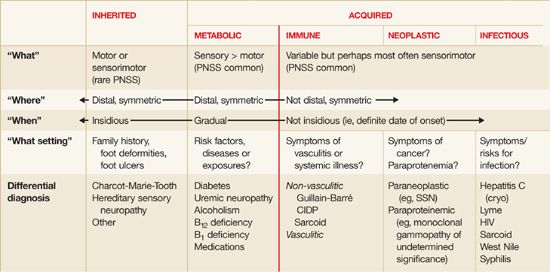
Step 1: What system is involved – motor, sensory, autonomic or mixed? a. Sensory involvement Positive neuropathic sensory symptoms (PNSS) – suggest Acquired polyneuropathy prickling, tingling, asleep like numbness Pain – suggest Small fiber neuropathy due to toxic, metabolic, ischemic or idiopathic cause electric shock, burning, freezing, tightness, throbbing, allodynia…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
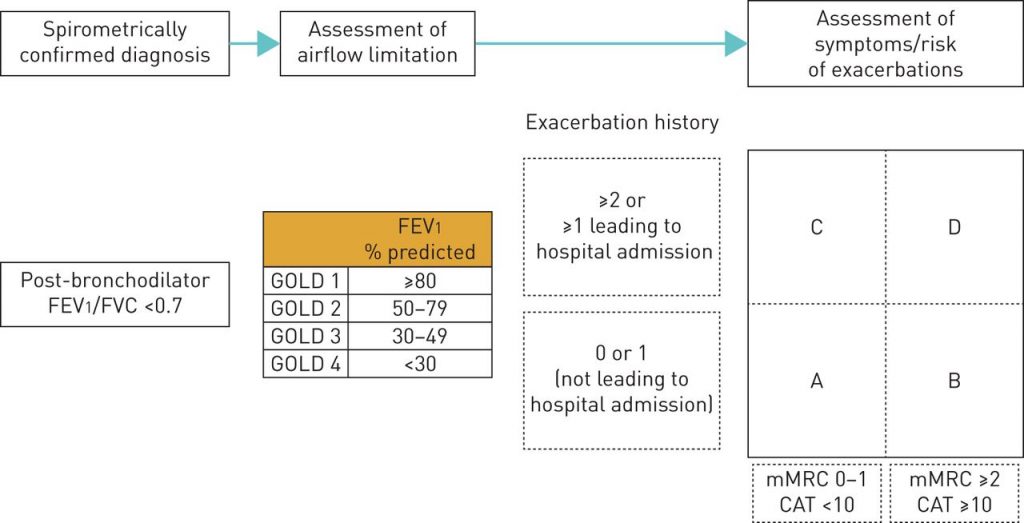
COPD Revision Notes
DEFINITION OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) According to GOLD, COPD is a common preventable and treatable (not curable) disease characterized by: Persistent airflow limitation (Post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC < 0.7), usually progressive (excludes Asthma) Due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities usually caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases. Chronic…
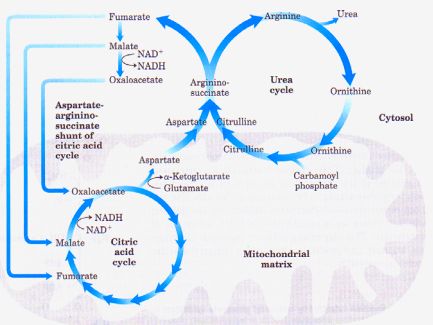
Urea Cycle and Defects with Mnemonics
Mnemonic for Urea Cycle Intermediates Orange Cola, Coffee, Alcohol of Argentina For Aggressive Urine Orange: Ornithine Cola: Carbamoyl Phosphate Coffee: Citrulline Alcohol: Aspartate (enters cycle) Argentina: Arginosuccinate For: Fumarate (leaves cycle) Aggressive: Arginine Urine: Urea (leaves cycle) Structure of Urea NH2-CO-NH2 (1 amide from aspartate and 1 from ammonia) Amide…
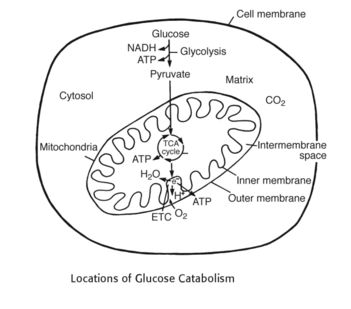
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) and Oxidative Phosphorylation : Mnemonic
General concepts of ETC and Oxidative Phosphorylation: 1. Occurs in cell cytosol: Glycolysis 2. Occurs in mytochondrial matrix: Kreb’s (TCA) cycle 3. Occurs in mitochondrial inner membrane: ETC – Stepwise movement of electrons from high energy to low energy that activates proton pump which transports proton from the mitochondrial matrix to mitochondrial inter-membrane and…
