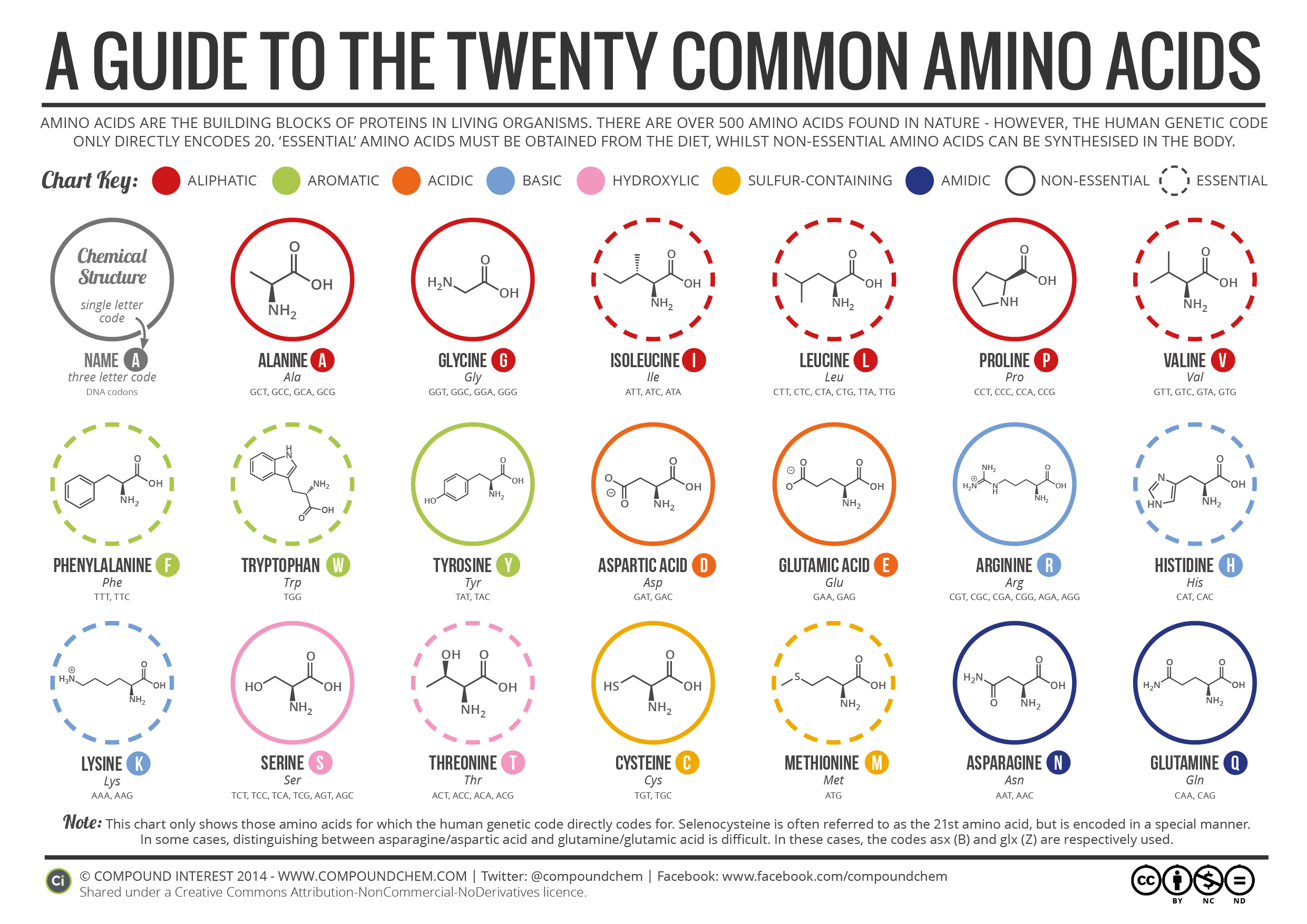
What are amino acids ?
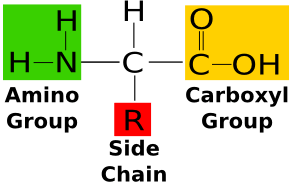
Amino acids are molecules containing:
- An amine group
- A carboxylic acid group
- A side chain that varies between different amino acids
Assign the names of these amino acids to 20 different alphabets
The technique that you are going to use to remember all these are given just below the list.
