Associations of Dupuytren’s Contracture Mnemonic: DEAFEST LIAR Dupuytren’s diathesis Mnemonic: ABCDEF Severity and recurrence risk is increased in: If all 6 diathesis risk factors are present: risk of recurrence is 71% If none of diathesis risk factors are present: risk of recurrence is 23% Involvement of fingers Mnemonic: RaSMIT In…
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
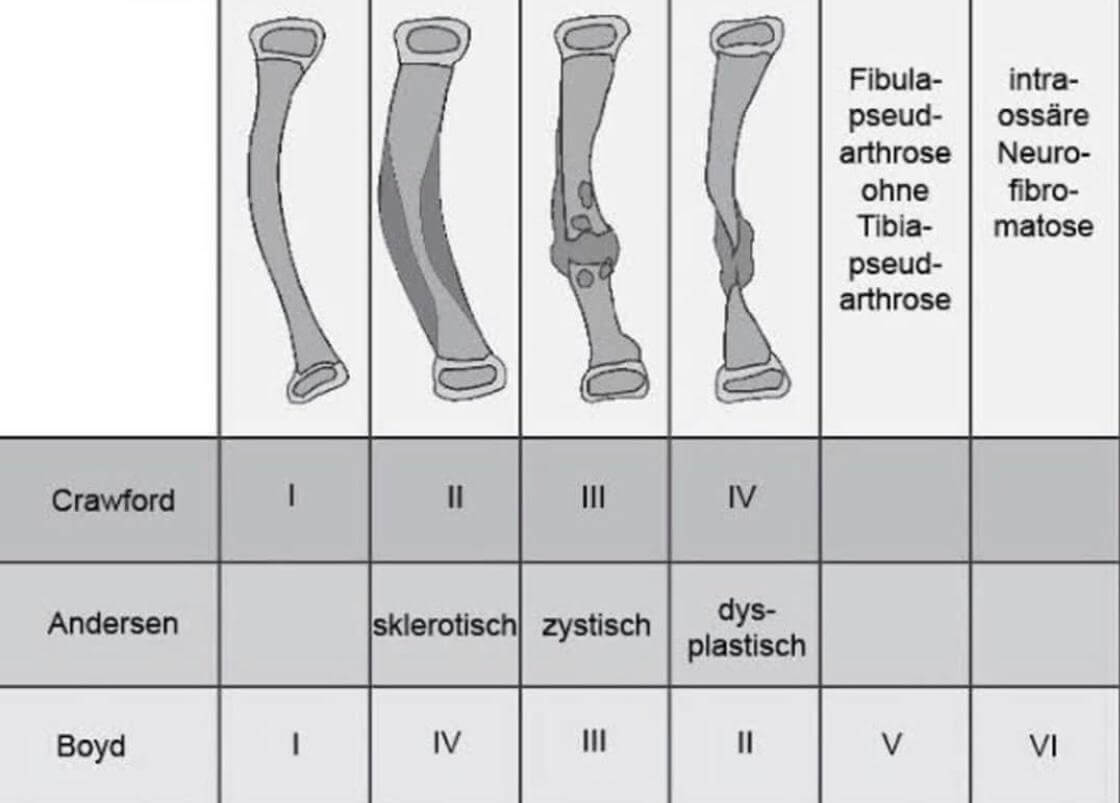
Congenital Pseudoarthrosis of Tibia (CPT)
Origin of Pathology Periosteum Clinical features Mnemonic: ABCDeF Boyd Classification Mnemonic: B-2C-2D-E I – Bowing II – Constriction (hourlgass) III – Cyst IV – Dense (Sclerotic) V – Dysplastic fibula VI – “Endosseous” (Intraosseous) neurofibroma or schwannoma Paley Classification Type Bone ends Pseudoarthrosis mobility Previous surgical intervention 1 Atrophic Mobile…
