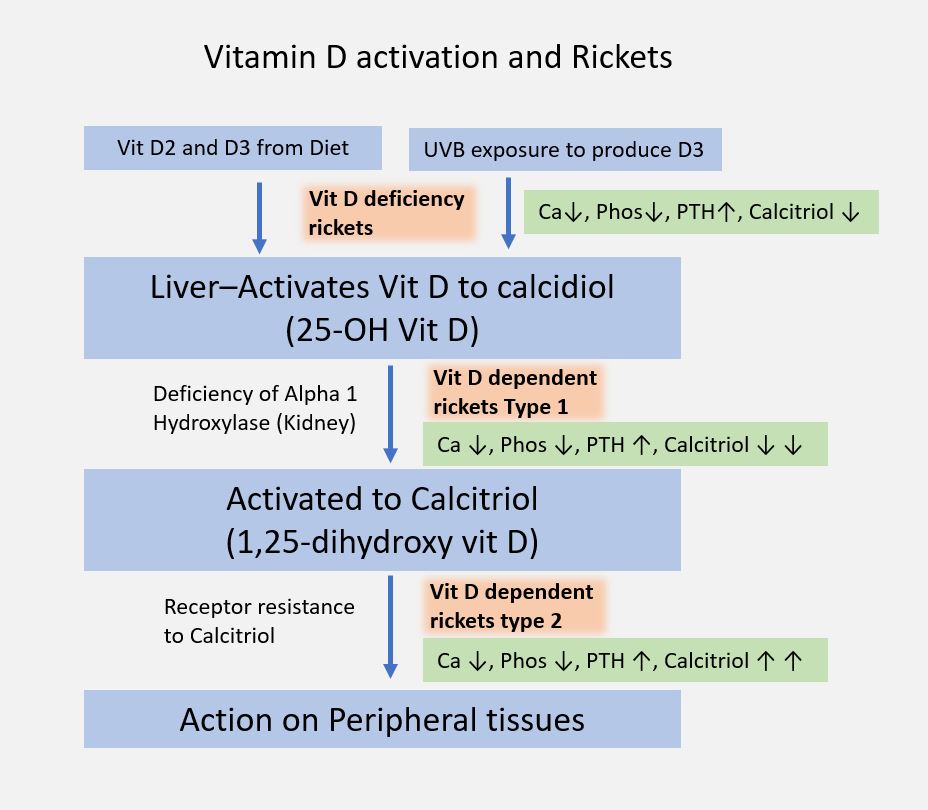
Types Type Pathology 25(OH) D 1,25(OH)2 D PTH Ca PO4 ALP Additional clinical findings Treatment Vitamin D deficiency (Nutritional) Hypovitaminosis D 🡢 Hypocalcemia 🡢 Secondary hyperparathyroidism 🡢 Rise of serum calcium towards normal level ↓ ↓ ↑ ↓/= ↓ ↑ Rachitic rosaryBowing of kneesMuscle hypotoniaWaddling gaitDental diseaseLooser zones/Milkman’s fracture (pseudofracture…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
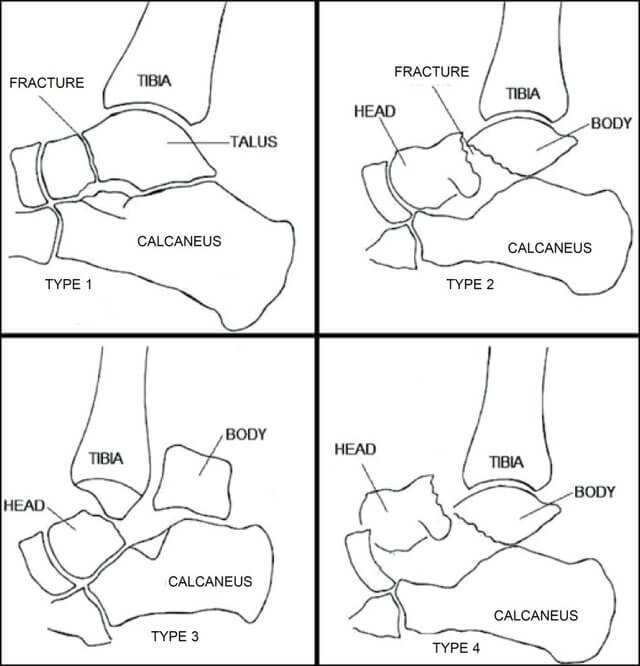
Hawkin’s Classification for Talus Fractures : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: NISA 10-50-90-100 Type I – Non-displaced Neck fracture (upto 10% risk of AVN) 1 blood vessel damaged (entering talar neck) Management: 8 weeks in cast and 4 weeks in CAM cast Type II – Type I + Inferior (subtalar) subluxation/dislocation (upto 50% risk of AVN) 2 blood vessels damaged…

Child with a limp : Mnemonic Approach
HISTORY AND EXAMINATION Mnemonic: LIMPINGS 1. Limping definition and onset Any deviation in walking pattern away from the expected normal pattern for the child’s age Limping is never normal Acute Acute infections Trauma Leukemia Unstable SCFE Epidural abscess Chronic SCFE DDH Neoplasm Child abuse Neuromuscular conditions Leukemia 2. Injury Mnemonic:…
