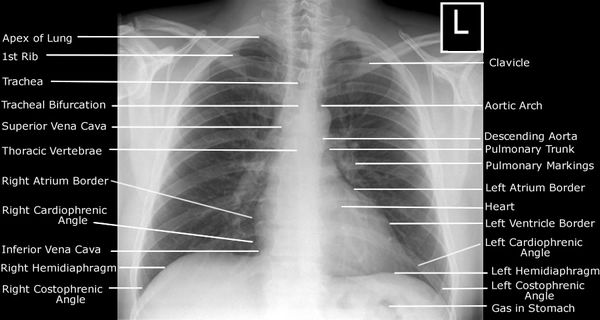
To make an appropriate diagnosis through a chest radiograph, it must be analyzed in a systematic manner. One of the common mistakes that students do is to miss the regions that needs to be looked for – commonest being the rib fractures. A mnemonic has been devised for this purpose:…
Tag: Pediatrics
Section Editor: Dr. Sujit Kumar Shrestha, MD Pediatrics, Fellowship Neonatology
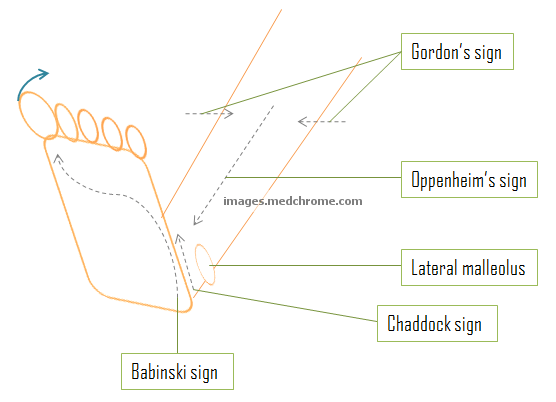
Pathological reflexes – Variations of Babinski
Normally, the pathological reflexes are not evident because they are suppressed by cerebrum at brainstem or spinal cord level by 6 months of age. Importance: Up-going (dorsiflexion) toe can be elicited at various sites and all indicated Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) lesion. Use a blunt-pointed object like fingernail or tip…
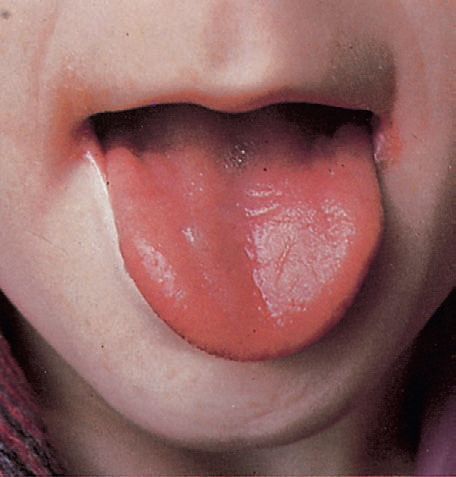
Hematological Signs – Angular Stomatitis and Atrophic Glossitis
ANGULAR STOMATITIS/CHEILITIS Definition: Maculopapular and vesicular lesions grouped on the skin at the corners (or ‘angles’) of the mouth and the mucocutaneous junction. It is made worse by licking the lips. Causes: 1. Oral candidiasis 2. Poorly fitting dentures 3. Bacterial infection 4. Less common Nutritional deficiencies (especially riboflavin, iron and pyridoxine) Iron…
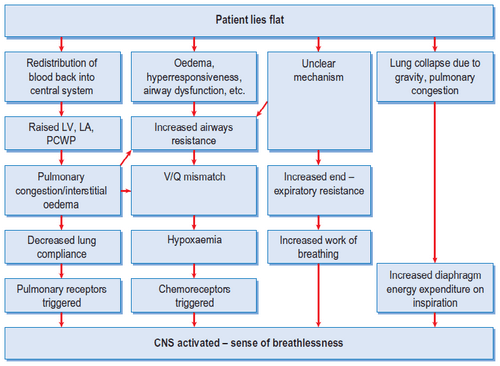
Respiratory Examination – Dyspnea
Definition: Breathlessness inappropriate to the level of physical exertion or even occurring at rest (subjective and not a sign) Mechanisms: Chemoreceptors: Peripheral: Carotid and aortic bodies (to pO2, pCO2 and H+) Central: Medulla (to pCO2, not pO2, change in pH of CSF) a. Increased work of breathing: Airflow obstruction: Bronchial…
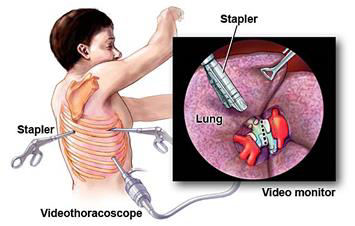
Text Presentation on Empyema Thoracis
A) INTRODUCTION Empyema (aka Empyema Thoracs or Empyema of the chest) is an accumulation of pus in the pleural space that occurs when an infection spreads from the lungs. It comes from the Greek word empyein, which means : pus–producing (suppurates). Empyema itself is not a disease but it is actually a condition complicated by another disease….
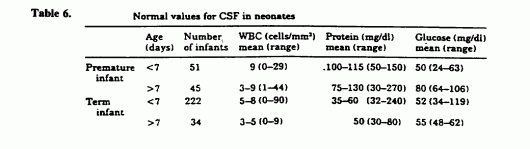
Practical Procedures : Lumbar Puncture (LP)
Synonyms: Spinal tap Definition: Puncture of subarachnoid space in the lumbar region of the spinal cord to withdraw cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic or therapeutic purpose or inject drugs for anesthetic purpose. Indications: A. Diagnostic: CNS infections: Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic or TB meningitis Subarachnoid hemorrhage Carcinomatosis meningitis (CNS involvement…
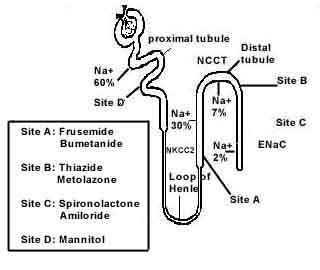
Approach to a Child with Edema
Before beginning the clinical approach to a child with edema, it is necessary to understand the basics of fluid compartments, starling forces and technique of eliciting edema. Life threatening causes of Edema: Generalized: Cardiac disease Congestive Heart Failure Pericardial effusion Renal disease Nephrosis Nephritis Hepatic failure Localized: Allergic reaction with…
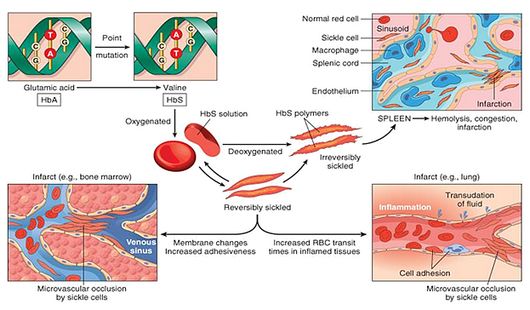
Salmonella Osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary disorder of hemoglobin synthesis caused by a mutation in the globin gene that changes the sixth amino acid from glutamic acid to valine resulting in abnormal sickling (rigid, inflexibled and sickle-shaped) of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) under low oxygen conditions. Sickle cell anemia…