Use: Alternative to hematoma block in reduction of distal radius and ulna fractures Advantage: Providing distance from the fracture hematoma (no theoretical risk of converting closed fracture into open fracture) Disadvantage: Risk of neurovascular injury on volar surface of forearm Local anesthetic and volume: 10–15 ml of 1 % plain lidocaine…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
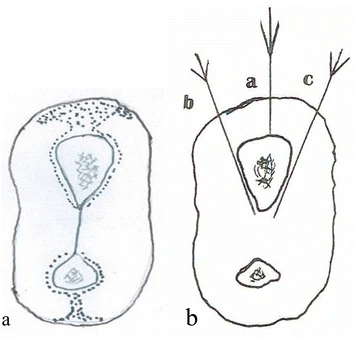
Facet Joint Orientation : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: BUM BUL BUM The superior articular process faces: 1. Cervical vertebra: BUM 2. Thoracic vertebra: BUL 3. Lumbar vertebra: BUM
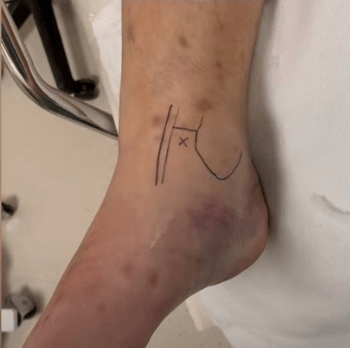
Anteromedial Ankle Hematoma Block
Mechanism of action of Hematoma Block Indications of Anteromedial Portal Injection Landmarks Technique
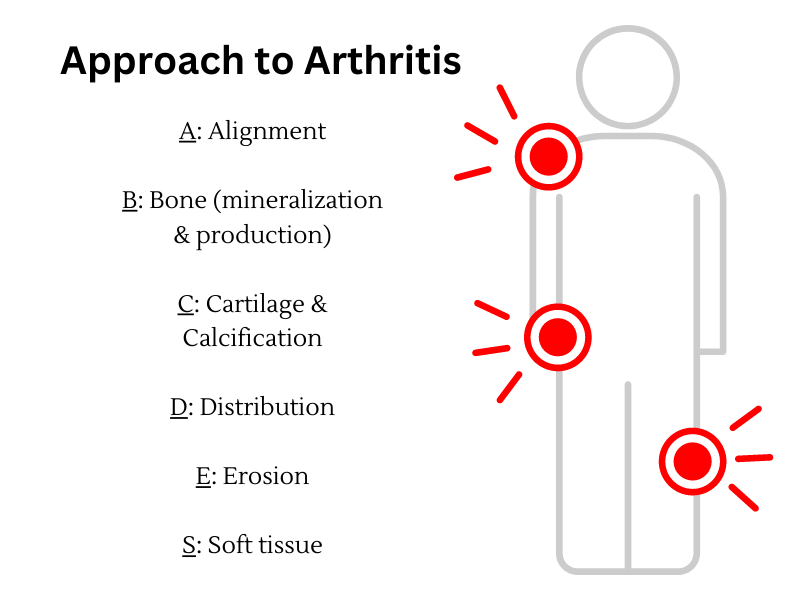
Radiological Approach to Arthritis : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: ABCDES Alignment Bone – mineralization Bone – production Cartilage (Joint space) Calcification Distribution Erosions Soft tissues ABCDES of Arthritis of Wrist and Hand Features RA PsA OA EOA CPPD Gout Alignment (subluxation) Ulnar Multidirection Lateral Lateral None None Bone mineralization Osteopenia Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Bone production None…
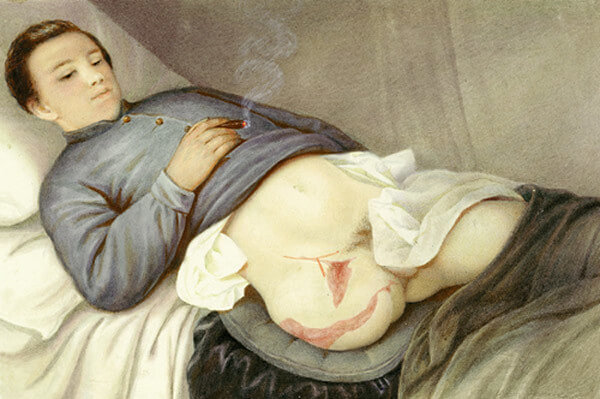
Extremity Amputations – Review
