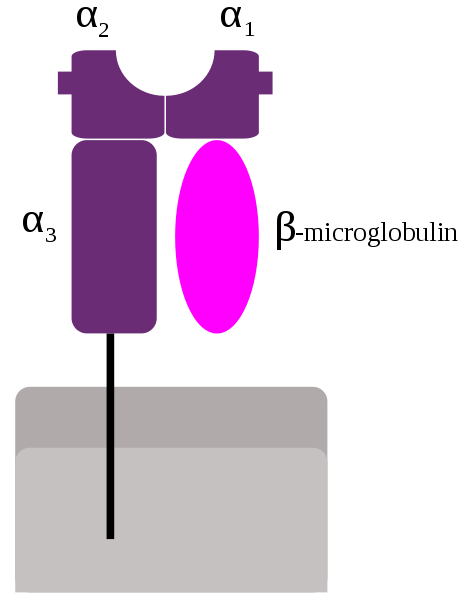
The genes that encode HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) are on chromosome 6. MHC class Type Location Function I HLA-A, -B, -C All cells Recognized by CD8+ lymphocytes II HLA-DP, -DQ, -DR Antigen presenting cells Recognized by CD4+ lymphocytes III Complement components Plasma Chemotaxis, opsonization, lysis of bacteria and cells The…
Author: Epomedicine
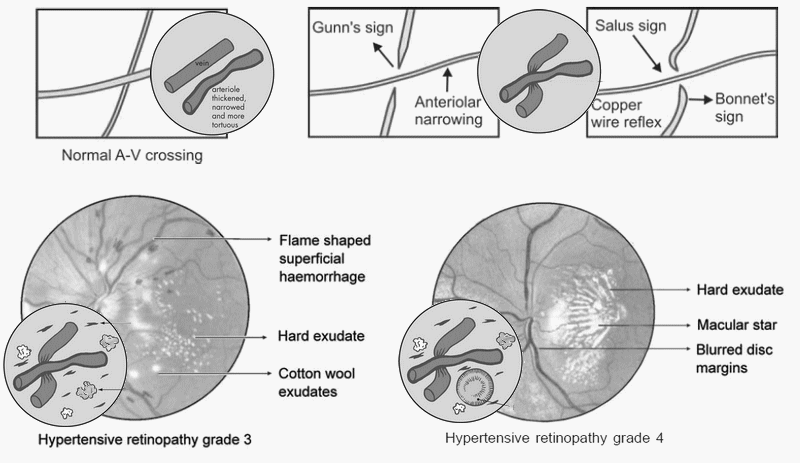
Hypertensive Retinopathy Grading – Simplified
Hypertensive retinopathy has been classified by Keith, Wagener & Barker and Scheie (hypertensive and arteriosclerotic features). With this mnemonic, we will have a grading with combination of all these classifications. Mnemonic: SAFEs I – Slight Systemic (generalized) narrowing of arterioles II – AV deflection (at Angle) and focal narrowing of…
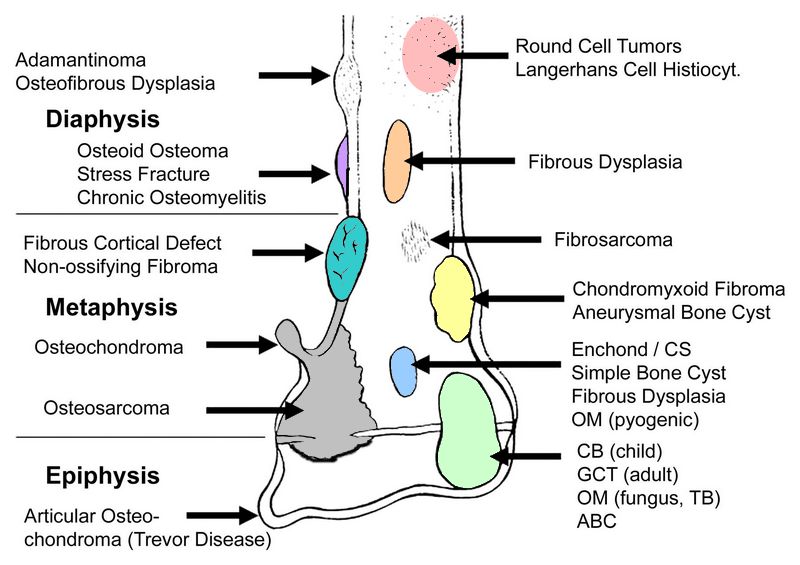
Differential Diagnoses of Bone Tumors : Mnemonic Approach
Lytic and Sclerotic Bone Lesions Mnemonic for Solitary lytic lesions: FEGNOMASHIC Fibrous dysplasia Enchondroma Eosinophilic granuloma Giant cell tumor Nonossifying fibroma Osteoblastoma, Osteosarcoma (telangiectatic) Metastases Myeloma Aneursymal bone cyst Simple bone cyst Hyperparathyroidism (brown tumor) Infection Chondroblastoma Chondromyxoid fibroma Mnemonic for Multiple lytic lesions: FEMHI Fibrous dysplasia Eosinophilic granuloma/Enchondroma Metastasis/Mutiple…

