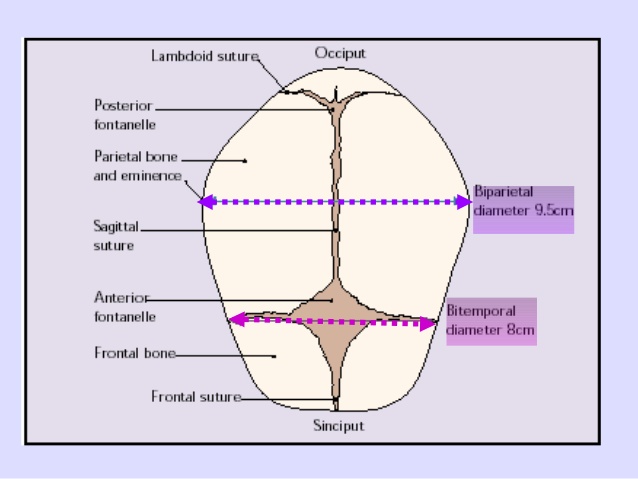
Anteroposterior Diameters Mnemonic: Larger the alphabets, larger the diameter (V>F>B) Diameters with “sub” prefix are smaller than counterpart without it. mento-Vertical: 14 cm SUB-mento-Vertical: 11.5 cm occipito-Frontal: 11.5 cm SUB-occipito-Frontal: 10.5 cm sub-occipito-Bregmatic: 9.5 cm sub-mento-Bregmatic: 9.5 cm Transverse Diameters Mnemonic: MTP (Medical Termination of Pregnancy) in increasing order. bi-Mastoid:…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
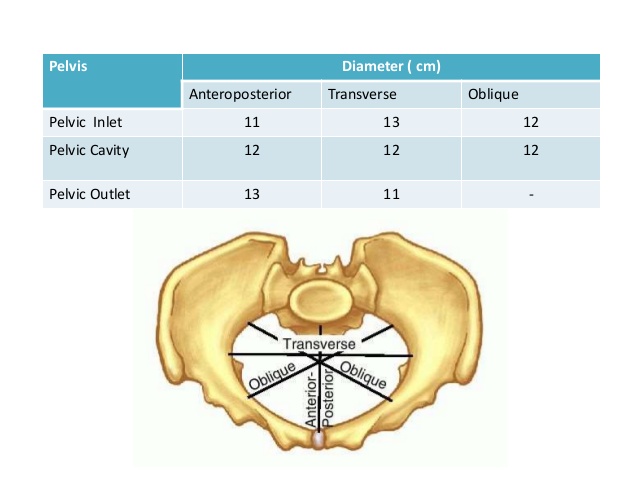
Pelvic Dimensions : Mnemonics
Shapes of the female pelvis Mnemonic: GAP (In order of most common to the least common) Only pelvis with AP diameter > Transverse diameter is Anthropoid pelvis. Mnemonic: ANthrOPoid Android and Anthropoid (AN) pelvis are common causes of occipito-posterior (OP) presentation. In platypelloid pelvis (broad and flat): Sub-public angle: It…
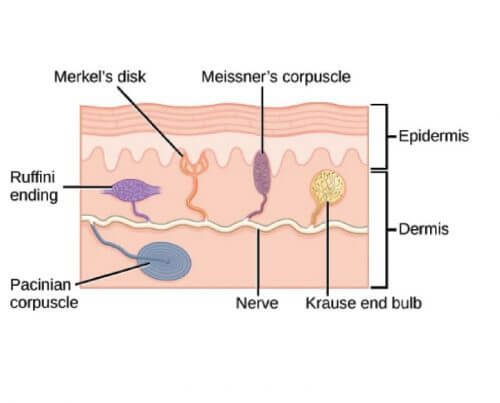
Mechanoreceptors : Mnemonic
