Occipital bone
- Floor: Occipital bone
- Roof: Tentorium cerebelli (separates cerebellum from cerebral hemispheres)
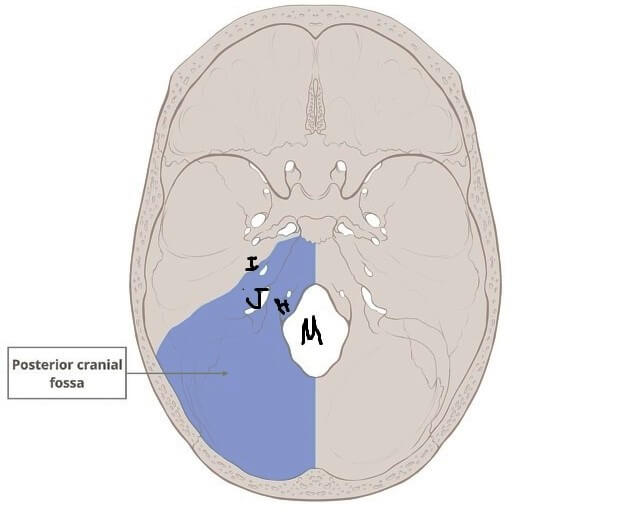
Foramina
Mnemonic: IJHM (International Journal of Hospitality Management) from lateral to medial
1. Internal acoustic meatus (IAM)
- CN VII
- CN VIII
- Nervus intermedius or Intermediate nerve of Wrisberg (sensory and parasympathetic branch of CN VII)
- Labyrinthine vessels (branches of AICA)
2. Jugular foramen
Mnemonic: IPS 9, 10, 11
IPS + SS = IJV
- CN IX
- CN X
- CN XI
- Internal Jugular vein (IJV)
- Inferior Petrosal sinus (IPS)
- Sigmoid sinus (SS)
3. Hypoglossal canal
- CN XII
- Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery
- Hypoglossal venous plexus
4. foramen Magnum
- Medulla oblongata
- Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- Vertebral and posterior spinal arteries
- Apical ligament of dens
- Membrane tectoria
Contents
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla
- Cerebral and Cerebellar hemispheres
- Dura and Tentorium cerebelli (encloses occipital sinus, superior sagittal sinus and paired transverse sinus)
Clinical consideration
Pediatric posterior fossa tumors:
- Mnemonic: MAGE (In order of prevalence)
- Medulloblastoma: 30-40%
- Astrocytoma (pilocytic): 25-35%
- Glioma: 20-25%
- Ependymoma: 10-15%
Cerebellar tonsil herniation: Herniation of pons and medulla oblongata through the foramen magnum due to raised ICP