Errors and P-value
Statistical hypotheses Null hypothesis (H0): No difference or relation exists; e.g. Treatment A is not better than Treatment B Alternative or research hypothesis (H1): Some difference or relation exists, e.g. Treatment A is better than Treatment B Statistical errors Type I error (alpha): False positive (Falsely rejecting Null-hypothesis; i.e. null…

Baye’s theorem derived PPV and NPV
Let’s unveil the mathematics behind the relation between: Prevalence (Pre-test probability) Predictive value (Post-test probability) Sensitivity Specificity SYMBOLS: Total screened population = nPrevalence = PSensitivity = SnSpecificity = SpTrue positive = TPTrue negative = TNFalse positive = FPFalse negative = FNWith disease = D+Without disease = D-Positive predictive value =…
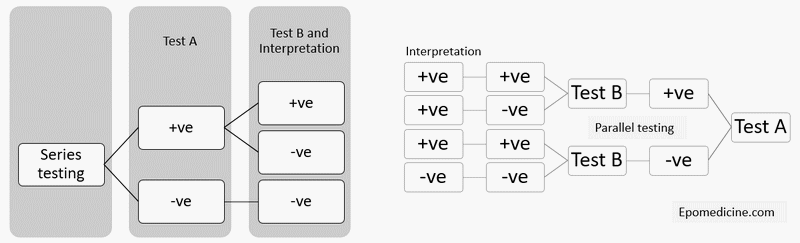
Screening tests in Series and Parallel
A. Parallel testing 2 screening tests are applied simultaneously: So, this test will have: B. Series testing After the 1st screening test is conducted, those who test positive are only tested with the 2nd screening test: So, this test will have: Formulae for combined specificity and sensitivity A. Parallel testing:…

Sustainable Development Goal 3 – Points to Remember
Total SDG goals: 17 Time frame: 2016-2030 Goal 3: Good health and well beings for all ages Important targets of Goal 3 (Targeted by 2030) A. Maternal and Child health (MCH) Mnemonic: 12 letters in “NEONATE DEATH or NEWBORN DEATH“. 1. NMR reduction target: 122. U5MR reduction target: 12 X…
Key Health Indicators of Nepal to Remember (NDHS, 2022)
These rates, ratios and proportions are often questioned in PGMEE, pediatrics, obstetrics and preventive and social medicine (PSM) or community medicine examinations. NDHS = National Demographic and Health Survey a. Neonatal mortality rate (NMR): 21 per 1000 live births (i.e. 3/4 of infant deaths) b. Infant mortality rate (IMR): 28…