Adaptation of Mechanoreceptors Mnemonic: Life is fast for MPs (Member of Parliament) and slow for MRs. In alphabetical order, meIssner’s come becore meRkel. Hence, Meissner’s corpuscle are the quicker among two. 1. Fast adapting receptors: MP Meissner’s corpuscle Pacinian corpuscle 2. Slowly adapting receptors: MR Merkel disc Ruffini corpuscle/ending Location of…
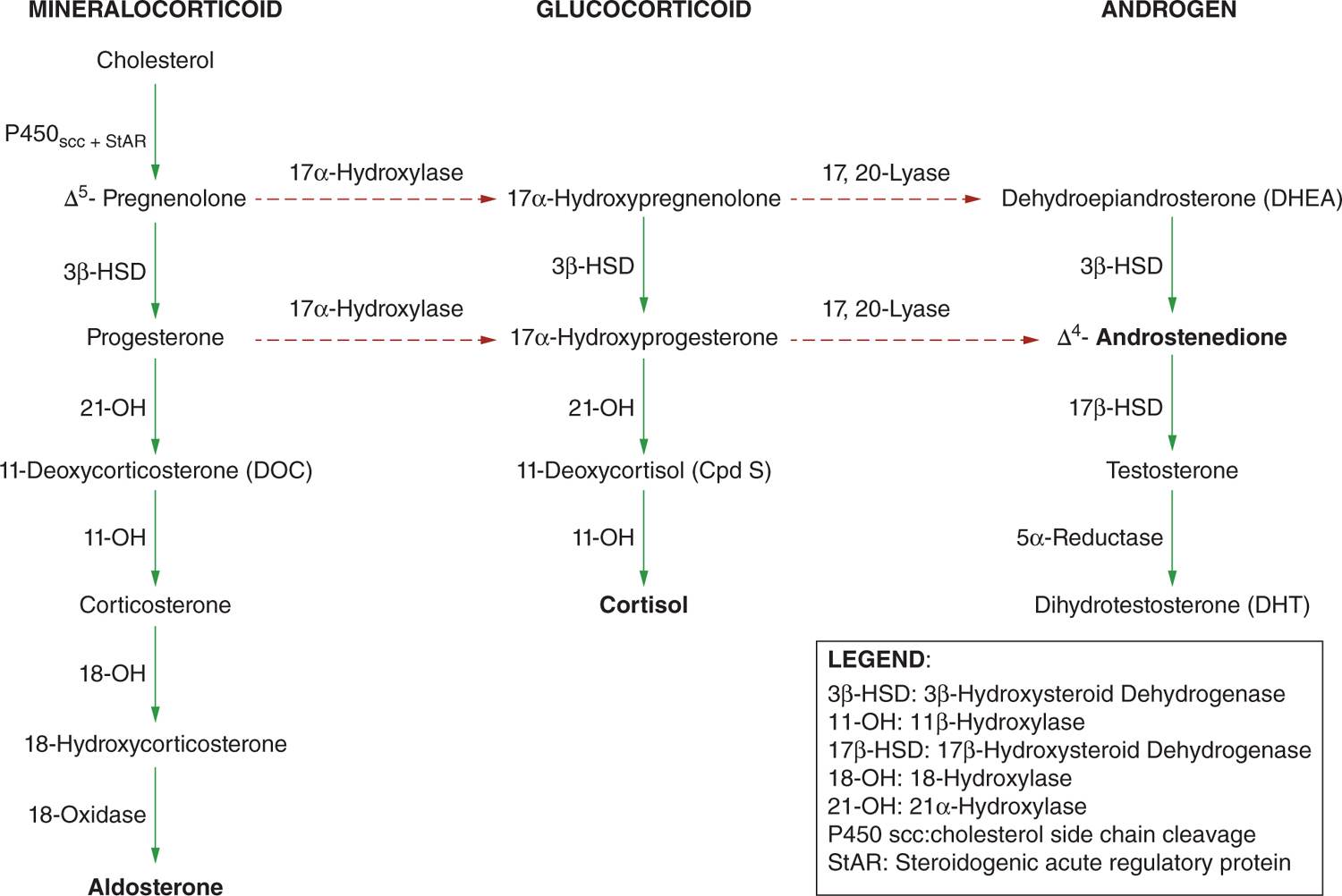
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Basics : Explained with Mnemonics
Adrenal cortex synthesize steroids. Mnemonic: GFR – Salt, Sugar, Sex Zona gomerulosa: Salt (Aldosterone) Zona fasciculata: Sugar (Cortisol) Zona reticulosa: Sex (Testosterone) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) Deficiency of 3 different enzymes can cause Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Mnemonic: Remember the mnemonic GFR, first layer of cortex synthesizes aldosterone and the last layer…
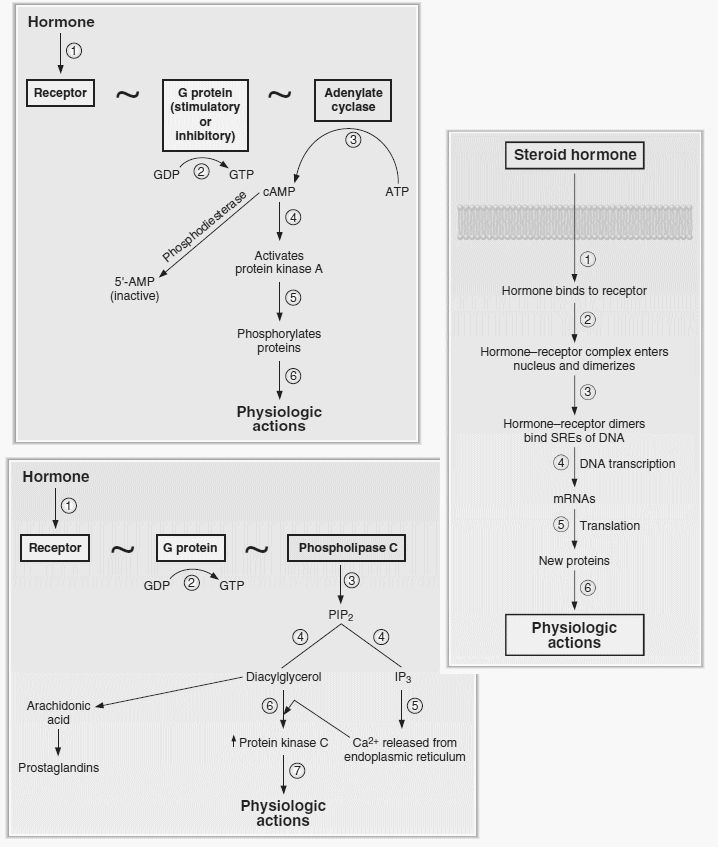
Signaling Pathways of Hormones : Mnemonic
cAMP Mechanism Mnemonic: FLAT CAMP B-HCGS Remember “B-FLAT” mnemonic for hormones secreted by basophilic cells of the anterior pituitary. This is the same “FLAT” here. Also CAMP matches cAMP. Beta-HCG works by cAMP mechanism. All 2 except Beta 1 and 5-HT1 So, this is an easy mnemonic to remember. FSH…
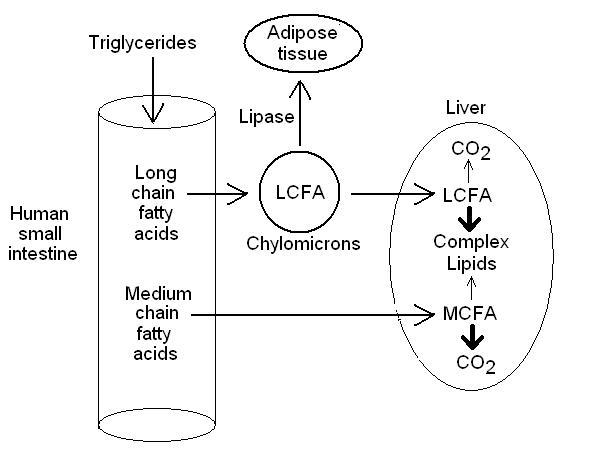
