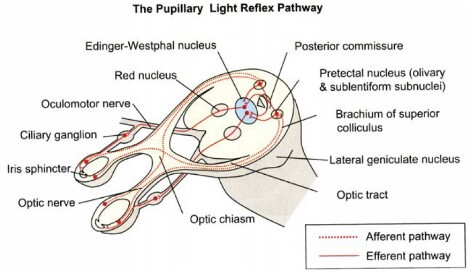
Everyone must be aware of the normal visual pathway and their defects. Here, I’ve tried to enlist the topics related to the visual pathway that are “nice to know” but you may have missed it or failed to understand properly. Below is the basic visual pathway: Wilbrand’s knee Anterior…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
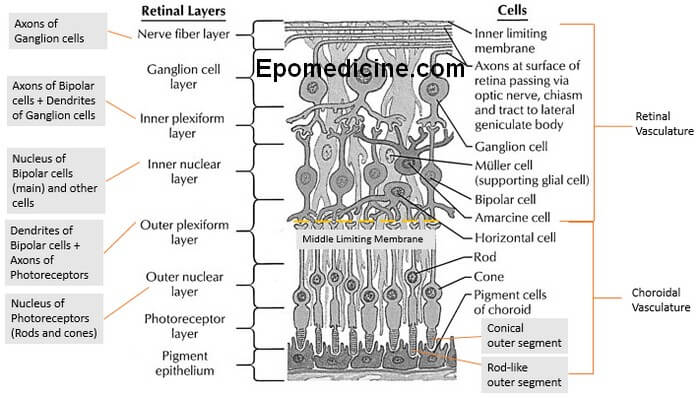
Retinal Layers Simplified
The ten layers of retina – this microscopic anatomy is frequently asked in examinations and also important from the physiological viewpoint. There are plenty of mnemonics around the web, but we will proceed in a different approach to remember the 10 retinal layers easily. A. Retina is 3 neuron system…
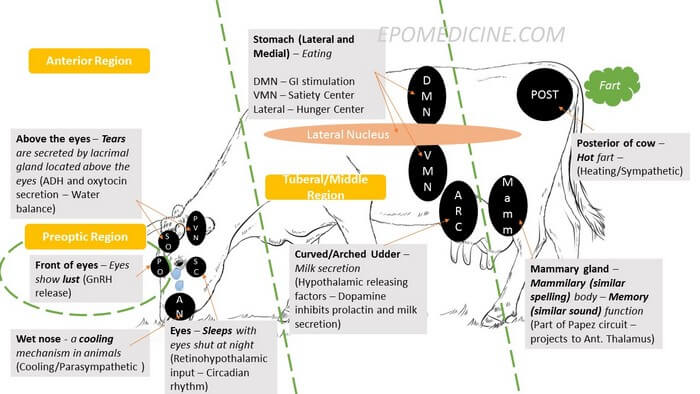
Nuclei of Hypothalamus – Mnemonic
Hypothalamus is composed of several nuclei with different important functions – hence, it is important and confusing at the same time. I have devised a pictorial or visual mnemonic to make things easier for you. Hypothalamus is a Cow Imagine a Crying and Farting Cow when recalling the Hypothalamus. Preoptic:…
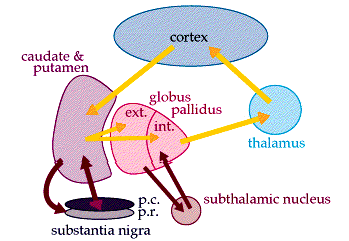
Basal Ganglia Pathways Simplified
The combination of excitatory and inhibitory signals in the basal ganglia circuit is pretty confusing. Let’s break the circuit and make them easy to understand. There are 2 pathways in Basal ganglia circuit: Excitatory pathway Inhibitory pathway Let’s declare 2 things first: Dopaminergic nigrostriatal projection increases motor activity. Cholinergic striatal…
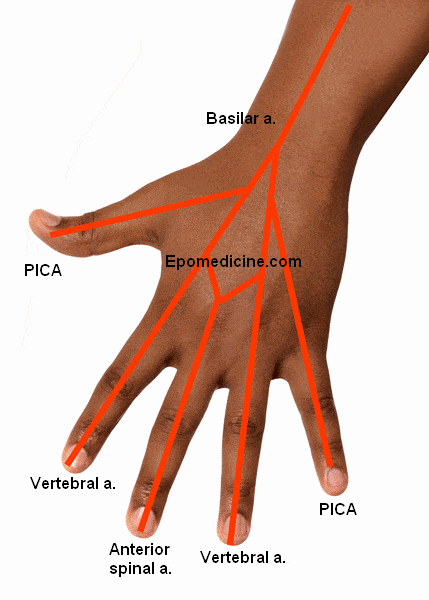
Vertebrobasilar Arterial System and Syndromes Simplified
