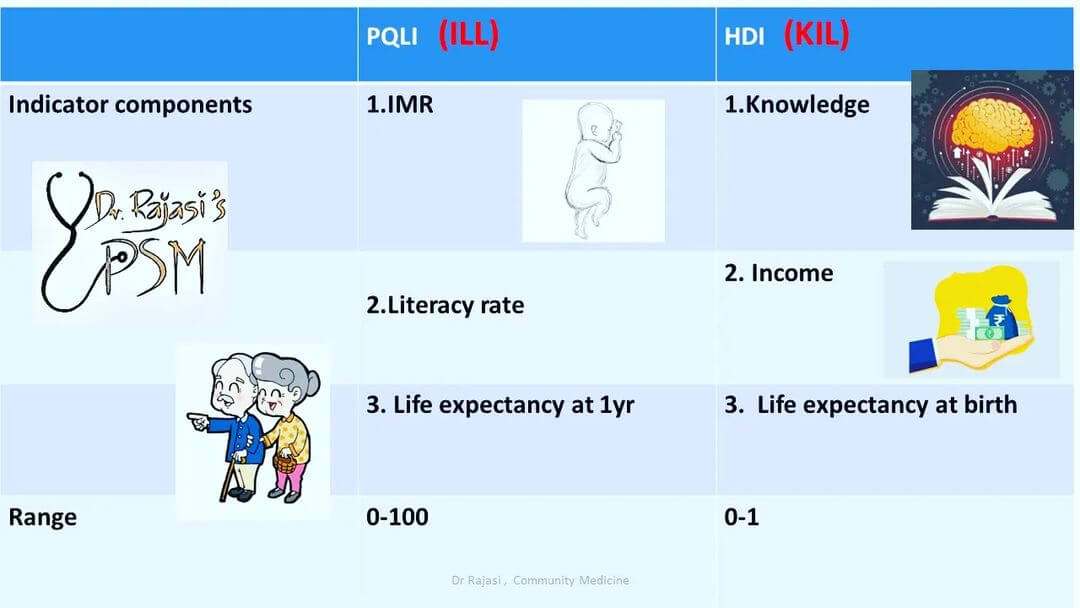
PQLI and HDI are similar, the main difference between the two being the inclusion of income in HDI & exclusion of same from PQLI. HDI represents both physical and financial attributes of development and PQLI has only physical aspects of life. PQLI HDI Full form Physical Quality of Life Index…
Tag: Community medicine
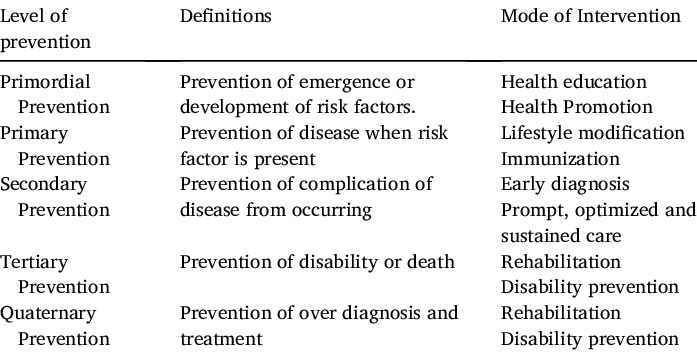
Levels of Disease Prevention : Mnemonic
Level Mnemonic Target population Goals Mode of intervention Primordial Prevent risk factors General population Prevent emergence of risk factors Health educationHealth promotion Primary Prevent disease General population Prevent disease onset Lifestyle modificationImmunization Secondary Screening Subclinical (asymptomatic) Prevent symptom onset Early diagnosisPrompt optimized & sustained care Tertiary Treatment Clinical (symptomatic) Prevent…

Phases of Clinical Trial : Mnemonic
Clinical trials conduct ‘human experiments’. Three fundamental principles apply: Blinding: Phases: Mnemonic: I SWIM Phase Purpose Name Sample Blinding and control 0 Initial (Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics) Microdosing studies Healthy volunteers (smaller) No I Safe? (Safe maximum dose and tolerability) Human pharmacology and safety Healthy volunteers (larger) No II Works? (Efficacy)…

Errors and P-value
Statistical hypotheses Null hypothesis (H0): No difference or relation exists; e.g. Treatment A is not better than Treatment B Alternative or research hypothesis (H1): Some difference or relation exists, e.g. Treatment A is better than Treatment B Statistical errors Type I error (alpha): False positive (Falsely rejecting Null-hypothesis; i.e. null…

Baye’s theorem derived PPV and NPV
Let’s unveil the mathematics behind the relation between: Prevalence (Pre-test probability) Predictive value (Post-test probability) Sensitivity Specificity SYMBOLS: Total screened population = nPrevalence = PSensitivity = SnSpecificity = SpTrue positive = TPTrue negative = TNFalse positive = FPFalse negative = FNWith disease = D+Without disease = D-Positive predictive value =…
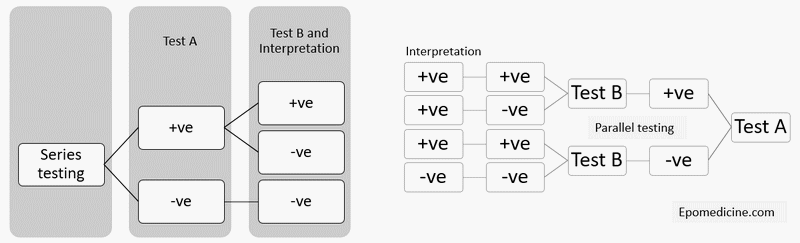
Screening tests in Series and Parallel
A. Parallel testing 2 screening tests are applied simultaneously: So, this test will have: B. Series testing After the 1st screening test is conducted, those who test positive are only tested with the 2nd screening test: So, this test will have: Formulae for combined specificity and sensitivity A. Parallel testing:…

Sustainable Development Goal 3 – Points to Remember
Total SDG goals: 17 Time frame: 2016-2030 Goal 3: Good health and well beings for all ages Important targets of Goal 3 (Targeted by 2030) A. Maternal and Child health (MCH) Mnemonic: 12 letters in “NEONATE DEATH or NEWBORN DEATH“. 1. NMR reduction target: 122. U5MR reduction target: 12 X…
Key Health Indicators of Nepal to Remember (NDHS, 2022)
These rates, ratios and proportions are often questioned in PGMEE, pediatrics, obstetrics and preventive and social medicine (PSM) or community medicine examinations. NDHS = National Demographic and Health Survey a. Neonatal mortality rate (NMR): 21 per 1000 live births (i.e. 3/4 of infant deaths) b. Infant mortality rate (IMR): 28…