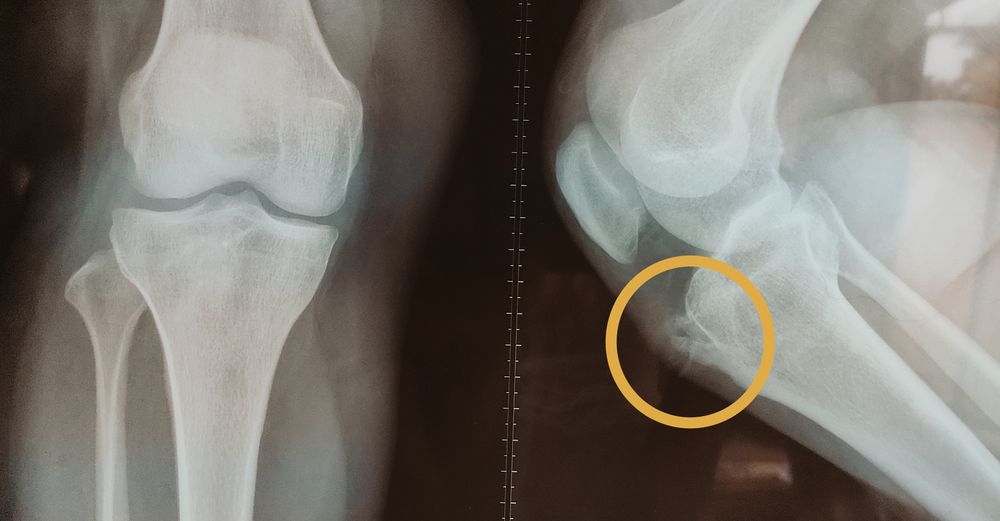
Mortarmen’s knee
Synonym: Adult onset tibial tubercle exostoses History: Pain over anterior surface of upper tibia Pain during running, jumping, squatting, kneeling and descending stairs Usually no history of trauma, anterior knee pain or Osgood-Schlatter disease Physical examination: Tenderness over hypertrophic tibial tubercle Quadriceps tightness (Ely’s test) X-rays: AP, lateral and tangential…
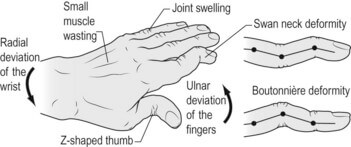
Swan neck deformity vs Boutonniere deformity
Alterations in the relationships between the balanced extrinsic and intrinsic musculature of the hand due to trauma or secondary to the effects of systemic disease may cause the development of functional deformities such as a boutonnière or swan-neck deformity. Swan-neck deformity Boutonniere deformity Deformity PIPJ Hyperextension PIPJ Flexion DIPJ Flexion…
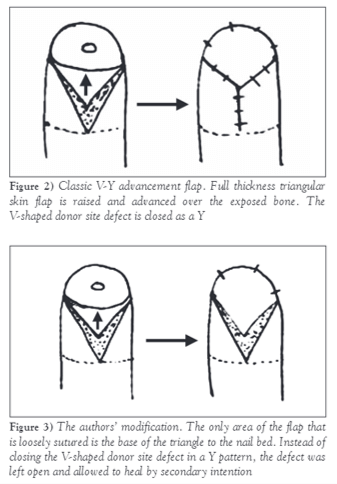
Volar V-Y advancement flap for fingertip amputations
Indications Contraindications Advantages Disadvantage Tension (maximum tension occurs in mid portion of the defect) especially with large defects Blood supply of flap Oblique terminal branches of the digital arteries arising from the trifurcation of distal interphalangeal joint (a subcutaneous pedicle flap) Technique References:
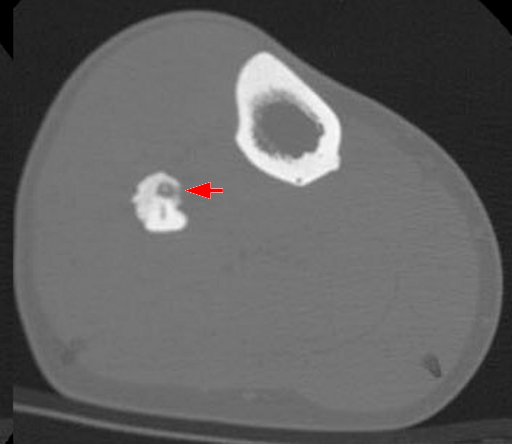
Osteoid Osteoma : Mnemonic
Epidemiology and Clinical features Mnemonic: LMNOP Lower extremity predilection (proximal femur > tibial diaphysis) Male predilection (2:1 to 3:1) Night pain relieved by NSAIDs (absent in osteoblastoma) Osteogenic benign tumor Prostaglandins (PGE2) and Cyclooxygenase (COX1 and 2) release by nidus (explains night pain and response to NSAIDs) 3 Concentric layers…
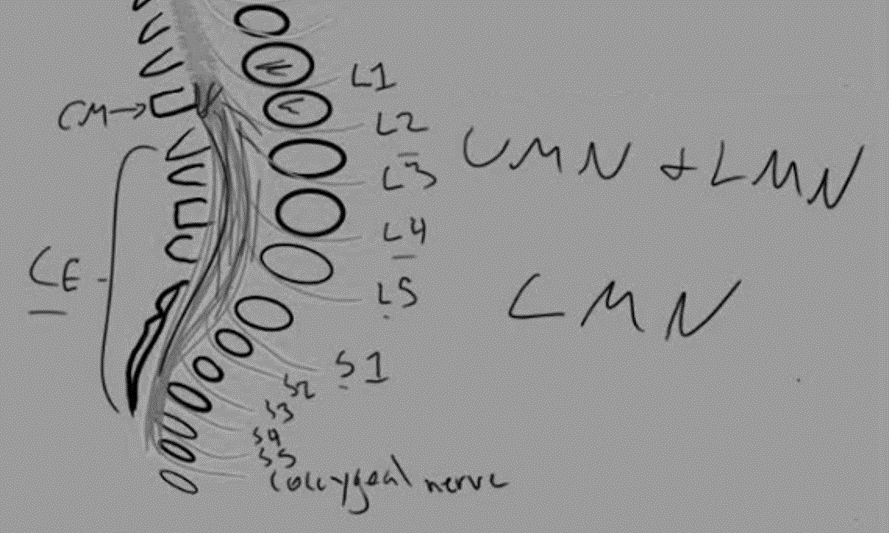
Conus Medullaris Syndrome vs Cauda Equina Syndrome : Anatomical basis and Mnemonic
Definitions Condition Vertebral level of injury Neurological level of injury ISNCI level of injury Conus Medullaris Syndrome (CMS) T12-L2 T12-S5 T11 Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) L3-L5 L3-S5 L2 Anatomy The spinal cord ends as a tapered structure called the conus medullaris at the level of L2–L3 disc in the neonate…