Both Somogyi effect and Dawn phenomenon are the cause of MORNING FASTING HYPERGLYCEMIA.
Mnemonic:
Somogyi = So Much Insulin
Dawn = Down Insulin
a. Somogyi effect:
Excess exogenous insulin → Middle night hypoglycemia → Release of counter-regulatory hormones → Rebound morning hyperglycemia
b. Dawn effect:
Normal release of morning hormones (growth hormones, cortisol, catecholamines) → Inadequate endogenous insulin production → Morning hyperglycemia
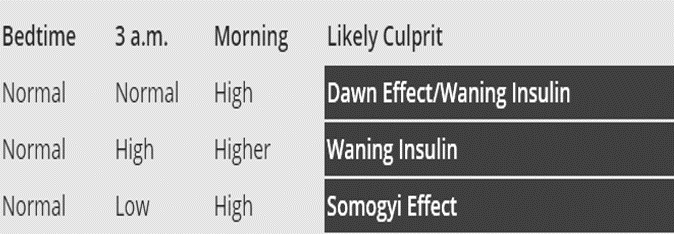
Differentiating somogyi and dawn effect as the cause of morning hyperhlycemia:
Measure blood glucose at 2-3 AM, and at normal wake-up time for several nights:
- Low blood glucose at 2-3 AM: Somogyi effect
- Normal or high blood glucose at 2-3 AM: Dawn phenomenon
Good morning.Excellent mnemonics.
Great mnemonics, awesome