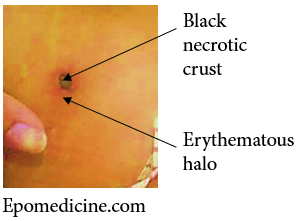
Synonyms Tache noire Definition of Eschar An eschar is a local skin lesions coated by a thick coagulated crust or slough that usually results from burn or infection. Causes of Eschar Tick bite fever Scrub typhus Anthrax Tularaemia Spider bites Disseminated fungal infection Post-burn Diagnostic Clues Cigarette-burn Sign In scrub…
Tag: Pediatrics
Section Editor: Dr. Sujit Kumar Shrestha, MD Pediatrics, Fellowship Neonatology
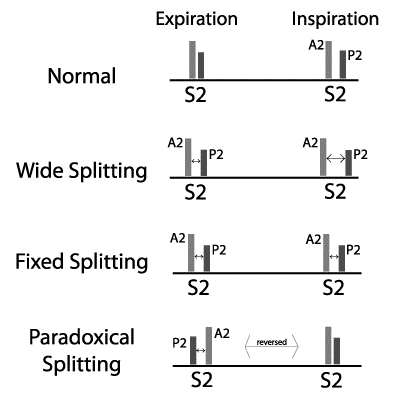
Abnormalities of First and Second Heart Sound
In the chapter of cardiac cycle, we have discussed the mechanism of production of heart sounds and their physiologic splitting. First Heart Sound (S1) Mechanism Closure of atrioventricular valves. It is best appreciated in mitral and tricuspid area of chest for respective components. Loud S1 Slamming a door from a…
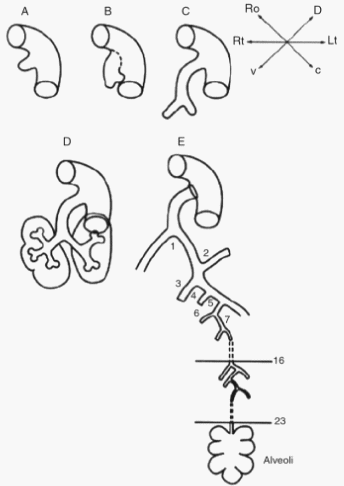
Lung Development – Embryology Made Easy
Remember the mnemonic – “Every Premature Child Takes Air“. The development of lungs comprises of 5 distinct stages: Embryonic (3-8 weeks, i.e. embryonic period) Pseudoglandular (5-16 weeks) Canalicular (16-26 weeks) Terminal saccular (26-36 weeks) Alveolar (36 weeks to 40 weeks and continues to childhood) The first and last stages, i.e….
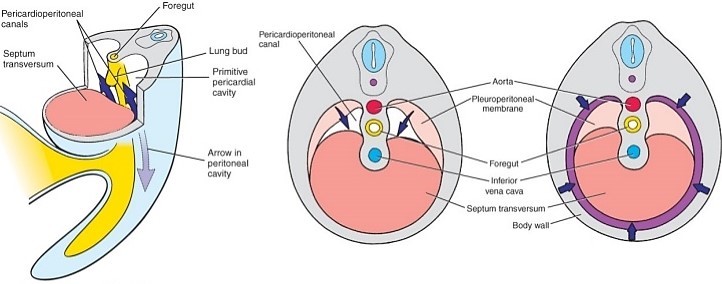
Diaphragm and Body Cavities Development – Embryology Made Easy
Let’s go back to the 4th week during the development of heart. The primitive intraembryonic coelom forms in the lateral and cardiogenic mesoderm during 4th week of development. Like the heart fields, the intraembryonic coelom has a horse-shoe configuration during this period: A thick mesodermal plate called “septum transversum” lies…
