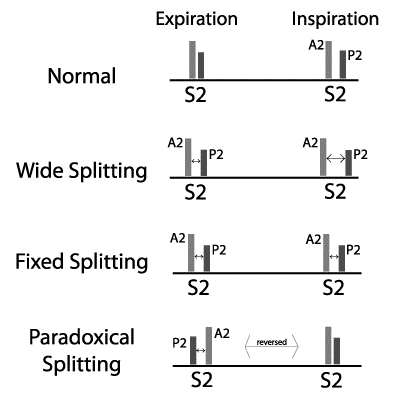
In the chapter of cardiac cycle, we have discussed the mechanism of production of heart sounds and their physiologic splitting. First Heart Sound (S1) Mechanism Closure of atrioventricular valves. It is best appreciated in mitral and tricuspid area of chest for respective components. Loud S1 Slamming a door from a…
Tag: Physiology
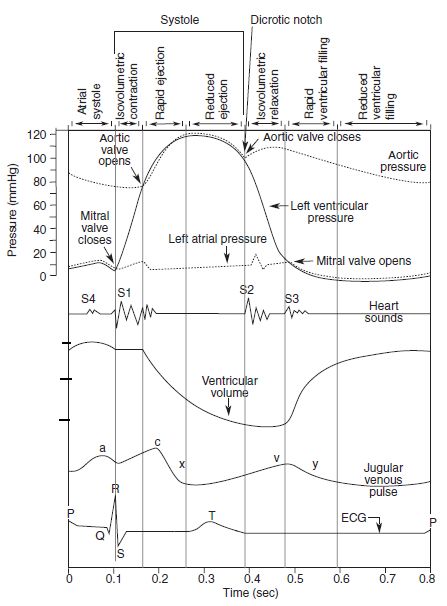
Cardiac Cycle – Summary and Wigger’s Diagram
Cardiac Cycle Opening and closing of valves When the valve opens, different compartments act as a single chamber (atrio-ventricle or aorto-ventricle). For a blood to flow, pressure in “giver” must be higher then that in “receiver”. Pressure difference opens or closes the valve: Role of atrial contraction in Ventricular filling…
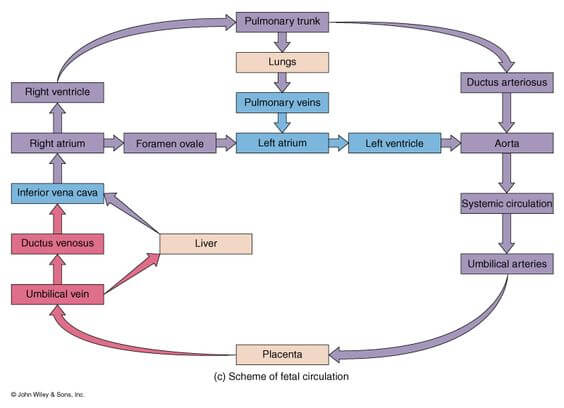
Fetal Circulation Made Easy
Following are the important features of fetal circulation: 1. Placenta plays the role of lungs; lungs are not functional: Like pulmonary veins, left umbilical vein carries highly oxygenated blood from placenta to heart. Like pulmonary artery, right and left umbilical arteries braing deoxygenated blood to placenta. 2. Mixing potentially occurs…
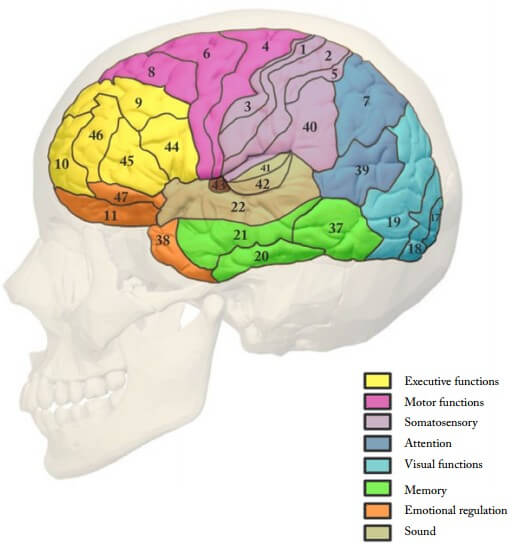
Brodmann Areas and Lesions
Frontal Lobe Area 4 (Precentral gyrus): Primary motor cortex (gigantopyramidal – only area that contains giant pyramidal cells of Betz) Lesion: Contralateral spastic paralysis (UMNL) Area 6 (Superior frontal gyrus; agranular frontal): Premotor cortex and Supplementary motor cortex (Motor planning) Lesion: Apraxia (Unable to perform movements in correct sequence) Area…