Vertebral Artery I use the analogy of hand to remember the vertebral artery and it’s branches: Origin: Branch of subclavian arteries Course: Ascends through transverse foramina on C6 through C1 and enters posterior fossa through foramen magnum Continue up the ventral surface of medulla Converge at the ponto-medullary junction to form…
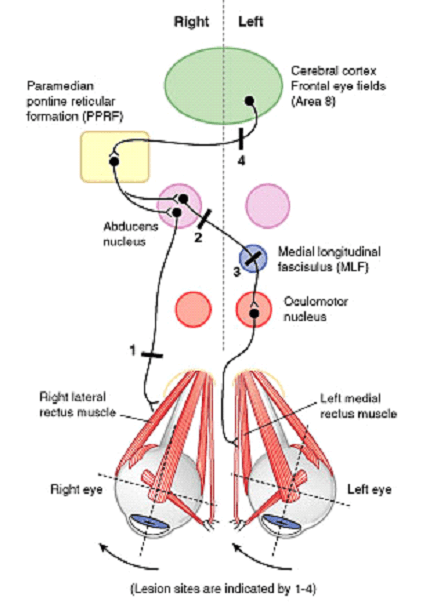
Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway
Components of Pathway For both eyes to look at a side: Contralateral Frontal Eye Field (Brodmann area 8) Ipsilateral PPRF (Paramedial Pontine Reticular Formation) Ipsilateral CN VI Nucleus Contralateral Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF) Contralateral CN III Nucleus Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway Lesions of Conjugate Gaze Pathway Abducens (CN VI) nerve:…
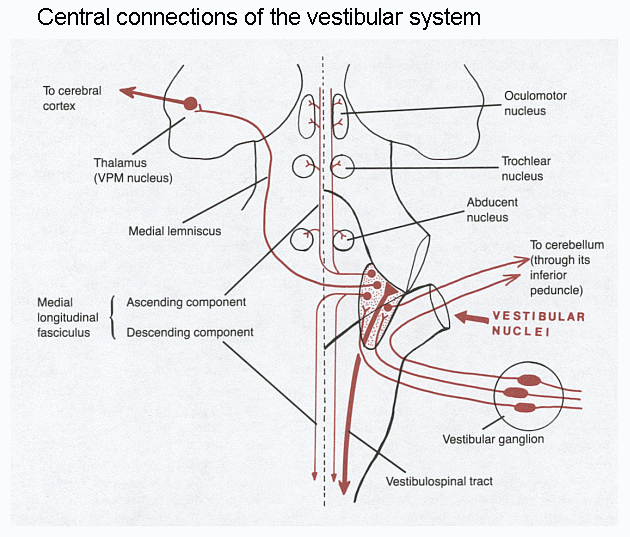
Vestibular Pathway Simplified
Vestibule and Sensory receptors Location: Medial to tympanic membrane and Posterior to Cochlea Sensory receptors 1. Macula: Present in otolith (calcium carbonate crystals) organs – saccule (anteriorly) and utricle (posteriorly) Both are connected by corresponding ducts, which together will form endolymphatic duct, this passes through a bony canal (the vestibular…
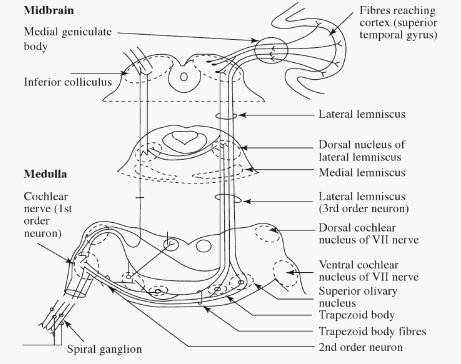
Auditory Pathway Mnemonic
Auditory Pathway Component Mnemonic E.C.O.L.I.M.A Ascending from peripheral to central the components are: Ear receptors (Hair cells) in Cochlea and Eighth Cranial nerve (CN VIII) Cochlear nucleus Superior Olivary nucleus Lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Medial geniculate body Auditory cortex Explanation of the Mnemonic Ear receptors and Eighth cranial nerve (Organ…