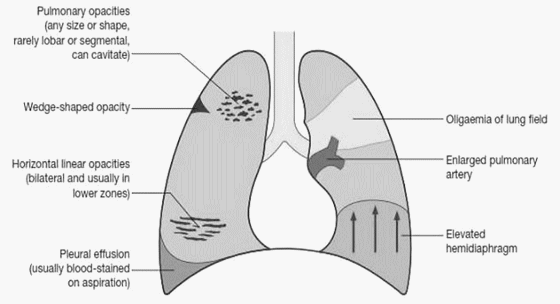
1. Classic presentation is normal X-ray in patient with dyspnea and hypoxia 2. Atelectasis or parenchymal abnormality (68%) 3. Elevated hemidiaphragm 4. Pleural effusion (Felson’s sign – pleural effusion on left > right) 5. Hampton’s hump: peripheral pleural based wedge-shaped density above the diaphragm due to pulmonary infarct 6. Westermark’s…
Tag: Emergency medicine
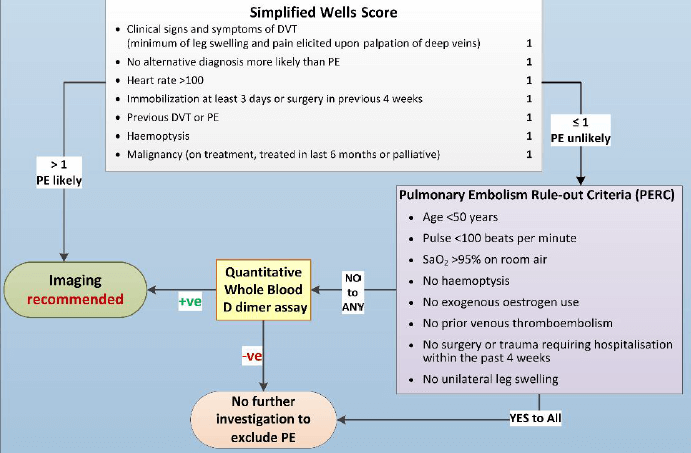
Well’s and PERC Criteria for Pulmonary Embolism : Mnemonic
Well’s Criteria (Modified and Simplified) Mnemonic: CHADS (Remember, this is not the CHADS2 score for Atrial Fibrillation) Clinical features of DVT Cancer Heart rate > 100/min Hemoptysis Alternative diagnosis less likely DVT/PE in past Surgery in past 4 weeks or Immobilization for 3 days Well’s criteria Original score Simplified score…
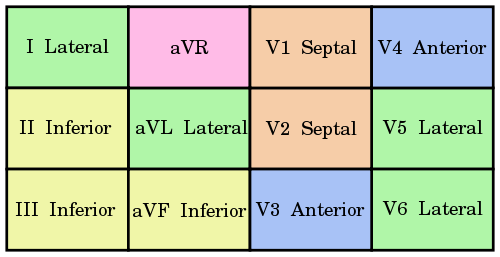
Acute STEMI Management – Mnemonic based approach
60 year old smoker patient came with epigastric pain and shortness of breath for 4 hours. The patient was tachypneic with SpO2 90%. Other vital signs were relatively stable. ECG was done, Troponin I was positive and CK-MB was 100 IU/l. What is there in ECG above? ST elevation and…
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) – Mnemonic Approach
Approach the patient with 9 Ps. 0-10 minutes (Possibility of Success): Anticipating difficult airway Mnemonic: LEMON approach 1. Look externally: Remember “BONES“ Beard Obesity No teeth Elderly Sleep apnea/Snoring 2. Evaluate 3-3-2 rule: Ideal dimensions for visualization of larynx 3 fingers in mouth: adequate mouth opening 3 fingers under the…

