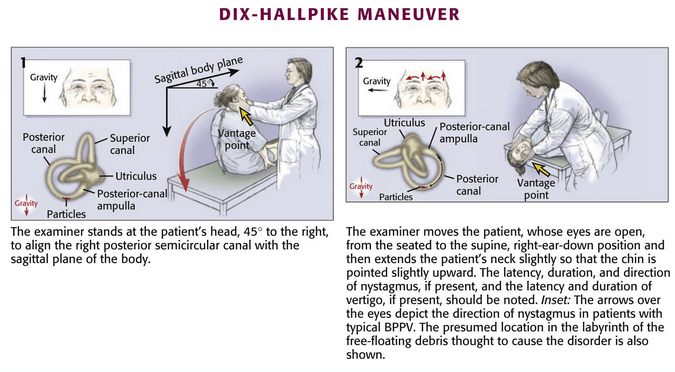
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is the commonest cause of episodic vertigo and is characterized by acute attacks of transient vertigo initiated by certain head positions, lasting seconds to minutes, accompanied by nystagmus that fatigues on repeated testing. Important terminologies linked with pathogenesis of BPPV: Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals released…
Tag: Otorhinolaryngology

Examination of Facial Nerve (7th Cranial Nerve)
The anatomy of facial nerve has already been discussed in detail earlier. It is essential to have proper knowledge of anatomy to understand this section of clinical examination of facial nerve. A) Inspection: Observe: Face at rest for any facial asymmetry Any facial tics, symmetry of eye blinking or eye…
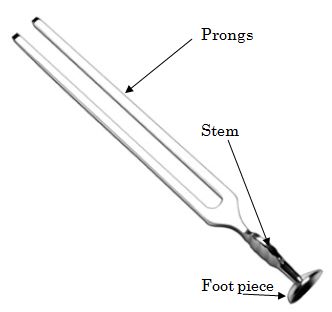
Hearing tests with Tuning fork
Tuning fork Parts of a tuning fork 1. Foot piece 2. Stem 3. Prongs How to use tuning fork? Hold the stem of the tuning fork between the index finger and thumb of your right hand without touching the prongs. Strike the junction of superior 1/3 and inferior 2/3 of the…
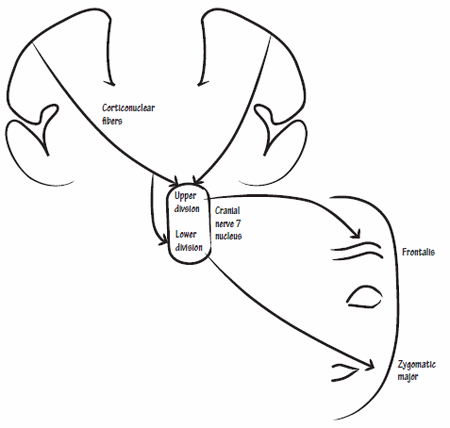
Facial Nerve Anatomy
SYNONYMS: Cranial nerve seven (VII), Nervus facialis Supranuclear pathways 1. Somatomotor cortex: controlling motor component of facial nerve lies in precentral gyrus (Broadmann area 4,6,8) 2. Volitional component: Corticonuclear tracts descend and cross to supply both ipsilateral and contralateral facial (mainly to the contralateral side) nucleus i.e. frontal branch components…
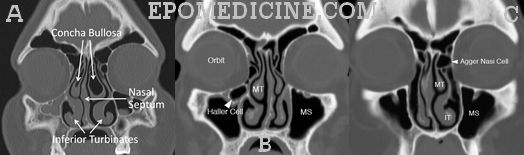
Anatomy of Ostiomeatal complex
Synonyms: Ostiomeatal unit, Osteomeatal complex, OMC Definition: The term “ostiomeatal unit” represents the area on the lateral nasal wall (middle meatus) that receives drainage from the anterior and medial ethmoid cells, frontal sinus, and maxillary sinus. It is an antomically constricted area that is prone to blockage, especially in the…
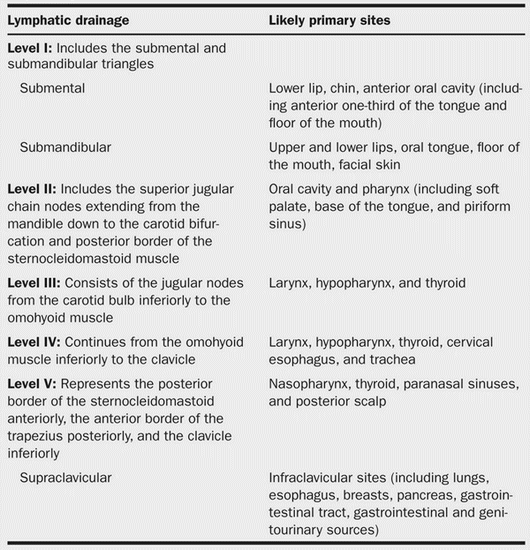
Triangles and Lymph node levels of Neck
There are 2 major triangles in the neck, containing other smaller triangles. 1. Anterior triangle: Midline of neck – Mandible – Anterior border of SCM Posterior triangle: Posterior border of SCM – Trapezius – Clavicle (level V); 2 triangles inside separated by inferior belly of omohyoid Surgically, cervical lymph nodes…
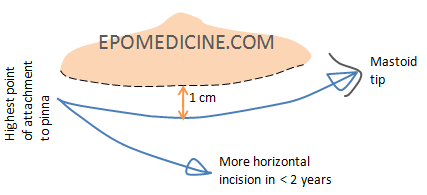
Approaches to Middle ear and Mastoid surgery
Endomeatal (Transcanal or Transmeatal) Approach: Not used commonly in children owing to relatively small ear canal This incision is used when the mesotympanum and hypotympanum are the surgical sites A posterior tympanomeatal flap is raised to enter into the middle ear. The flap includes skin over the medial two-thirds of the bony…
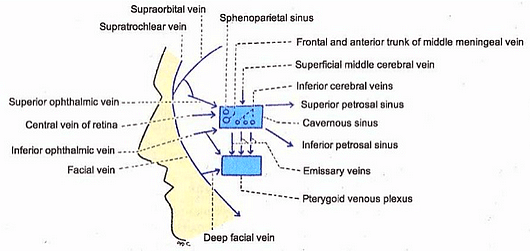
Cavernous Sinus – Simplified
Synonyms: Sinus cavernosus, Lateral sellar compartment Definition and Extent Size: 2 cm long and 1 cm wide Walls: Extent: Contents of Cavernous sinus These are closely related to the floor of sinus and are separated from the interior of sinus by endothelium. 4 nerves in the lateral wall: Note: Mandibular…