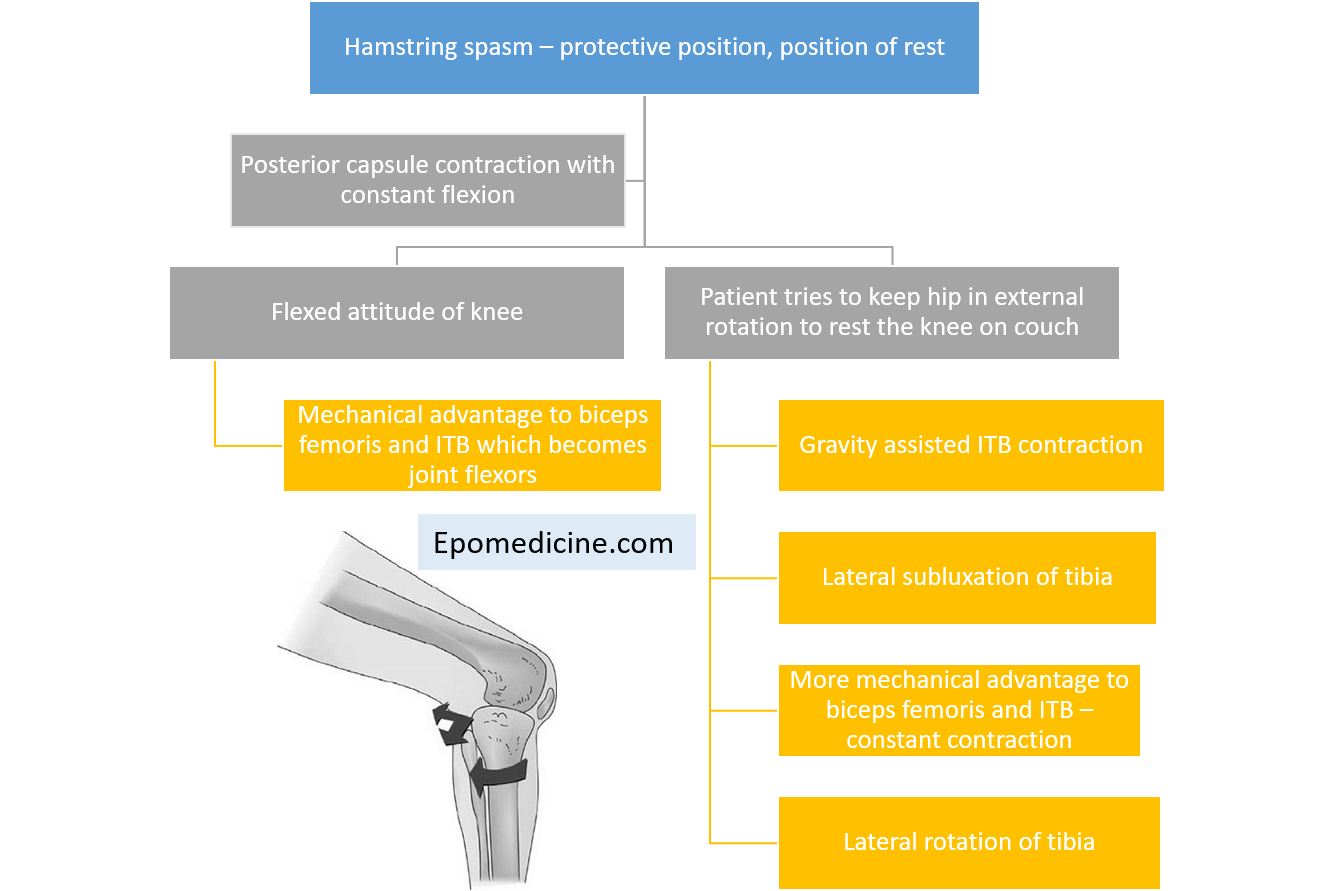
Triple deformity of Knee : Mnemonic
Triple deformity of knee consists of 3 components: 1. Flexion deformity at knee 2. Posterolateral subluxation of tibia 3. External rotation of tibia over femoral condyle Mechanism behind triple deformity of knee: Causes of Triple deformity of knee: Mnemonic: TRIPLE 1. Tuberculosis (TB) knee – commonest cause 2. Rheumatoid arthritis…
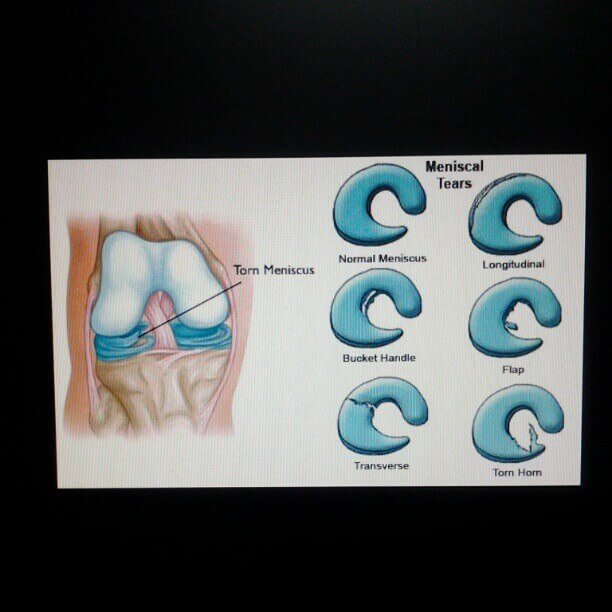
Meniscus Injury : Mnemonics
Meniscus structure Mnemonic: CD RS McMurray test Mnemonic: The heel of the foot points towards the injured meniscus Meniscus attachments in knee Each meniscus has something attached to it: Tear Patterns Mnemonic: LaHORe FC Tear pattern Description Potential to repair Longitudinal Oriented parallel to edge of meniscusa. Complete tear with…
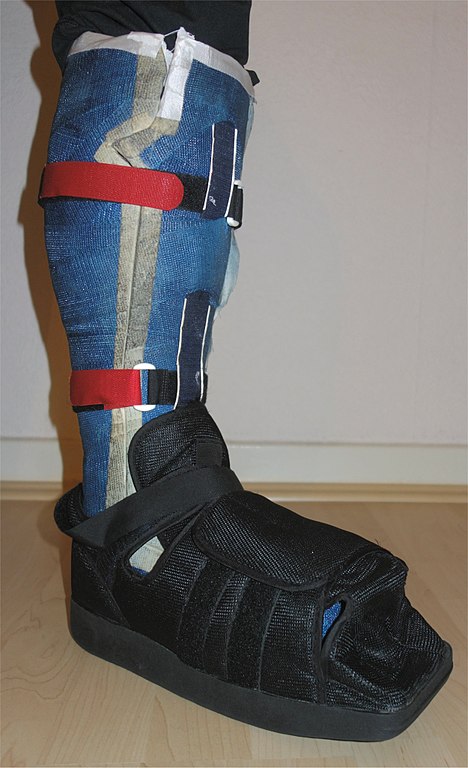