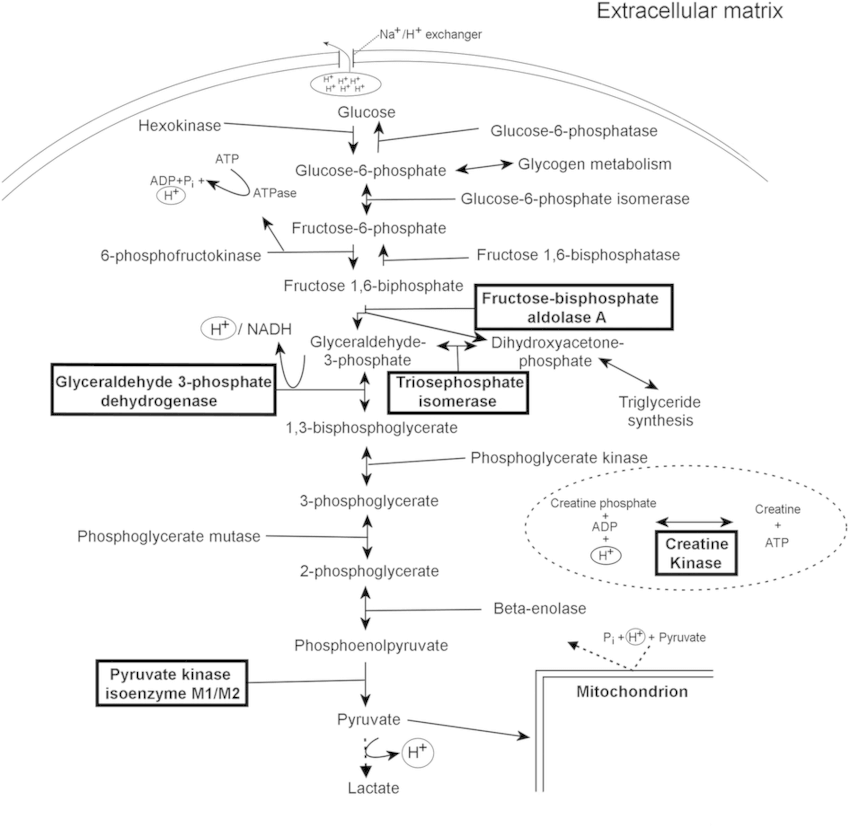
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Mnemonics
It is not necessary to memorize each and every step of the process. We will only look into the major events. A. Meaning: Glyco (Sugar) + Lysis (Breaking or splitting) B. Synonyms: Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (EM Pathway) C. Site: Cytoplasm D. Enzyme basics: Kinase: Adds or removes phosphate from substrate (uses…
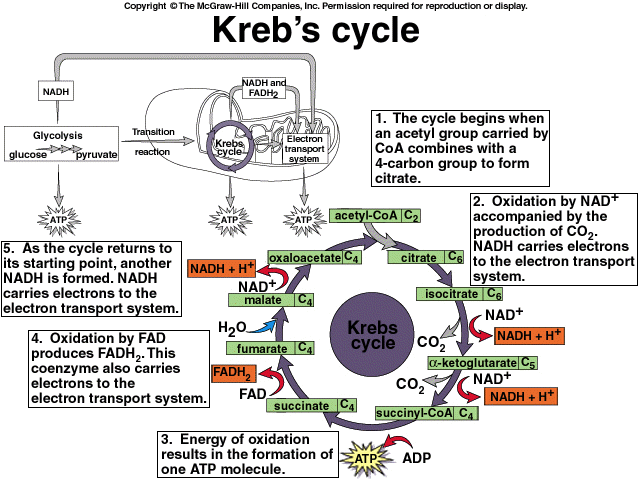
Kreb’s cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: Our City Is Kept Safe And Sound From Malice Remember the enzymes of the cycle: All the enzymes are in the matrix of mitochondria except succinate dehydrogenase which is in inner mitochondrial membrane. Pyruvate from aerobic glycolysis enters mitochondria, where it may be converted into acetyl-CoA (irreversible reaction) under…
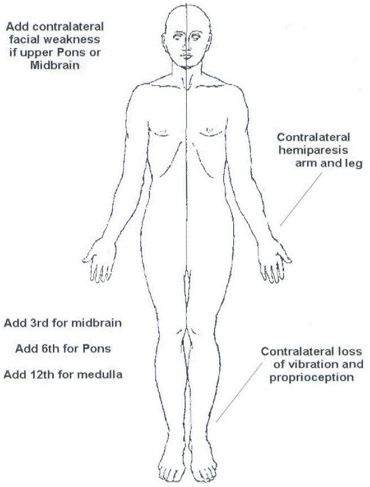
Medial Medullary (Dejerine’s) Syndrome : Anatomical basis mnemonic
As already discussed in the previous section about Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome: 6 “S” pass/lie on the Side (latetral) of Medulla Except the anteromedian part supplied by vertebral artery, rest of the medulla is supplied by PICA Let us now review the relevant anatomy and physiology of the medial portion…
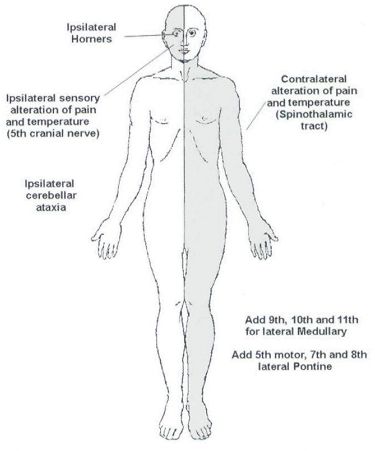
Anatomical basis of Wallenberg (Lateral Medullary) Syndrome : Mnemonic
Before proceeding into the disease itself, let’s review – relevant anatomy of the medulla with a simple mnemonic. The Side (lateral) part of Medulla contains 6 “S“ 1. Spinocerebellar tract Posterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters to ipsilateral cerebellum via ipsilateral inferior cerebellar peduncle Anterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters…