Synonyms: Paradoxical pulse, Paradoxic pulse, Reversed Bernheim sign Definition of Pulsus Paradoxus There is normal physiological fall in Blood pressure upto 10 mmHg during inspiration. Pulsus paradoxus is the exaggeration of this normal decline in blood pressure more than 10 mmHg during inspiration. The “paradox” refers to the fact that…
Tag: Clinical examination
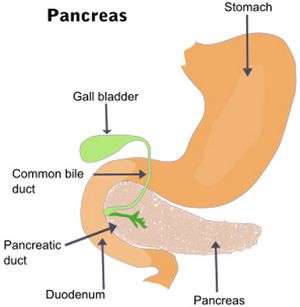
Courvoisier’s law of Obstructive Jaundice
Synonyms: Courvoisier’s sign, Courvoisier syndrome, Courvoisier-Terrier sign, Bard-Pic disease Over years, the use of the term Courvoisier’s sign or gallbladder has been suggested instead of law, because of rising number of exceptions. Eponymous to: Ludwig Courvoisier (1843-1918) Definition of Courvoisier’s law Courvoisier’s (koor-vwah-zee-ayz) law states that ‘a palpable non-tender gallbladder…

Summary of Clinical Tests and Signs in Orthopedics
Adson’s test: for thoracic outlet syndrome Allen’s test: for testing patency of radial and ulnar arteries Alli’s test: for DDH Anvil test: for testing tenderness of the spine Ape thumb: for median nerve injury Apley’s grinding test: for meniscus injury Apprehension test: for recurrent dislocation of the shoulder Barlow’s test:…
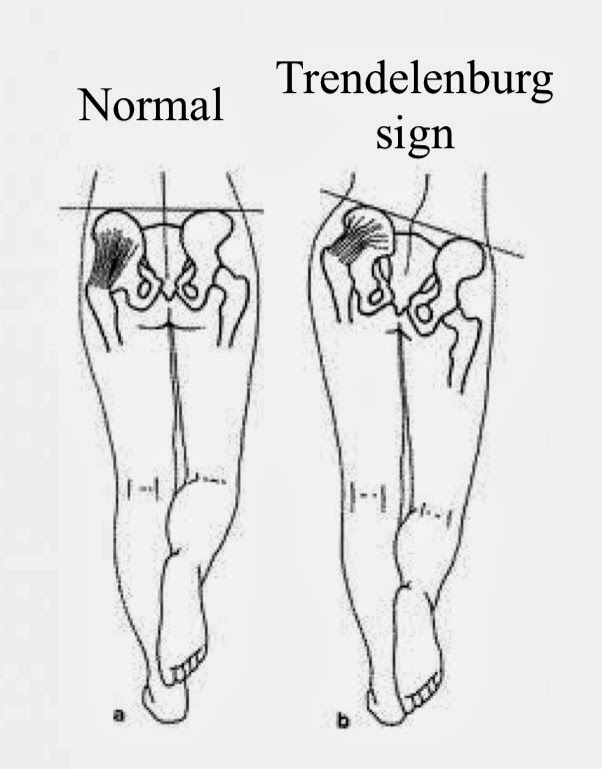
Trendelenburg test or sign
Method: The patient is then asked to stand on one leg and bend the opposite knee to 90° without flexing the hip. This action eliminates the role of hip flexors as they play a role in pelvic stability and may affect the Trendelenburg sign. The test is then repeated by…
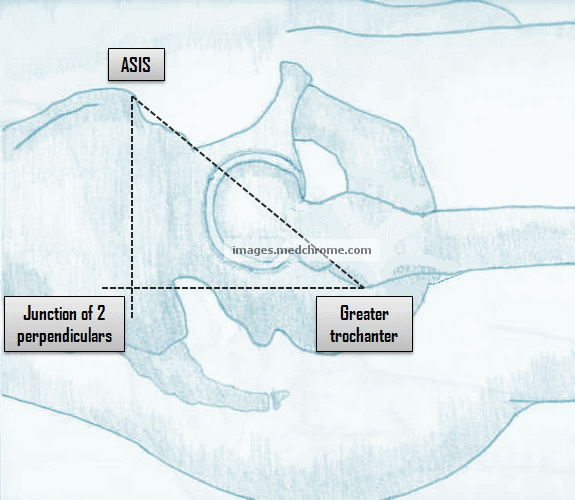
Bryant’s triangle (Examination of Hip)
Synonyms: Iliofemoral triangle Position: The patient lies supine with the pelvis square, and the limbs in identical position. Points of the Bryant’s triangle: The Bryant’s triangle is a right angled formed by: Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) Tip of Greater trochanter Junction of perpendiculars from the 2 points above (1st draw…
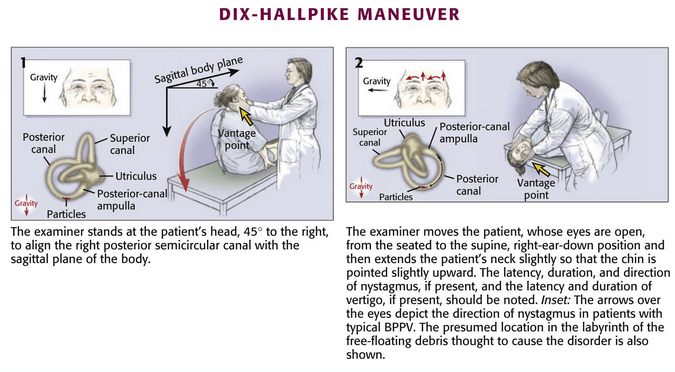
Vestibular examination : Dix-Hallpike Maneuver for BPPV
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is the commonest cause of episodic vertigo and is characterized by acute attacks of transient vertigo initiated by certain head positions, lasting seconds to minutes, accompanied by nystagmus that fatigues on repeated testing. Important terminologies linked with pathogenesis of BPPV: Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals released…
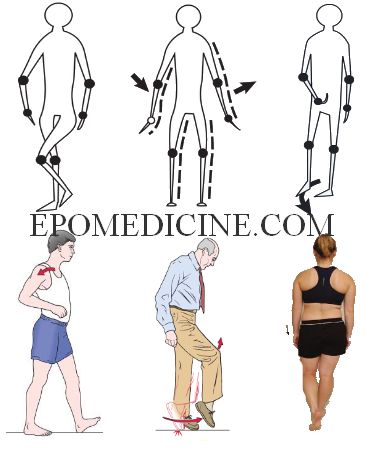
Examination of Gait
Definitions Gait: Gait is the cyclical pattern of musculoskeletal motion that carries the body forwards. It involves a cyclic loss and regaining of balance by a shift of the line of gravity in relation to the center of gravity. Normal gait is smooth, symmetrical and ergonomically economical. Gait cycle: The…

Examination of Facial Nerve (7th Cranial Nerve)
The anatomy of facial nerve has already been discussed in detail earlier. It is essential to have proper knowledge of anatomy to understand this section of clinical examination of facial nerve. A) Inspection: Observe: Face at rest for any facial asymmetry Any facial tics, symmetry of eye blinking or eye…
