Meniscus structure
Mnemonic: CD RS
- Circumferential fibers: Deep layer
- Resist hoop stress
- Due to this arrangement, vertical mattress sutures are stronger than horizontal mattress sutures as they capture circumferential fibers
- Radial fibers: Superficial layer
- Support circumferential fibers
McMurray test
Mnemonic: The heel of the foot points towards the injured meniscus
Meniscus attachments in knee
Each meniscus has something attached to it:
- Medial meniscus: Medial collateral ligament
- Lateral meniscus: Popliteal muscle
Tear Patterns
Mnemonic: LaHORe FC
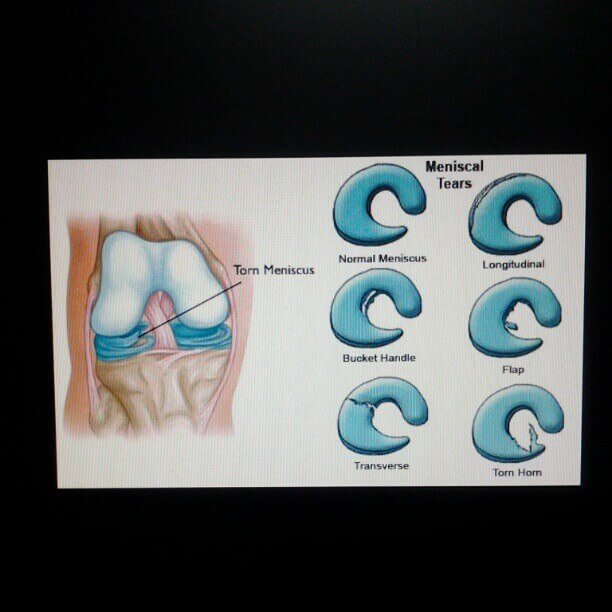
| Tear pattern | Description | Potential to repair |
| Longitudinal | Oriented parallel to edge of meniscus a. Complete tear with inner fragment displaced over into the intercondylar notch – Bucket handle tear (Double PCL sign or Double anterior horn sign in MRI) b. Tear is near the menisco-capsular attachment of meniscus – Peripheral tear | Repairable |
| Horizontal | Tears in the same horizontal axis as the meniscus tissue | Irreparable |
| Oblique | Full thickness tears running obliquely from the inner edge of meniscus out into the body of meniscus | Irreparable |
| Radial | Extend from medial rim toward lateral rim of meniscus – can be complete or incomplete; almost unique to lateral meniscus (Ghost meniscus sign in MRI) | Potentially repairable |
| Flap | Like oblique tear but have a horizontal cleavage element rather than being purely vertical | Irreparable |
| Complex | Combination of above-mentioned tears; more common in chronic meniscal lesions | Irreparable |
Management of Meniscus Tear
Mnemonic: 3 R
- Resection
- For tears that cannot be repaired and history of 2 failed repairs
- Goal: Minimal resection, Stable contour
- Repair (healing capacity better in red-red zone, vertical tear and with early repair)
- Inside-out: Gold-standard
- Indications: All tears except direct posterior
- Highest mechanical strength
- Outside-in
- Indications: Anterior horn (lateral meniscus)
- Less risk of neurovascular injury
- Requires arthroscopic knot typing
- All-inside: Bio-absorbable anchors; Increasingly popular
- Indications: Body and posterior tears
- No incisions required
- Lower mechanical strength
- Inside-out: Gold-standard
- Replacement
- For younger patients requiring near-total or total menisectomy
- Meniscus graft size must match native meniscus within 5–10%
- Contraindications: Grade III-IV Osteoarthritis or Inflammatory arthritis
Meniscus Repair Versus Resection
Mnemonic: LAST Qualifiers
| L – Location from capsule (rim width) | <2 mm | 0 |
| 2-3 mm | 1 | |
| 4-5 mm | 2 | |
| A – Age | <20 years | 0 |
| 20-40 years | 1 | |
| >40 years | 2 | |
| S – Size | 1-2 cm | 0 |
| 2-3 cm | 1 | |
| >4 cm | 2 | |
| T – Tissue quality | Excellent | 0 |
| Good | 1 | |
| Fair | 2 | |
| Qualifiers | Unstable | 2 |
| Malalignment | 1 | |
| Chondromalacia grade III | 1 | |
| Radial tear | 2 | |
| ACL reconstruction or fibrin clot | -1 |
Higher scores are associated with higher failure rates.
Repair is indicated if score ≤ 4.