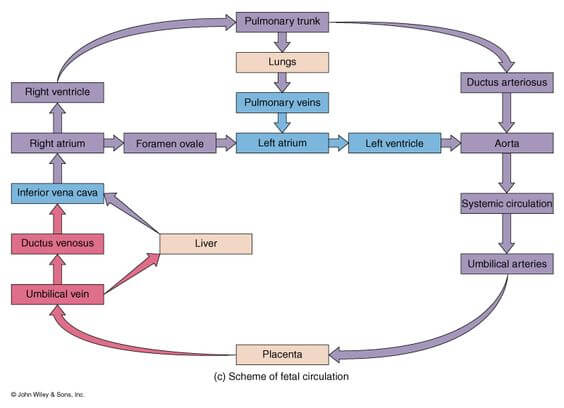
Fetal Circulation Made Easy
Following are the important features of fetal circulation: 1. Placenta plays the role of lungs; lungs are not functional: Like pulmonary veins, left umbilical vein carries highly oxygenated blood from placenta to heart. Like pulmonary artery, right and left umbilical arteries braing deoxygenated blood to placenta. 2. Mixing potentially occurs…
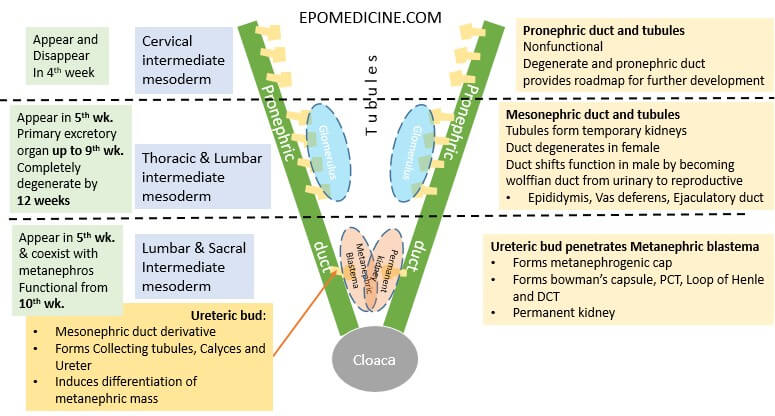
Renal (Kidney) Development – Embryology Made Easy
Kidney development occurs chronologically from cranial to caudal direction from urogenital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) in 3 different phases. Intermediate mesoderm → urogenital ridge (longitudinal elevation along dorsal body wall) → nephrogenic cord → Pronephros, Mesonephros and Metanephric mesoderm/blastema Remember the embryology of brain – from cranial to caudal, the primordial…
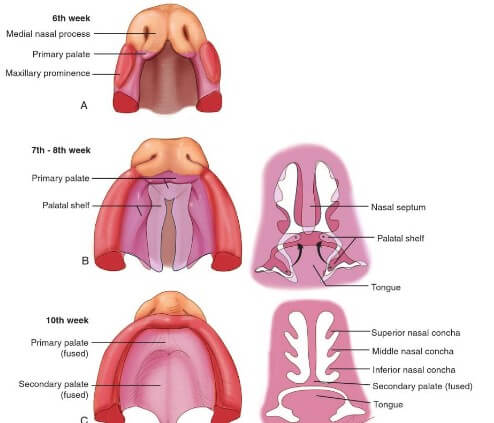
Face and Palate Development – Embryology made Easy
4 week embryo 5 mesenchymal prominences (facial primordia) appear in relation to the stomodeum (a depression in the surface ectoderm which marks the future mouth and oral cavity): Cranially: Frontonasal prominence (unpaired) Laterally: Maxillary prominence (paired; 1st pharyngeal arch) Caudally: Mandibular prominence (paired; 1st pharyngeal arch) 5 week embryo Localized…
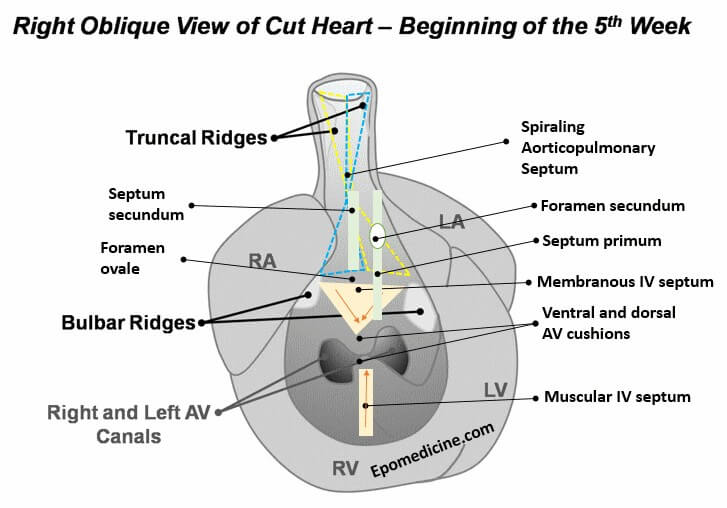
Heart Development – Embryology Made Easy
Heart Tube At the beginning of 4th week of development, heart is a continuous and valveless linear tube that resembles a chicken hung upside-down. It consists of 5 embryonic dilatation, that are destined to be the inflow and outflow tract and compartments of the hear without septum and valves. From cranial…