FIGO has published a new classification for ovarian cancer. These new cancer staging rules will be incorporated into the 8th Edition of the UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, which is thought to be effective from 2017. Cancer of the ovary has 3 major stages (I, II and III) and…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
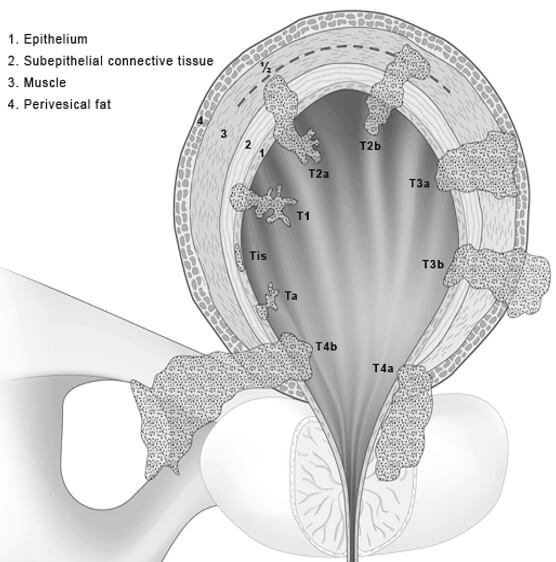
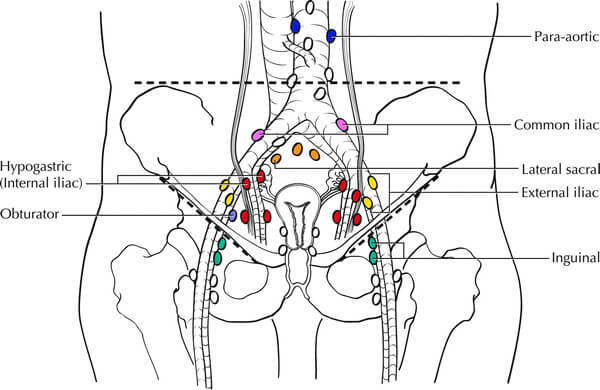
TNM and staging of Urinary Bladder Cancer Simplified
As discussed earlier in – TNM Classification and Cancer Staging Simplified, Urinary bladder is a hollow organ whose “T” classification resembles that of the gastrointestinal tract. Since, the regional lymph nodes of the urinary bladder also lie beyond the serosa like in colon and rectum, positive regional nodes are usually…
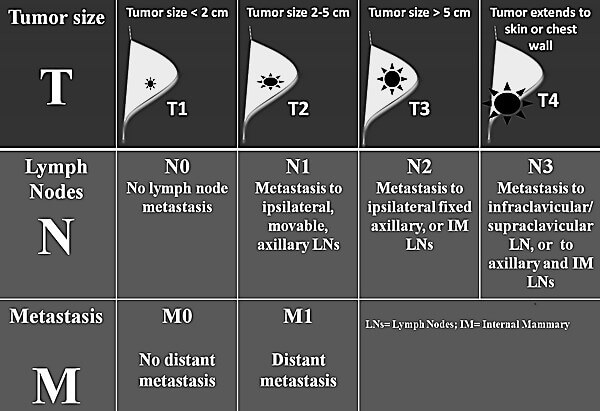
TNM and Staging of Breast Cancer Simplified
TNM Classification for Breast Cancer Primary Tumor (T) T1: ≤2 cm (20 mm) mi: ≤1 mm a: 1-5 mm b: 5-10 mm c: 10-20 mm T2: 2-5 cm T3: >5 cm T4: Direct extension to chest wall and/or skin a: Chest wall (exclude only pectoralis muscle adherence/invasion) b: Ipsilateral ulceration, satellite nodules…
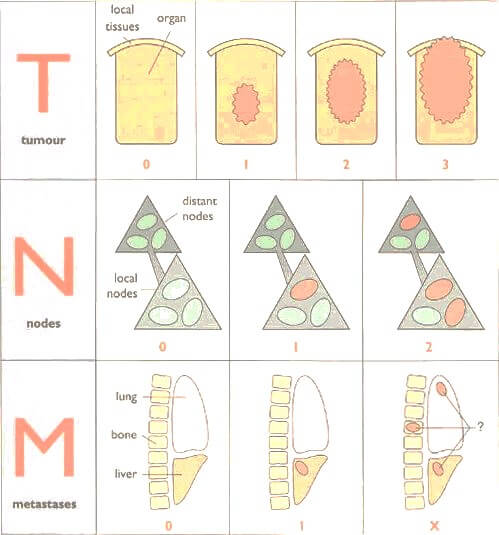
TNM Classification and Cancer Staging Simplified
You must be asking yourself – “how to remember the TNM staging system?” and looking here and there for mnemonics only to find nowhere. Understanding the oncoanatomy helps to understand the staging system of the cancers. Tumor Status (T) T1 T2 T3 T4 Depth of invasion Solid organs Confined Capsule,…
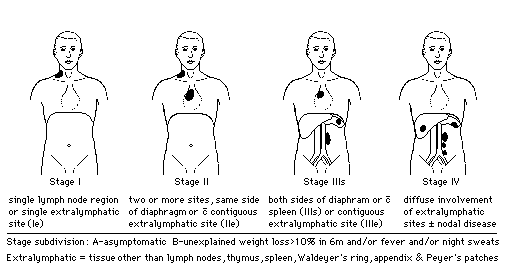
