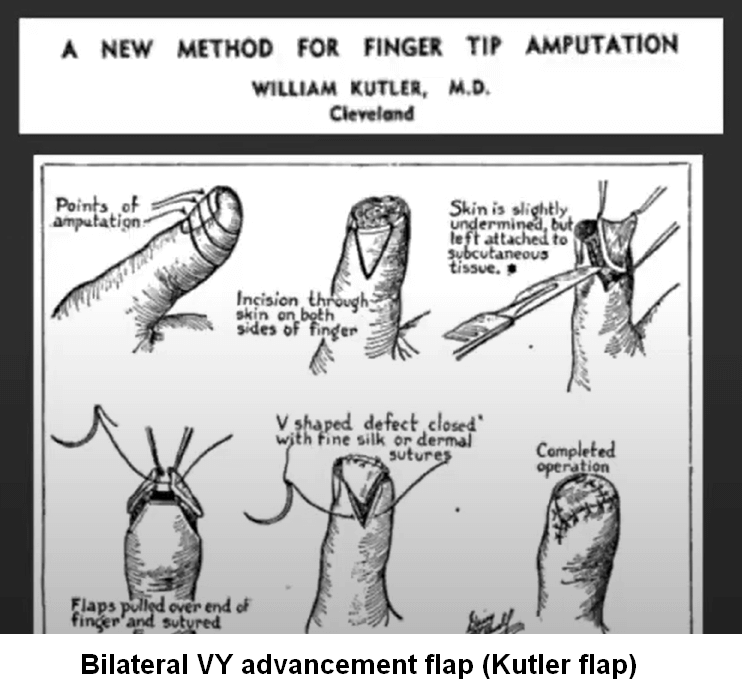
Indications Classically, this flap is indicated in patients with transverse or volar oblique amputations. In actuality, the patient in whom this flap is useful generally will have an amputation where there is more tissue on the radial and ulnar margins of an amputation and exposed distal phalanx. Limitations Generally, the…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
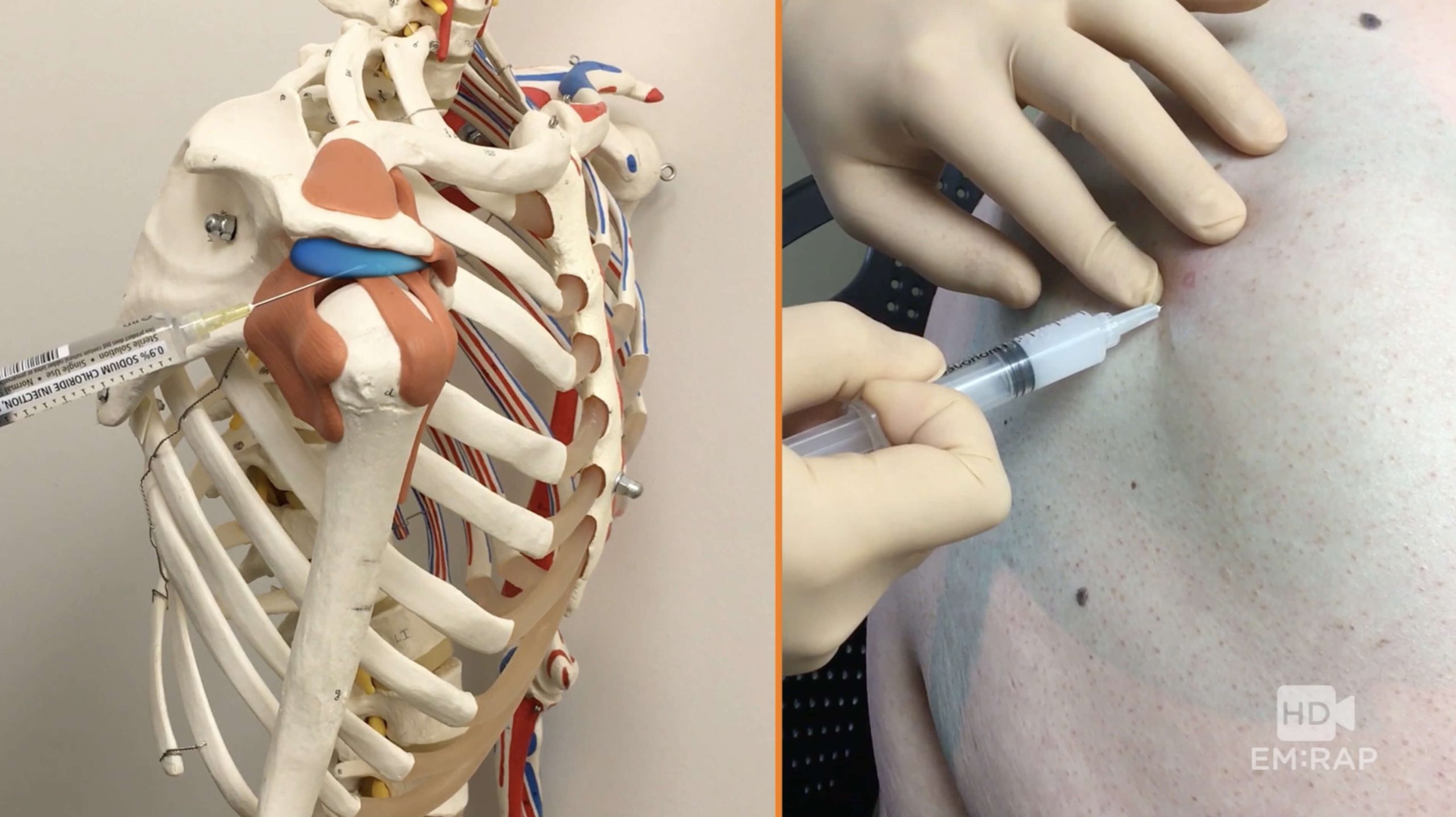
Subacromial Injection
Indications: Diagnostic and therapeutic purposes of – Syringe preparation: Position: Comfortably seated with the arm at the side and the hands resting on the lap. Posterior approach: Lateral approach:

Aberdeen Knot
To end continuous suture, either a square knot, surgeon’s knot or an Aberdeen knot is required. The Aberdeen knot has been shown to be superior to a surgeon’s knot. Recommendations on number of throws: Technique/Steps:
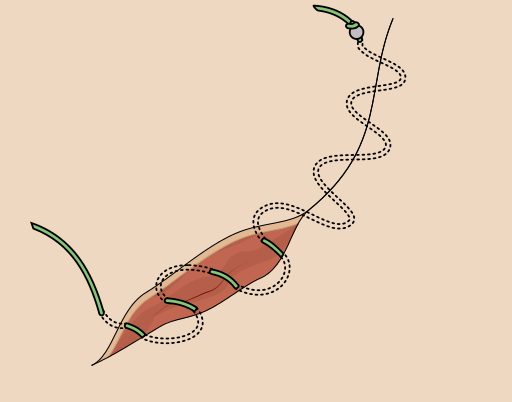
Running subcuticular suturing
1. Start with a buried knot at distal apex of the wound. 2. Take a bite deep to the epidermis that should curve parallel to the skin surface and exit in the same plane approximately 5-10mm along the wound, taking care to stay at the same level. 3. Continue step…
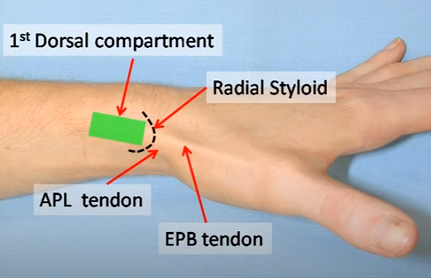
