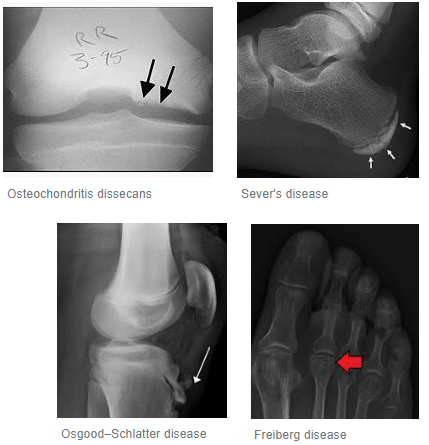
Osteochondritis of the capitulum of humerus (elbow): panner’s disease Osteochondritis of the lunate bone: keinbock’s disease Osteochondritis of the femoral head: perthe’s disease Osteochondritis of lateral part of medial femoral condyle: osteochondritis dissecans Osteochondritis of the tibial tubercle: osgood schlatter’s disease Osteochondritis of lower part of patella: sinding larsen johansson…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
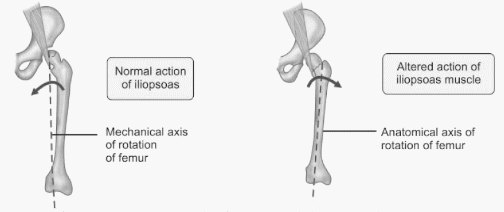
Hip and Shoulder Deformities
HIP Flexion, Abduction, External rotation (FABER) + apparent lengthening: Synovitis Flexion, Abduction, External rotation (FABER) + true lengthening: Anterior dislocation of hip (Obturator) Extension+ Abduction + External rotation (EABER): Anterior dislocation of hip (Superior or Pubic) Flexion, Adduction, Internal rotation (FADIR) + true shortening: Arthritis, Posterior dislocation of hip Flexion,…
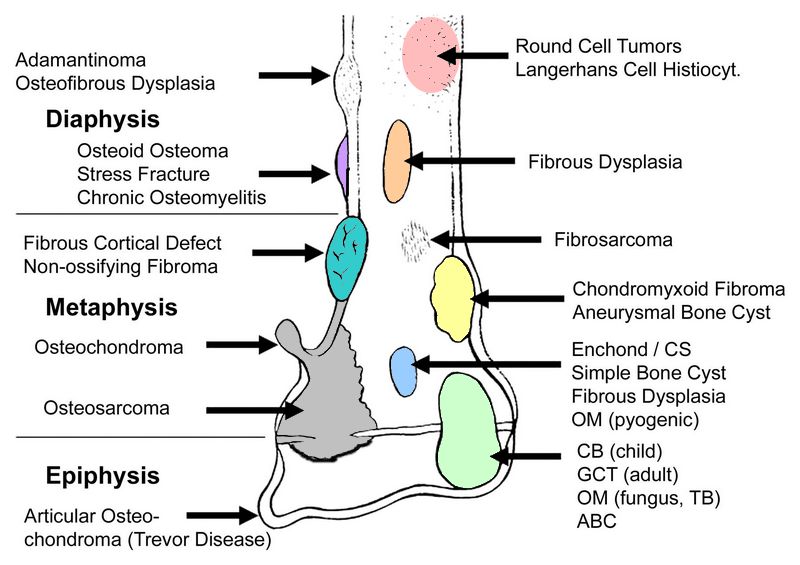
Differential Diagnoses of Bone Tumors : Mnemonic Approach
Lytic and Sclerotic Bone Lesions Mnemonic for Solitary lytic lesions: FEGNOMASHIC Fibrous dysplasia Enchondroma Eosinophilic granuloma Giant cell tumor Nonossifying fibroma Osteoblastoma, Osteosarcoma (telangiectatic) Metastases Myeloma Aneursymal bone cyst Simple bone cyst Hyperparathyroidism (brown tumor) Infection Chondroblastoma Chondromyxoid fibroma Mnemonic for Multiple lytic lesions: FEMHI Fibrous dysplasia Eosinophilic granuloma/Enchondroma Metastasis/Mutiple…
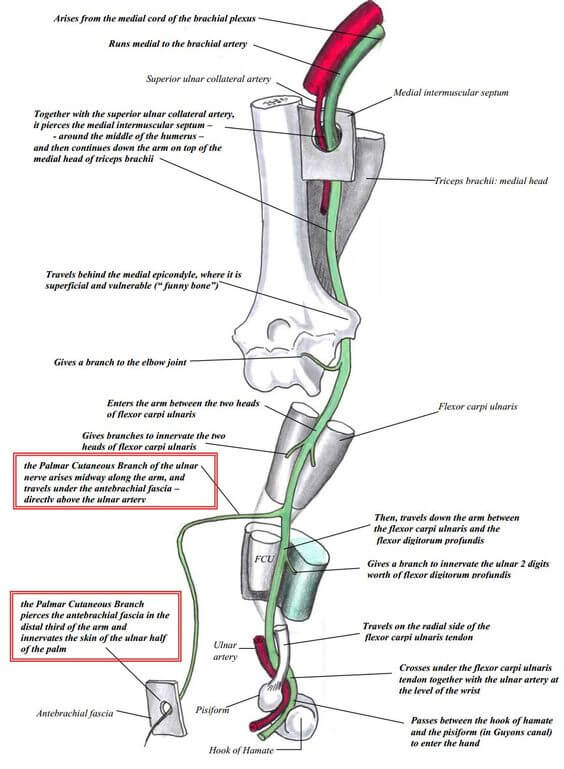
Ulnar nerve Anatomy – Course and Innervation
Origin: C(7), C8, T1 (medial cord of Brachial plexus) Course: Motor innervation: 1. Forearm: Flexor carpi ulnaris (weakness of ulnar deviation and flexion of wrist), Medial half of flexor digitorum profundus (branches near the elbow) 2. Hand: branches near wrist Sensory innervation: Palmar branch at forearm and Digital branch at wrist…