Fatty acid chain length and GI absorption site : Mnemonics
Major fat absorption takes place in upper small intestine (mainly jejunum and duodenum) except short chain fatty acids which is abosrbed in colon. MCT (Medium-Chain Triglyceride) – 10 to 12 Carbons long May Cross Through enterocytes and pass directly into the “Portal” circulation LCT (Long-Chain Triglyceride) – > 12 Carbons long…
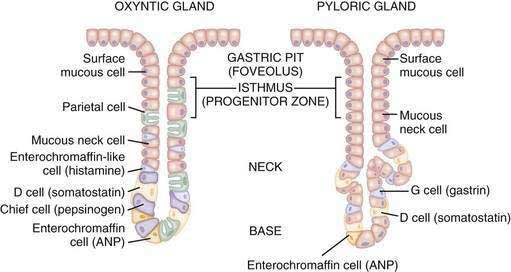
Gastric glands and cells
Anatomically, stomach can be divided into 3 parts from above to below: Gastric pits deepen as we move below from cardiac to pyloric glands. Mucus secreting cells: Present in all 3 glands – cardiac, fundic and pyloric but predominate in cardiac and pyloric glands. Pyloric glands have 1 more cell…
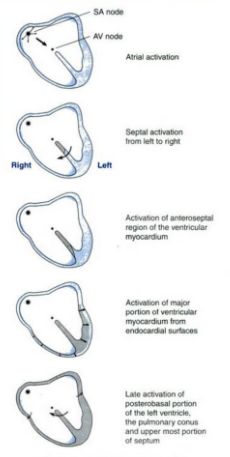
Physiology of Conducting System of Heart
Origin and Spread of Cardiac Impulse Mnemonic: SAIL MRS. SAVE APPS 1. SA node (generates impulse at highest rate, i.e. 70-80/min) 3 Internodal pathways: 2. AV node Bundle of His 3. Interventricular septum – Left 4. Midportion Right Septal activation Purkinje System 5. Septum (upper to lower) – purkinje system…