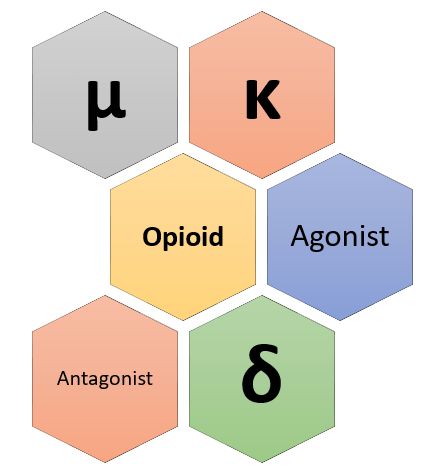
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. Mu (µ) Receptor (MOP) Mnemonic: MU CARDS Miosis eUphoria Constipation Analgesia (Supraspinal + Spinal) Respiratory depression Rigidity (truncal) Dependency Sedation µ1 mediates supraspinal analgesia, and most of other effects including spinal analgesia is mediated by µ2. Kappa…
Tag: Anesthesia
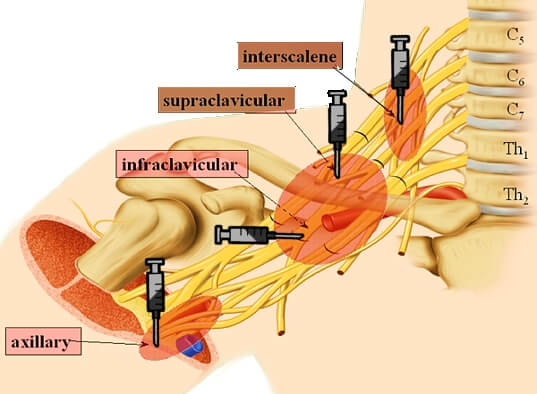
Brachial Plexus Block Made Easy
Brachial plexus is sub-divided from proximal to distal into: Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Branches. This can be easily remembered with a mnemonic: Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer. Approaches for Brachial Plexus Block Basically, there are 4 approaches to the brachial plexus block at different levels as described in the mnemonic…
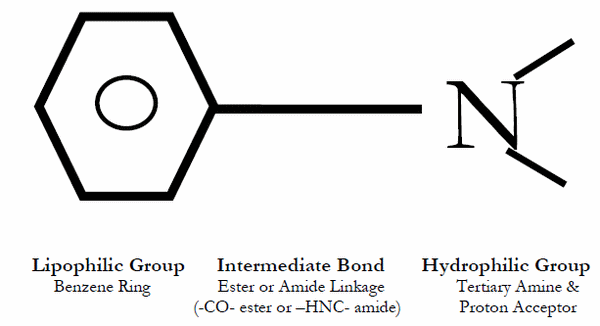
Local Anesthetics Mnemonic
All Local anesthetics contain suffix “-caine”. Local Anesthetics (LA) can be classified as: Esters and Amides. Esters vs Amides A mnemonic device is that the names of amides contain 2 “i”s compared with only 1 “i” seen in esters. Remember: One-eyed ester or Amide word has an “i” in it…
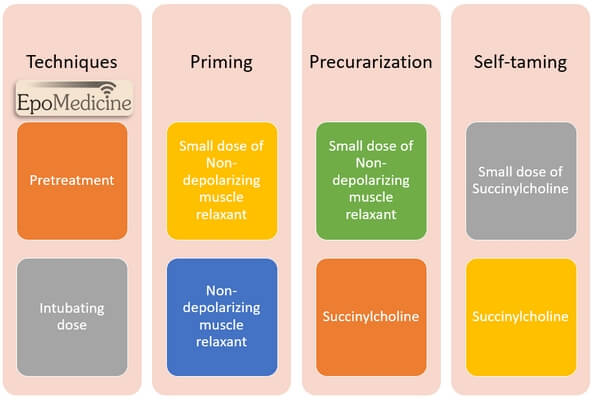
Priming, Precurarization and Self taming
Priming Administration of a small sub-paralyzing dose of non-depolarizing muscular blocking agent (usually 10% of the intubating dose) is given 2-4 minutes before administering a 2nd large dose for tracheal intubation to accelerate the onset of non-depolarizing NM blockade by 30-60 seconds. Mechanism and Concept of Priming 2 theories have…
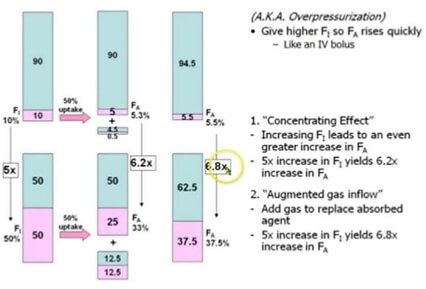
Concentration effect, Second gas effect and Diffusion hypoxia