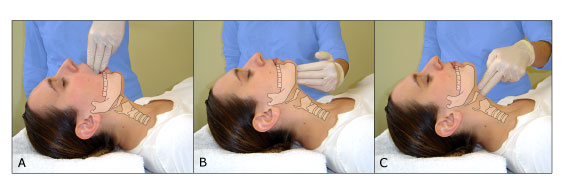
Log Rolling Maneuver : Steps
Step 1: Rescuer 1 stabilizes head and neck in neutral position without applying traction. He/she should grasp the patient’s shoulders at the neck and gently position the patient’s head betweeen the forearms. Another rescuer should apply a semirigid extrication collar. Even with the collar in place, Rescuer 1 must maintain…
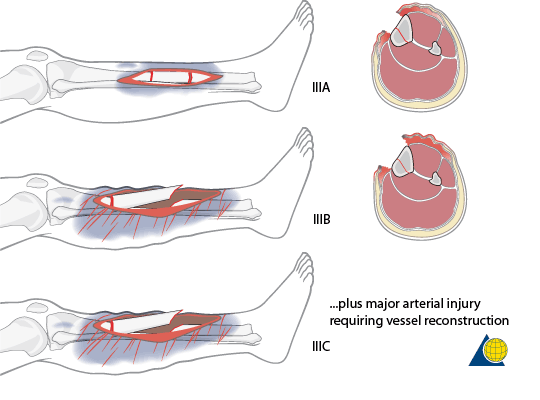
Open fractures : Mnemonics
Gustilo Anderson Classification Mnemonics:1. Parameters: ABCD’S (Area, Bone, Circulation, Dirt, Soft tissue)2. Classification: I, II, III then A, B, C Progression for grade I to III C implies a higher degree of energy involved in the injury, higher soft tissue and bone damage, and higher potential for complications. Type I:…
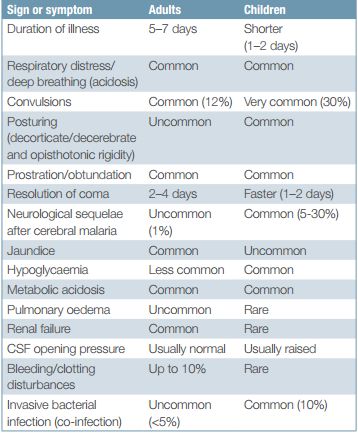
Severe Malaria : Quick revision
Criteria for Severe and Complicated Malaria Positive peripheral blood smear for P.falciparum + ≥1 of the CHAPLINS (Mnemonic) Convulsions: >2 in 24 hour Cerebral edema (Consciousness impaired) Hypoglycemia (glucose <40 mg/dl) Hemorrhage (DIC) Hemoglobinuria (Black water fever) Anemia (hemoglobin <5 gm/dl or PCV <15% in children; hemoglobin <7 gm/dl or…
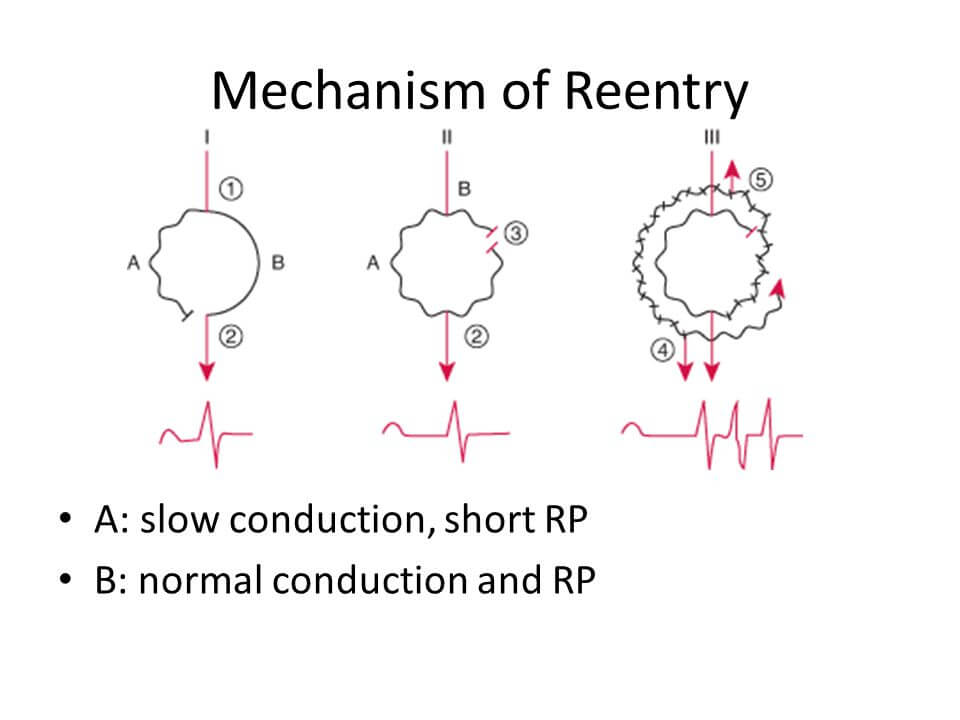
Short Approach to SVT and AVNRT management
This is an ECG from a patient who came with a complaint of palpitation: Analyze the ECG: Rhythm: Regular Heart rate: Around 170/min QRS: Around 0.08 s i.e. ≤0.1 s (narrow QRS complex) ECG diagnosis: Regular Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Now, look for P waves – There are no P waves In…