GRUNTING Definition: A short, explosive, moaning or crying sound heard on expiration (Child and neonates) Cause: Any cause of respiratory distress Mechanism: In attempt to increase FRC which helps to keep narrowed or collapsing airways open, creating a longer time for alveolar gas exchange STERTOR Definition: Non-musical, low pitched, snoring…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
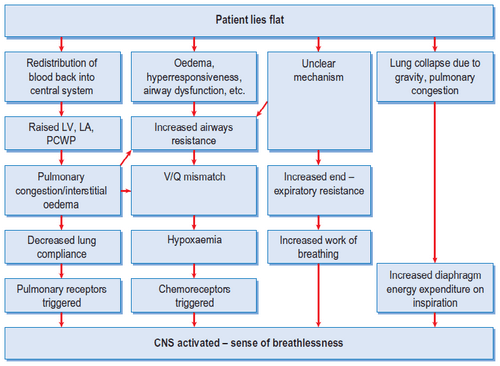
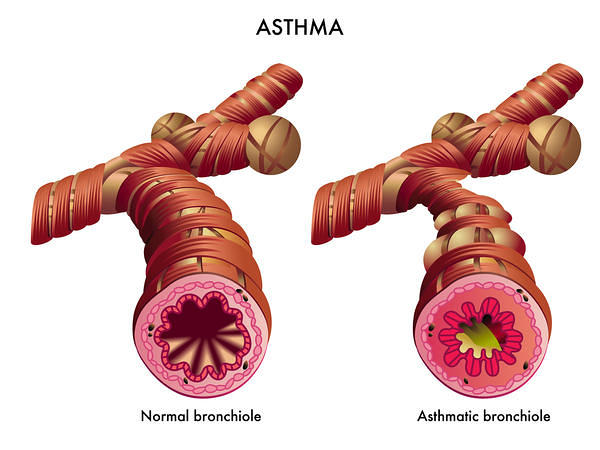
Respiratory Examination – Dyspnea
Definition: Breathlessness inappropriate to the level of physical exertion or even occurring at rest (subjective and not a sign) Mechanisms: Chemoreceptors: Peripheral: Carotid and aortic bodies (to pO2, pCO2 and H+) Central: Medulla (to pCO2, not pO2, change in pH of CSF) a. Increased work of breathing: Airflow obstruction: Bronchial…

Mendelian Inheritance : Basis of Genetics
Some important terminologies Gene: a functional part of the DNA molecule of a chromosome which directs the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. Allele (allelomorph): alternative form of a gene found at the same locus on a pair of homologous chromosomes. Homozygous: the presence of two identical alleles at a…
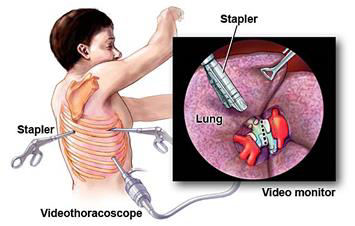
Text Presentation on Empyema Thoracis
A) INTRODUCTION Empyema (aka Empyema Thoracs or Empyema of the chest) is an accumulation of pus in the pleural space that occurs when an infection spreads from the lungs. It comes from the Greek word empyein, which means : pus–producing (suppurates). Empyema itself is not a disease but it is actually a condition complicated by another disease….
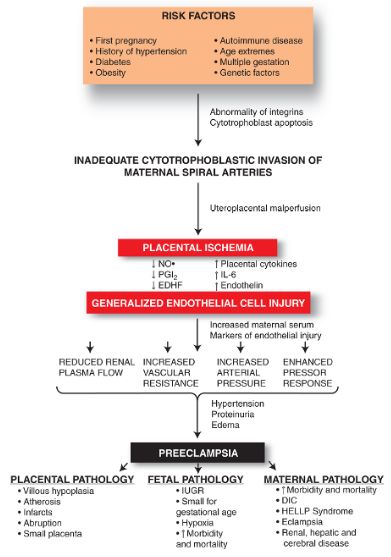
Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy – Basics
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy is a term that encompass wide range of blood pressure related disorders during pregnancy like gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, etc. Blood pressure in Normal Pregnancy: During middle trimester, due to the reduction in Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) and Arterio-venous (AV) shunting within the uterus and intervillous…
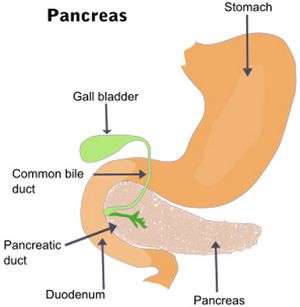
Courvoisier’s law of Obstructive Jaundice
Synonyms: Courvoisier’s sign, Courvoisier syndrome, Courvoisier-Terrier sign, Bard-Pic disease Over years, the use of the term Courvoisier’s sign or gallbladder has been suggested instead of law, because of rising number of exceptions. Eponymous to: Ludwig Courvoisier (1843-1918) Definition of Courvoisier’s law Courvoisier’s (koor-vwah-zee-ayz) law states that ‘a palpable non-tender gallbladder…

Summary of Clinical Tests and Signs in Orthopedics
Adson’s test: for thoracic outlet syndrome Allen’s test: for testing patency of radial and ulnar arteries Alli’s test: for DDH Anvil test: for testing tenderness of the spine Ape thumb: for median nerve injury Apley’s grinding test: for meniscus injury Apprehension test: for recurrent dislocation of the shoulder Barlow’s test:…
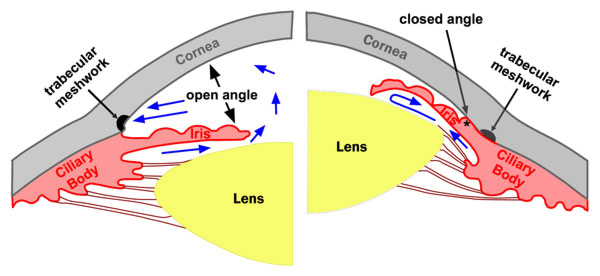
Glaucoma basics : Classification of Glacuoma
Definition: Glaucoma is a group of disorders characterized by a progressive optic neuropathy resulting in a characterstic appearance of the optic disc and a specific pattern of irreversible visual field defects that are associated frequently but not invariably with raised intraocular pressure (IOP). It is one of the commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world. Open-angle…