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – Staging and Prognostic Factors
Costwold Modified Ann-Arbor Staging I: 1 Lymph Node (LN) region (I) or 1 Extralymphatic site (IE) II: On the same side of diaphragm – ≥2 LN region (II) or Localized Extralymphatic extension + ≥1 LN region (IIE) III: On both the sides of diaphragm – LN regions (III) ± Spleen involvement (IIIS) ± Localized…
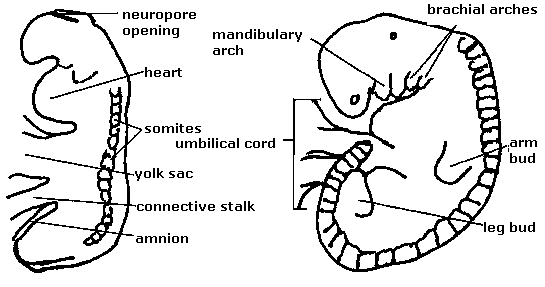
Embryology Week 4: Rule of Fours
Second week is the week of twos. In third week trilaminal germ disc is formed. And now, here I have attempted to fit the fourth week in development of embryo as the week of fours. Four folds of the embryo The embryo undergoes: Lateral folding Cranio-caudal folding It forms four…
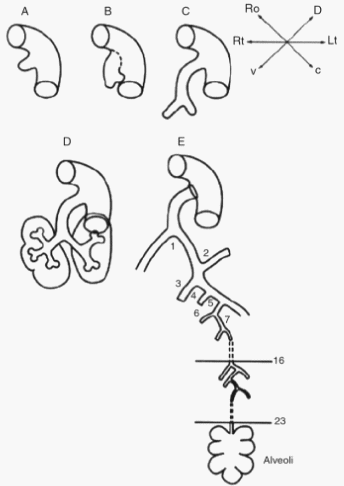
Lung Development – Embryology Made Easy
Remember the mnemonic – “Every Premature Child Takes Air“. The development of lungs comprises of 5 distinct stages: Embryonic (3-8 weeks, i.e. embryonic period) Pseudoglandular (5-16 weeks) Canalicular (16-26 weeks) Terminal saccular (26-36 weeks) Alveolar (36 weeks to 40 weeks and continues to childhood) The first and last stages, i.e….
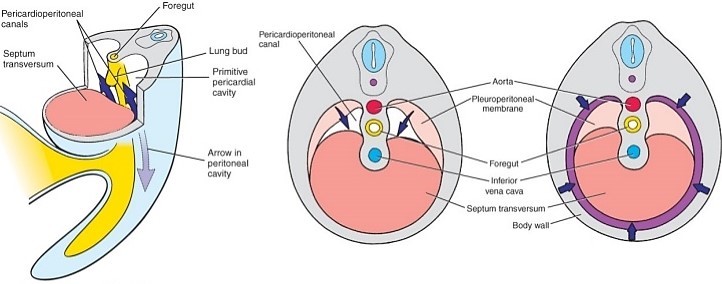
Diaphragm and Body Cavities Development – Embryology Made Easy
Let’s go back to the 4th week during the development of heart. The primitive intraembryonic coelom forms in the lateral and cardiogenic mesoderm during 4th week of development. Like the heart fields, the intraembryonic coelom has a horse-shoe configuration during this period: A thick mesodermal plate called “septum transversum” lies…