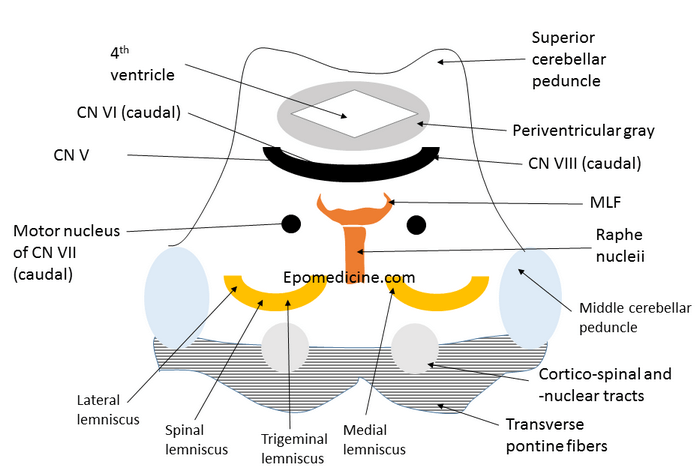
Pons in latin, refers to a “bridge”. Pons varolli is a part of brain-stem, that links thalamus with medulla oblongata. The cross-section of pons is similar to the midbrain as described earlier but few things must be kept in mind:
- The orientation of lemnisci in midbrain is more or less vertical, but in pons it is horizontal.
- Cranial nerve III and IV arises from midbrain and mainly Cranial nerve V, VI, VIII and VIII arises from pons.
- Cerebral aqueduct lies in midbrain and 4th ventricle lies in pons.
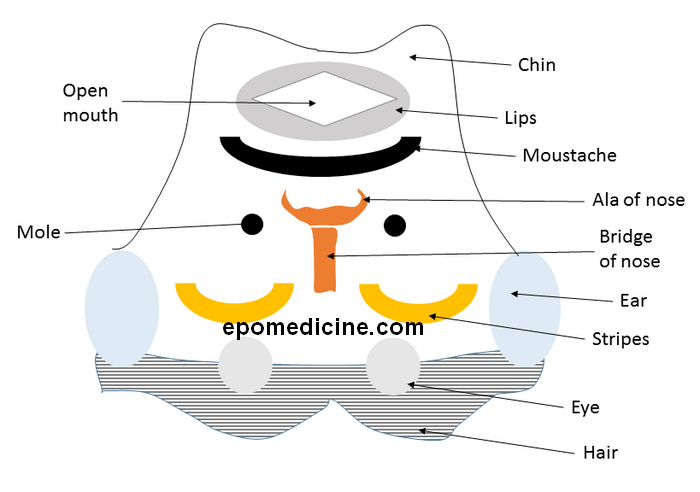
Earlier, we imagined transverse section of the midbrain as an inverted striped face of red-eyed demon. Similary, we will use the analogy of an “inverted face of a human” to draw the cross-section of pons.
Now, let’s label the structures shown above:
- Hair = Transverse pontine fibers
- Eye = Corticospinal and Corticonuclear tracts
- Ear = Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Stripes = Lemnisci
- Medially: Medial lemniscus
- Middle: Trigeminal lemniscus medially and Spinal lemniscus laterally
- Lateral: Lateral lemniscus
- Bridge of nose = Raphe nucleii
- Ala of nose = Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
- Mole = Facial nerve motor nucleus (In caudal pons)
- Moustache = Cranial nerve nucleii
- Medial most = CN VI or Abducens nerve (In caudal pons)
- Middle = CN V or Trigeminal nerve – motor and sensory (In rostral pons)
- Lateral most = CN VIII – Superior vestibular nucleus (In caudal pons)
- Lips = Periventricular gray
- Contains locus coeruleus
- Open mouth = 4th ventricle
- Chin = Superior cerebellar peduncle
Now, let’s look at the real picture:
You can compare with your own face to learn the pons. Wasn’t that easy? Leave comments below 🙂 .

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.

Helpful!! Thanks a lot
This is so helpful and creative! I loved the midbrain red-eyed demon too!
hii sir, could u please check whether the location of superior vestibular nucleus is at caudal level or rostral level,
i confused a lot regarding this , and i think its in causal part of pons , pls verify this sir
Hello Tharun, thank you for the correction. The four vestibular nuclei located in the rostral medulla and caudal pons. Superior and lateral vestibular nuclei are loacted in the caudal pons. Superior vestibular nucleus is located entirely within caudal pons while the lateral vestibular nucleus extends from the caudal pons to rostral medulla.
Reference: A Textbook of Neuroanatomy By Maria A. Patestas, Leslie P. Gartner
Thank you sir, love from Nigeria!
This website has been so helpful.
♥️ From a fellow Nigerian.