Concentration effect The higher the concentration of an inhaled anesthetic, the faster the alveolar concentration approaches the inhaled concentration. This is referred to as concentration effect and is clinically significant only in cases where gases are administered in high concentration: Nitrous oxide Xenon Ostwald’s blood gas solubility coefficient: ratio of…
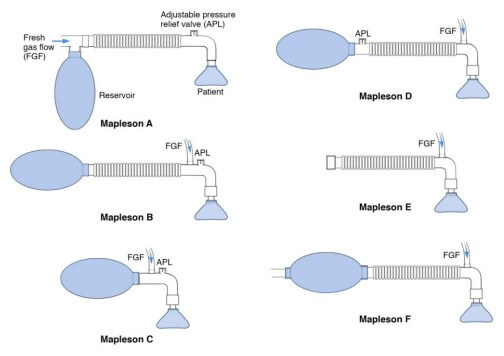
Mapleson Breathing Circuit Made Easy
Anatomy of Mapleson Breathing Circuit Basically, a mapleson breathing circuit consists of following parts: 1. Face mask (towards patient end) 2. Reservoir bag (towards operator end) Accommodates fresh gas flow during expiration acting as a reservoir available for the following inspiration. Acts as a monitor of patient’s ventilatory pattern during…
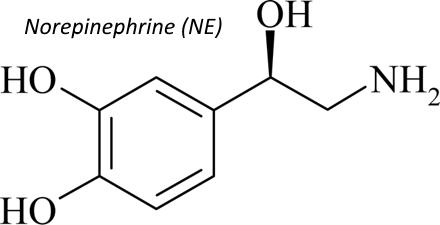
Early vs Delayed Norepinephrine Use in Septic Shock
Norepinephrine has numerous effects in sepsis including veno-constriction (increasing preload), arterial constriction (increasing systemic vascular resistance), positive inotropy, improved cardiac output, and improved renal perfusion. This addresses all the major derangements observed in cases of septic shock. It is important to realize that MAP doesn’t necessarily equate perfusion. Increasing the…
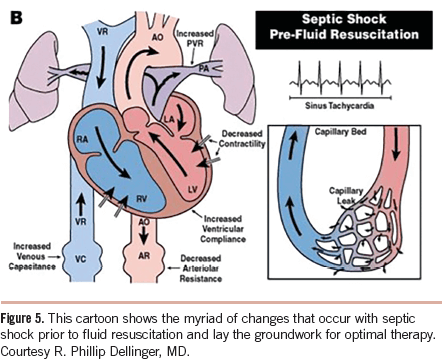
Septic Shock Fluid Resuscitation
Endpoints of resuscitation MAP: > or = 65 mmHg Urine output: > 0.5 ml/kg/hr; despite ↓RBF (Renal Blood Flow) it can be normal due to – Atrial natriuretic factor are elevated in sepsis Hypoproteinemia in sepsis – low plasma colloid osmotic pressure is less able to facilitate oncotic reabsorption. CVP:…