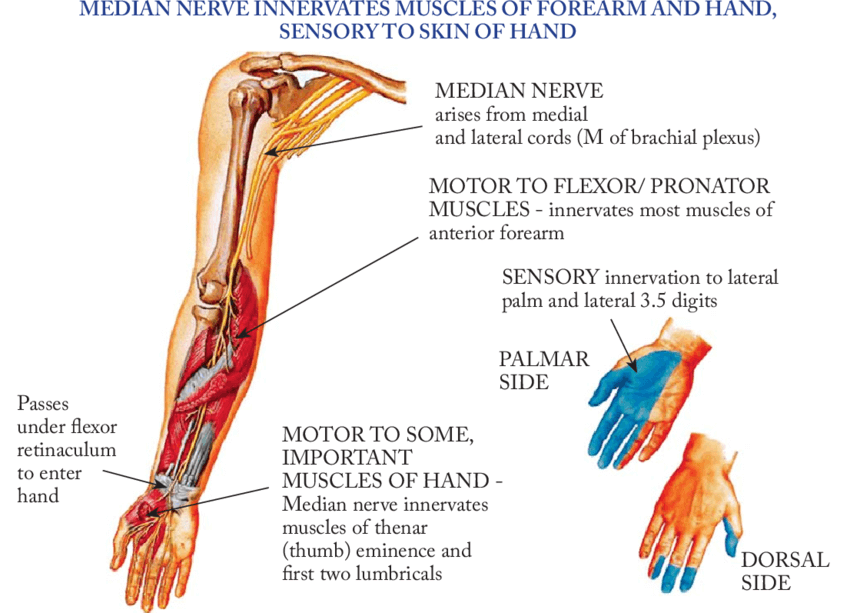
Median nerve Anatomy : Course and Innervation
Origin C5-T1 (lateral and medial cords of Brachial plexus) Course Motor innervation Muscles supplied: 2 lateral lumbricals, 3 thenars, 3Ps (2 pronator and 1 palmaris) and 4 flexors. Sensory innervation Clinical correlation 1. Martin-Gruber motor connection: occur in 17% of individuals between median and ulnar nerves resulting in variable innervations…
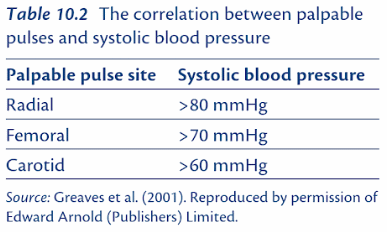
ATLS 80/70/60 Rule for Palpable Blood pressure
ATLS’ 80/70/60 rule On the basis of location of pulse palpable, minimum systolic blood pressure can be predicted as follows: Radial/Dorsalis pedis/Popliteal pulse: >80 mmHg Femoral pulse: >70 mmHg Carotid pulse: >60 mmHg Overestimation of SBP by Pulses Pulse characteristics are an unreliable sign and “should be used only as…
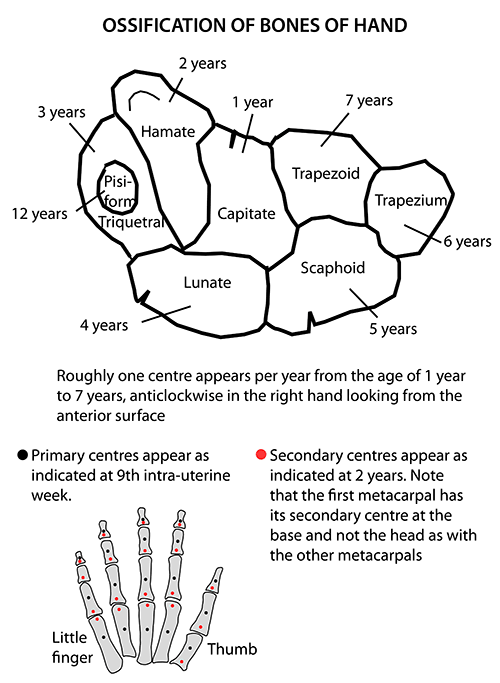
Carpal Bones Ossification: Mnemonic
Roughly one center appears per year from the age of 1 year to 7 years, anti-clockwise in right hand and clock-wise in left hand looking from the anterior surface, i.e. from ulnar side to radial side. Pisiform, being a sesamoid bone it gets left behind and only develops years later. capitate: 1-3 months hamate:…
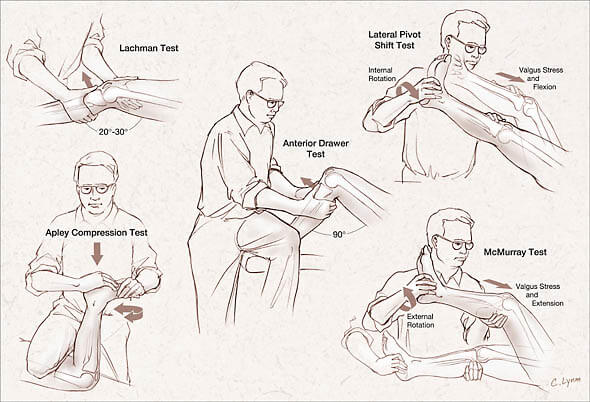
Tests for Knee Ligaments
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Lacchman’s test It is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed 20–30°. The examiner grasps the distal femur (from lateral side) with one hand and the proximal tibia with the other hand (from medial side). The lower leg is given a brisk forward tug…