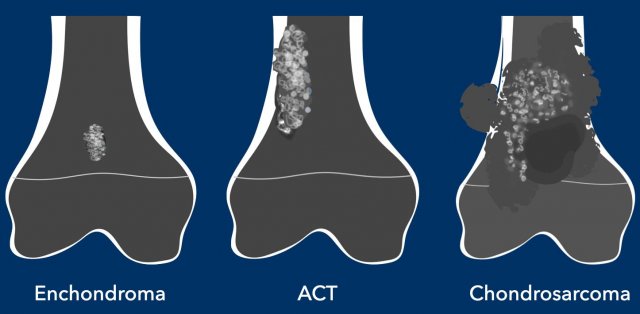
Among cartilaginous tumors, 2 pathologies can be misleading when trying to reach a correct diagnosis: enchondroma (E), a benign tumor, and low-grade chondrosarcoma (LGC), which is a low-aggressivity malignancy. This can be a problem when deciding treatment because E only requires regular follow-up, but LGC needs surgical treatment. Mnemonic: ABCDE…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
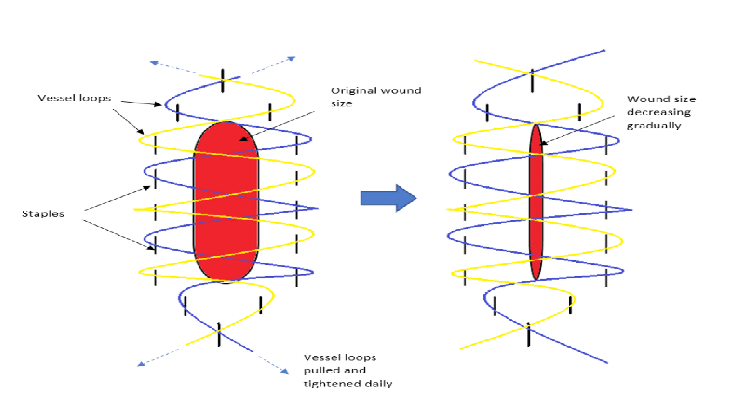
Shoelace technique for Delayed Primary Closure
Indication: Delayed primary closure of fasciotomy wounds Sutures that can be used: Anchors: Staples (can apply 2 staples) or Metal clips Knotting pattern: The suture is attached to one side and passed through the incision to be attached on the opposite side, in a sequence that resembles a zigzag from…
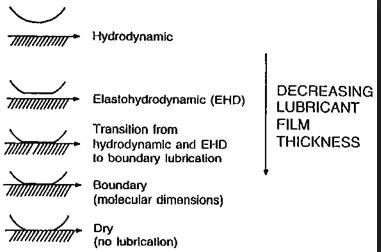
Joint Lubrication Made Easy
Boundary lubrication A monolayer of lubricant molecule (lubricin) adsorbed on each surface (boundary) of the joint prevents direct cartilage to cartilage (articular) contact Fluid-film lubrication Cartilage surfaces are separated by a fluid film 1. Hydrodynamic lubrication: 2. Squeeze film lubrication: 2. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication: Combination of hydrodynamic and squeeze film Mixed…
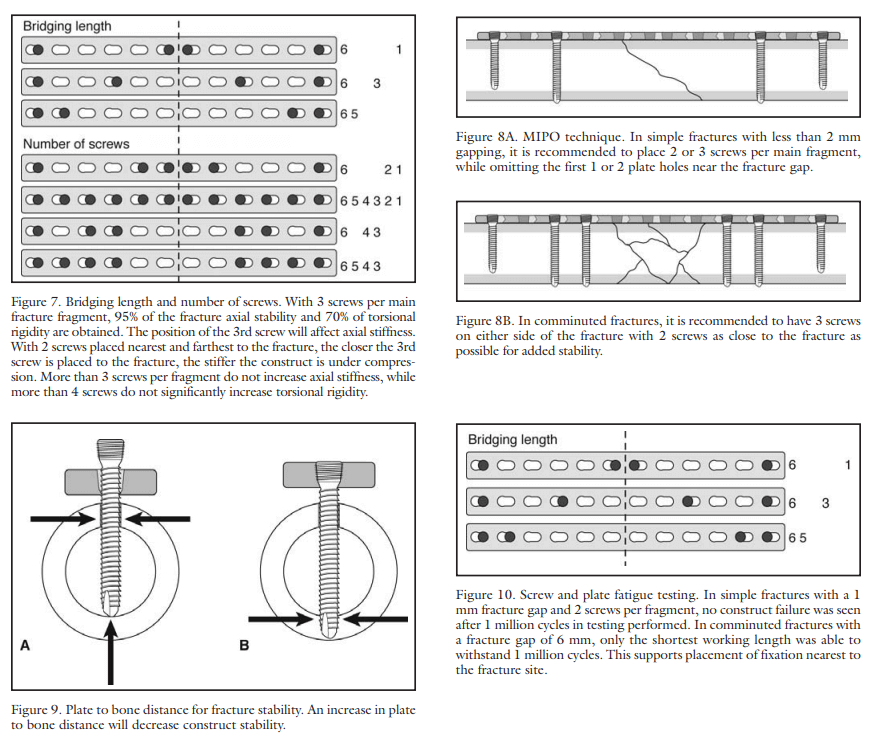
Biomechanics in MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis)
1. Provides optimal environment for fracture healing: 2. Relative stability of fracture: 3. Acts as internal fixator: 4. Plate length and Number of screws in Bridge plate function: 5. Plate working length: References:
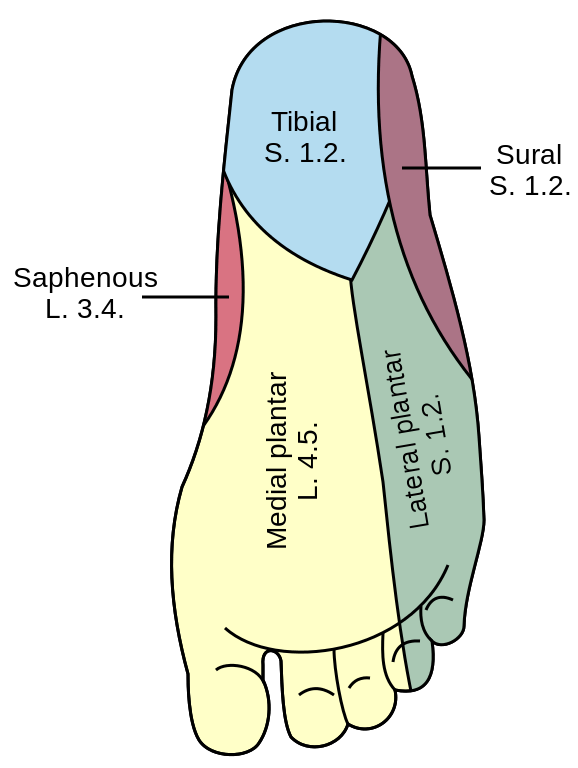
Medial and Lateral Plantar Nerves
Origin: Tibial nerve (both medial and lateral plantar nerve) Similar to: Course and innervation: Medial plantar nerve Lateral plantar nerve Origin Larger branch of tibial nerve Smaller branch of tibial nerve Course Deep to abductor hallucis muscleBetween 1st and 2nd plantar layers Deep to abductor hallucis muscleBetween 1st and 2nd…
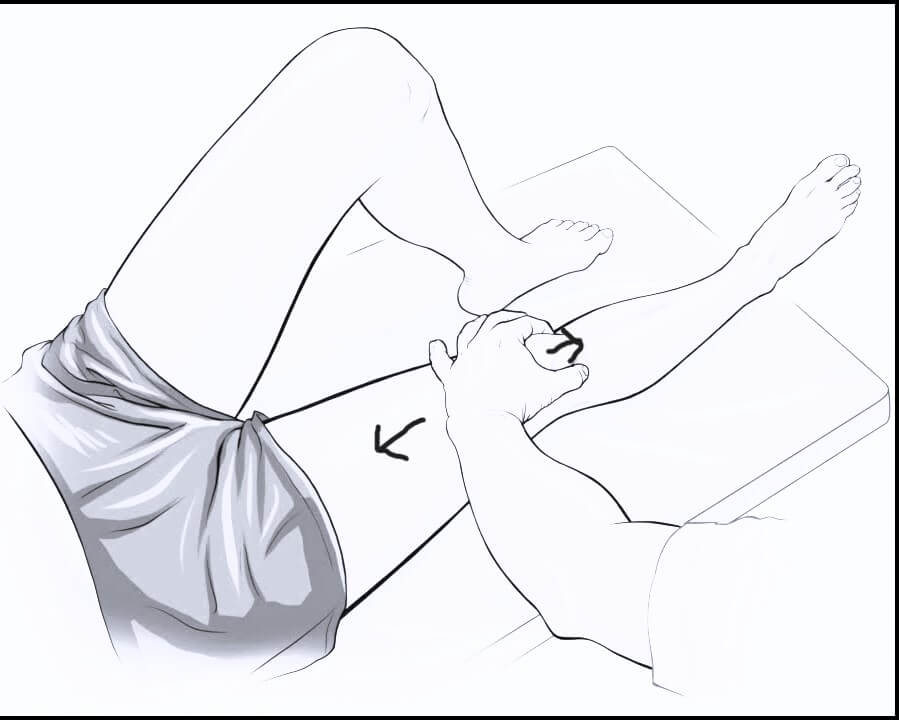
Clarke’s test