Indications Mnemonic: three Ds 1. Dead (or dying): Peripheral vascular disease (most common indication for amputation), Severe trauma (leading indication for amputation in younger patients), Burns, Frostbite 2. Dangerous (or deadly): Malignant tumors, Potentially lethal sepsis, Crush injury 3. Damned nuisance: Gross deformity, Recurrent sepsis, Sever loss of function Increase…
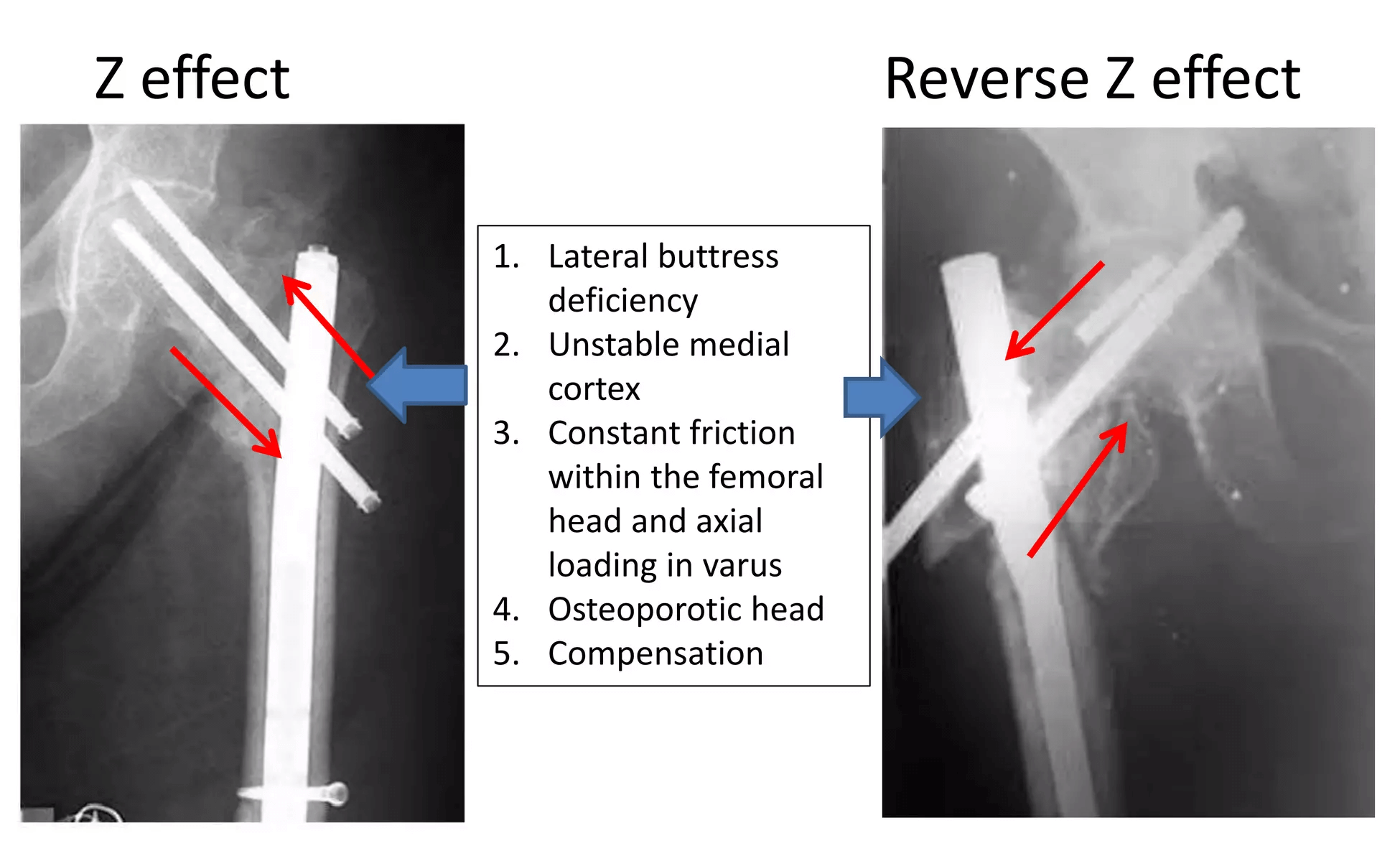
Z-effect and Reverse Z-effect in PFN
‘Z-effect’ and ‘Reverse Z-effect’ are complications relating to differential migration of screws that arise from fixation of unstable proximal femoral fractures with Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN) having 2 interlocking head screws. The 4 patterns of unstable intertrochanteric fracture hip are: Z-effect: The Z-effect involves the lateral migration of the lag…
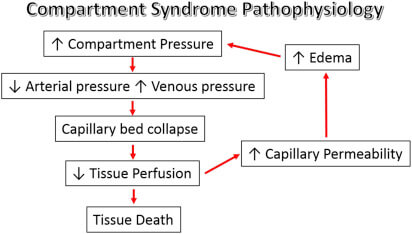
Pathophysiology of Acute Compartment syndrome
Definition Mubarak and Hargens (1981) defined compartment syndrome as an elevation of the interstitial pressure in a closed osseofascial compartment that results in microvascular compromise. Pathophysiology Tissue perfusion = Capillary perfusion pressure – Interstitial fluid pressure 3 major theories for microvascular dysfunction and ischemia: Tissue survival: Vicious cycle of compartment…
Natural Relief for Joint Pain: Tried and Tested Remedies
Joint pain is a common condition. This condition affects millions of people worldwide. Its causes include a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, or wear and tear on the joints. While over-the-counter pain relievers can offer temporary relief, they often have unwanted side effects. As a result, many people are…