Injection technique for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Syringe Preparation: Position: Comfortably seated with neutral forearm rotation with radial styloid facing upwards – position the wrist in slight ulnar deviation. Technique:

SCFE : Mnemonic Approach
Approach to a limping child General points Classification Management depends on 4 factors which can be remembered using the mnemonic SCFE. Stability and Severity a. Loder classification: b. Severity: Severity Southwick angle on frog-leg lateral view (Difference of head-shaft angle from normal side) Wilson slip % on AP or frog-leg…
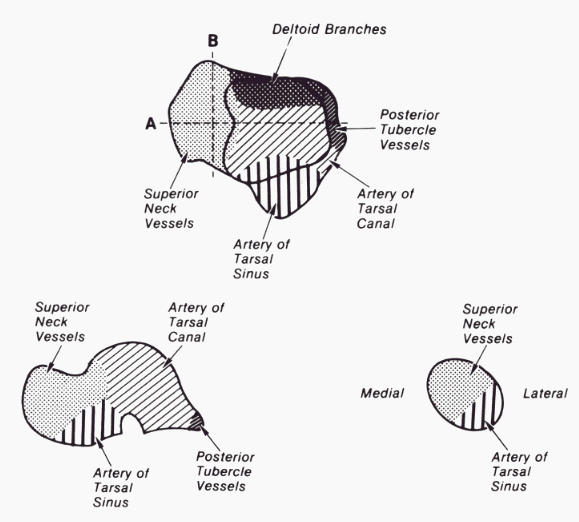
Talus Anatomy : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 0 : Attachments of muscles and tendons 1 : Sinus and Canal 2 : Processes and Tubercles 3 : Parts 4 : Blood vessels: 5 : Articulating surfaces
Management of Skeletal Tuberculosis – Principles
Classification Stage/Type Pott’s spine (Kumar’s) Pott’s paraplegia (Tuli) Hip and Knee Hip (Shanmugasundaram) I Predestructive (Straightening, spasm, hyperemia) Negligible (Objective plantar extensor response or ankle clonus) Synovitis (ROM 75-100%/Haziness, rarefaction)– Hip: FAbER, Apparent lengthening Normal (C) II Early destructive (Diminished space, paradiscal erosion, K<10) Mild (Subjective neuro-deficit but walks with…