Total Contact Cast (TCC) – Principles and Technique
Total contact cast (TCC) is a modification of traditional below knee plaster with minimal padding, covering to protect toes, and molding to the contour of the foot and leg so that there’s no movement withing the cast. Indications of Total Contact Cast Contraindications of Total Contact Cast 1. Absolute: 2….
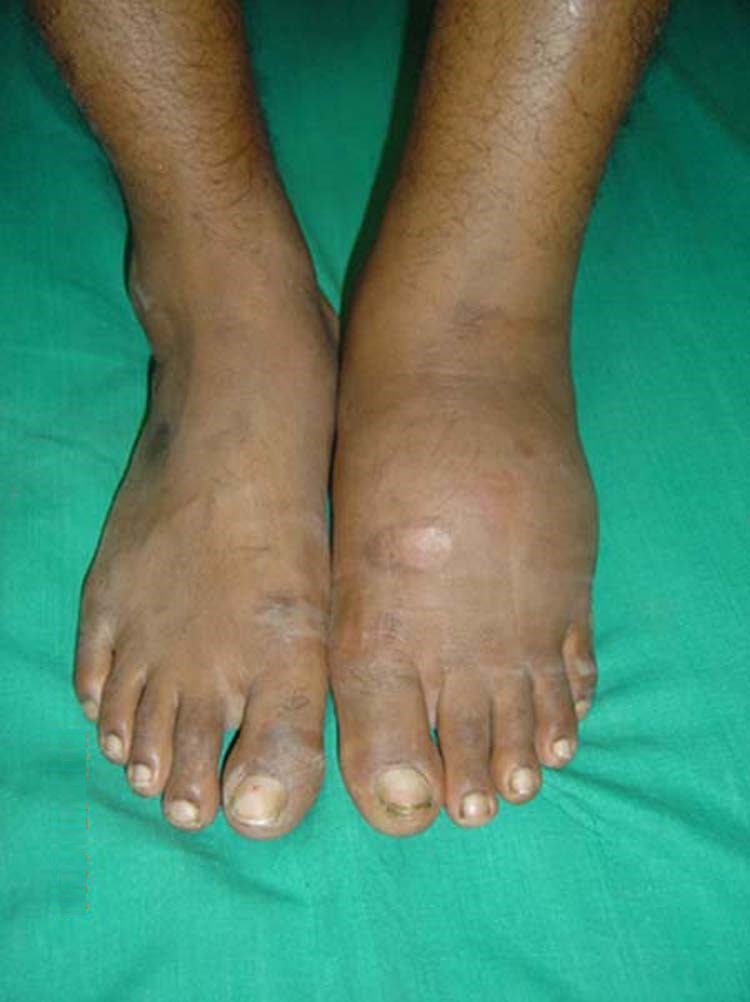
Charcot Arthropathy : Mnemonics
Causes of Charcot Arthropathy Mnemonic: 10 S 3 Theories of Charcot Arthropathy a. Neuro-traumatic: Damage to sensory feedback → Repeated microtrauma → Release of proinflammatory cytokines → Bone resorption b. Neuro-vascular: Change in vascularity caused by dysregulation of vasomotor and trophic nerve supply c. Neuro-inflammatory: Abnormal persistence of inflammatory response…
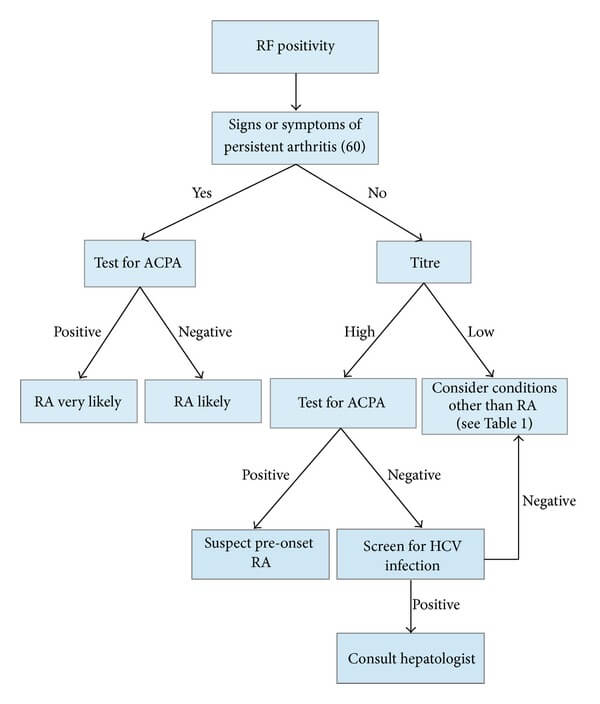
Approach to Rheumatoid Factor Positive test
Rheumatoid factor (RF; also mistakenly called RA factor) is an auto-antibody (commonly IgM and rarely IgG or IgA) directed against the Fc portion of IgG. Increase in both IgM and IgA RFs is almost exclusively observed in patients with RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis). Clinical Significance of Rheumatoid Factor 1. A positive…
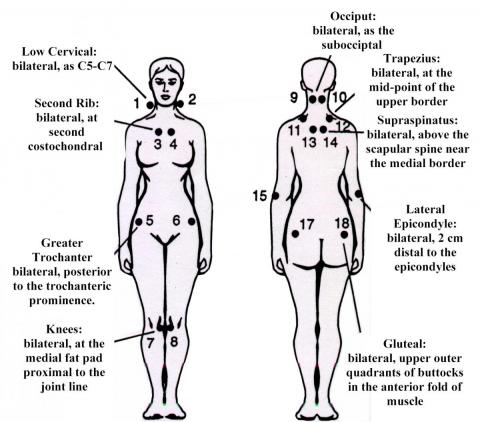
Pain all over body, Sleep disturbance, Fatigue, Headaches – Fibromyalgia
What is Fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia is a chronic illness characterized by many symptoms that occur all at once: 1. Widespread pain 2. Fatigue 3. Sleep problems 4. Cognitive disturbances (concentration, memory) 5. Altered mood (anxiety, depression) 6. Other symptoms: headache, digestive disorders, dizziness, muscle spasms, chills, low-grade fever, ringing in the…