Synonyms: Patellofemoral grind test, Patella hold test, Zohler’s sign Tests for: Patellofemoral dysfunction Patient position: Lying down with knees extended and relaxed (heels on table) Technique: 1. Place the webspace of thumb on the upper pole of patella and push it inferiorly. 2. Ask the patient to contract his/her quadriceps…
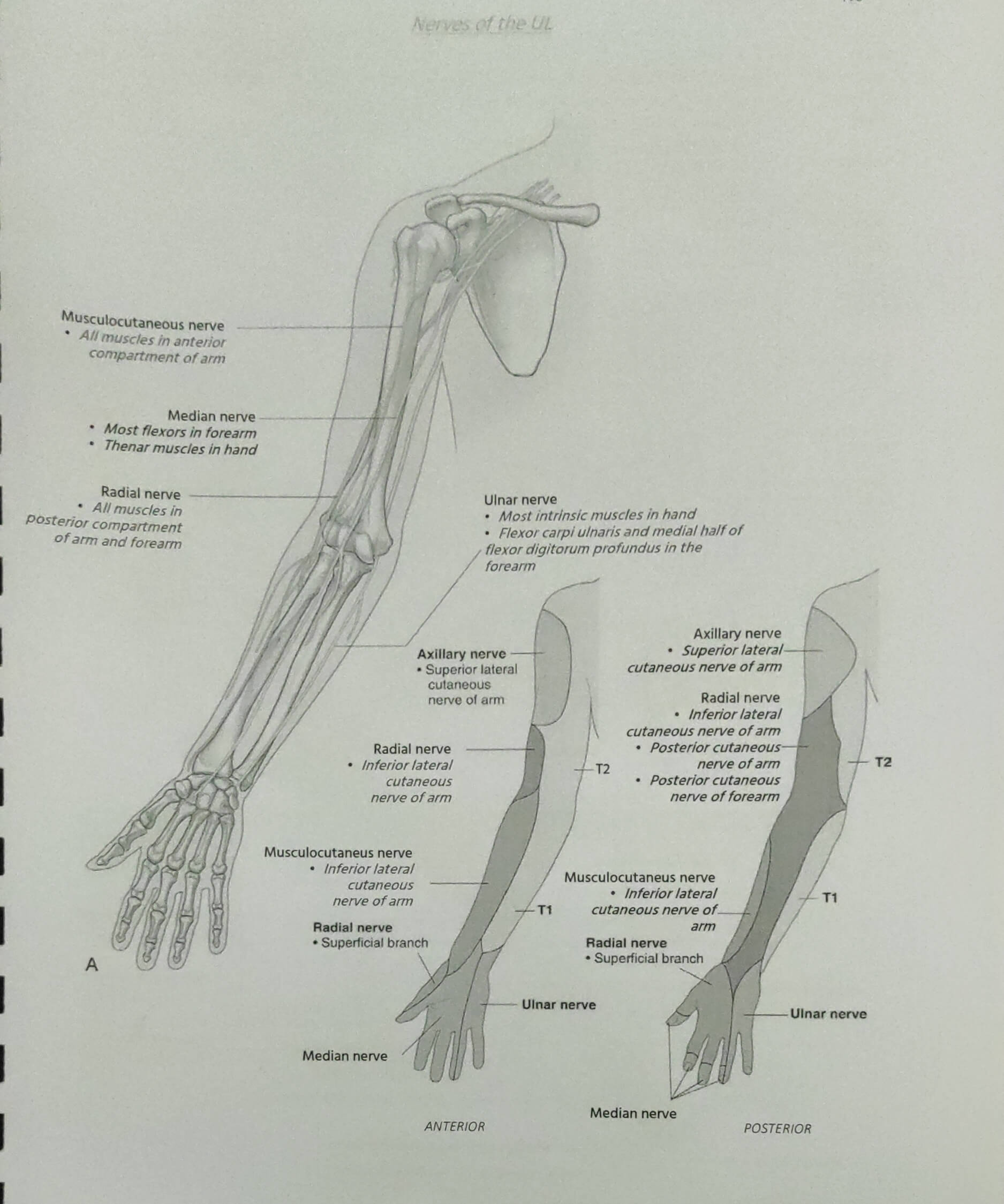
Median, Ulnar and Radial Nerve – Course and Innervation
Median nerve, Ulnar nerve and Radial nerve are the 3 major nerves of the upper limb originating from the brachial plexus. Some important neuroanatomic relationships in the forearm are: 1. Medial nerve: Crossed by brachial artery from lateral to medial just above the elbow to lie medial to brachial artery…
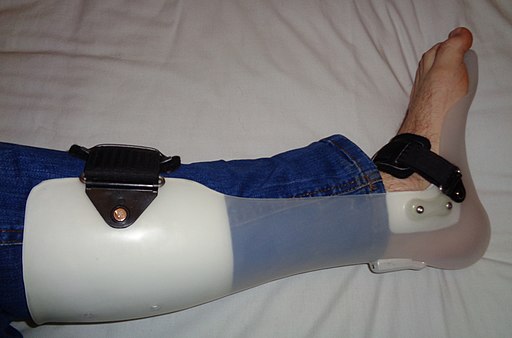
Foot Drop : Differentials
Foot drop can result from: L5 radiculopathy Lumbar plexopathy Sciatic neuropathy Peroneal neuropathy Causes Disc herniation, Spinal canal stenosis Pelvic surgery, hematoma, prolonged labor Hip surgery, Injection injury Compression/trauma Motor Weakness includes muscles and hip abductors Weakness includes hip abductors and anal sphincter Weakness includes tibial and hamstring muscles Weakness…