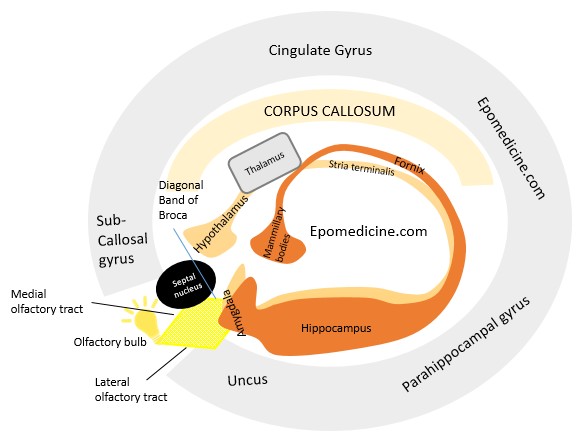
Limbic System Simplified
Limbic system is complex both structurally and functionally. It is located on either side of the thalamus, immediately below the cerebrum and consists of both the grey mater and white mater. Let us simplify the structure of limbic system: Hypothalamus is central to the limbic system Limbic cortex: 2 “C”…
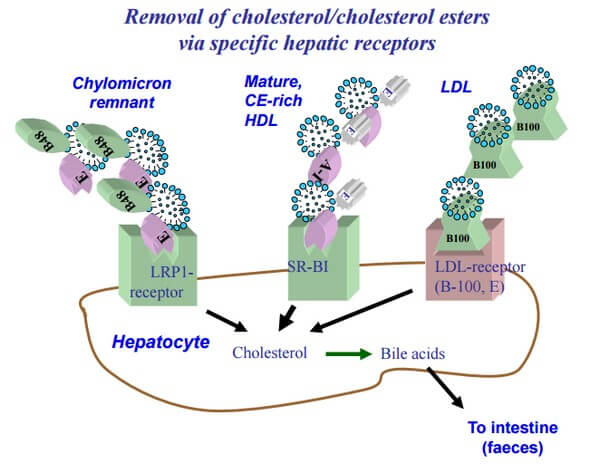
Lipoprotein Metabolism Simplified
Lipoproteins Composition of Lipoproteins: Non-polar core – mainly triglycerides and cholesteryl esters Single surface layer – amphipathic phospholipids and cholesterol Apoprotein or Apolipoprotein Class Abbreviation Density Protein Lipid content Electrophoretic mobility Chylomicrons CM lowest lowest highest (exogenous triacylglycerol) don’t migrate Very low density lipoproteins VLDL .. .. .. (endogenous triacylglycerol)…
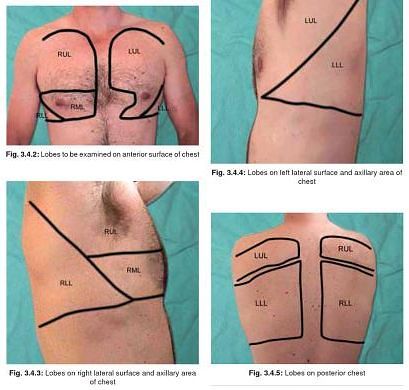
Respiratory Examination – Relevant Anatomy and Physiology
1. Division of Airway: Extrathoracic (Upper) airway: Nose to Upper trachea Intrathoracic (Lower) airway: Lower trachea to Alveoli and lungs Note: Vocal fold is also regarded as the demarcating line between upper and lower respiratory tract 2. Angle of Louis: Junction of body of sternum to manubrium (2nd costal cartilage…
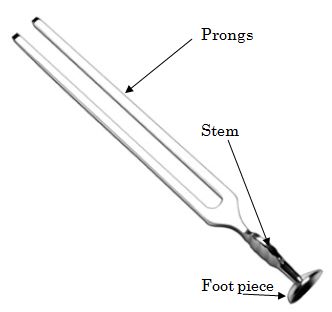
Hearing tests with Tuning fork
Tuning fork Parts of a tuning fork 1. Foot piece 2. Stem 3. Prongs How to use tuning fork? Hold the stem of the tuning fork between the index finger and thumb of your right hand without touching the prongs. Strike the junction of superior 1/3 and inferior 2/3 of the…