- A – Alanine
- B: ⊗
- C: Cysteine
- D: Aspartate
- E: Glutamate
- F: Phenylalanine
- G: Glycine
- H: Histidine
- I: Isoleucine
- J: ⊗
- K: Lysine
- L: Leucine
- M: Methionine
- N: Aspargine
- O: ⊗
- P: Proline
- Q: Glutamine
- R: Arginine
- S: Serine
- T: Threonine
- U: ⊗
- V: Valine
- W: Tryptophan
- X: ⊗
- Y: Tyrosine
- Z: ⊗
Technique to remember this representative alphabets
1. Amino acids with unique 1st letter:
- Cysteine (C)
- Histidine (H)
- Isoleucine (I)
- Methionine (M)
- Valine (V)
- Serine (S)
2. 1st letter for more than one amino acids – but reserved for representation of these:
- Alanine (A)
- Glycine (G)
- Leucine (L)
- Proline (P)
- Threonine (T)
3. Phonetically suggestive:
- Arginine (R-ginine)
- Phenylalanine (F-enylalanine)
- Tyrosine (tYrosine)
- Tryptophan (W-structure of tryptophan)
4. Others:
- Aspartate or Aspartic acid (asparDic)
- Asparagine (aspargiN)
- Glutamate or Glutamic acid (gluE-tamate)
- Glutamine (Q-tamine)
- Lysine (K is near L)
Amino acids Classified with Mnemonics
A. Basis of Structure:
1. Aliphatic side chains: GAVLI
- Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine
2. With OH group: STY
- Serine, Threonine, Tyrosine
3. Acidic: AAGG
- Aspartate, Aspargine, Glutamate, Glutamine
4. Sulphur containing: CM
- Cysteine, Methionine
5. Basic: HIstory of ARGentina was Lie
- Histidine, Arginine, Lysine
6. Aromatic: HTTP
- Histidine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Phenylalanine
7. Imide:
- Proline
B. Essential and Non-essential:
1. Essential Amino acids: PVT TIM HALL
- Phenylalanine
- Valine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Isoleucine
- Methionine
- Histidine
- Arginine
- Lysine
- Leucine
- Semi-essential are Histidine and Arginine
2. Non-essentia Amino acidsl: Rest of the 10 amino acids
C. Metabolic Fate of Amino acids:
1. Ketogenic: Lysine, Leucine
2. Partially Ketogenic/Glucogenic: Isoleucine and other 3 aromatic amino acids (Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Phenylalanine)
3. Glucogenic: Rest
D. Polarity:
1. Polar with no charge on R (Hydrophillic): STY (Serine, Threonine, Tyrosine), CNQ (Cysteine, Aspargine, Glutamine)
2. Polar with +ve R (Hydrophillic): Arginine, Histidine, Lysine (Basic)
3. Polar with -ve R (Hydrophillic): Aspartate, Glutamate (Acidic)
4. Non-polar (Hydrophobic): Rest, i.e. GAVLI MFWP (Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Proline)
Glycine
- Smallest and simplest amino acid
- Responsible for flexibility of protein
- Optically inactive
- Lacks chirality (handedness)
- Glycine withh arginine and methionine (GAM + Ornithine) synthesize cretaine.
- Glycine (with succinyl CoA) is used for Heme synthesis.
Histidine
- Most stable amino acid at physiologic pH
- Can serve as best buffer at pH 7
- Can protonate and deprotonate at neutral pH
- Precursor of histamine
Glutamine
- Storage and transport form of ammonia
- Removal of ammonia from brain
- Precursor of purines and pyrimidines
Phenylalanine and Tyrosine
- Phenylalanine is precursor of tyrosine
- Tyrosine is a precursor of:
- Catecholamines
- Thyroxine
- Melanin
Cysteine
- Can be synthesized in body from methionine (both contain sulphur)
- Responsible for reducing action of glutathione
Methionine
- Form S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) which is a major methyl group donor in body
Glutathione
- Antioxidant (reducing property is because of cysteine sulfhydryl group) – detoxify H2O2 by glutathione peroxidase
- Carrier in transport of certain amino acids across membrane in kidney
- Conjugation reaction
Tryptophan
- Precursor of niacin and serotonin (which form melatonin)
- 60 mg tryptophan form 1 mg niacin
- Also known as alpha-amino beta-3 indole propionic acid
Arginine
- Most basic amino acid
- Precursor of nitric oxide
Alanine
- Transport form of ammonia from muscle

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.
I believe that the list of acidic amino acids is incorrect on this website. Only aspartic acid and glutamic acid are truely acidic.
Thank you
For essential a a
President M.Vittal at Hamburg