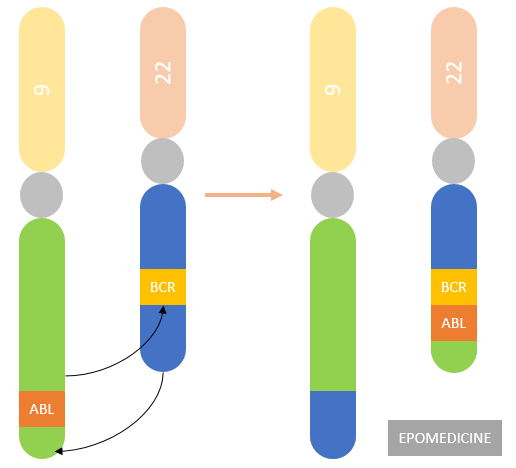
t(8;14): Burkitt’s lymphoma t(14;18): Follicular lymphoma t(11;14): Mantle cell lymphoma t(11,18): Marginal zone lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) t(9;22): CML (Philadelphia chromosome), Bad prognosis ALL t(8;21): AML M2 t(15;17): AML M3 (Promyelocytic AML) t(X;18): Synovial cell sarcoma t(11;22): Ewing’s sarcoma t(12;21): Pre-B ALL (good prognosis ALL) t(4;11) and t(1;19): Bad prognosis ALL
Tag: Hematology
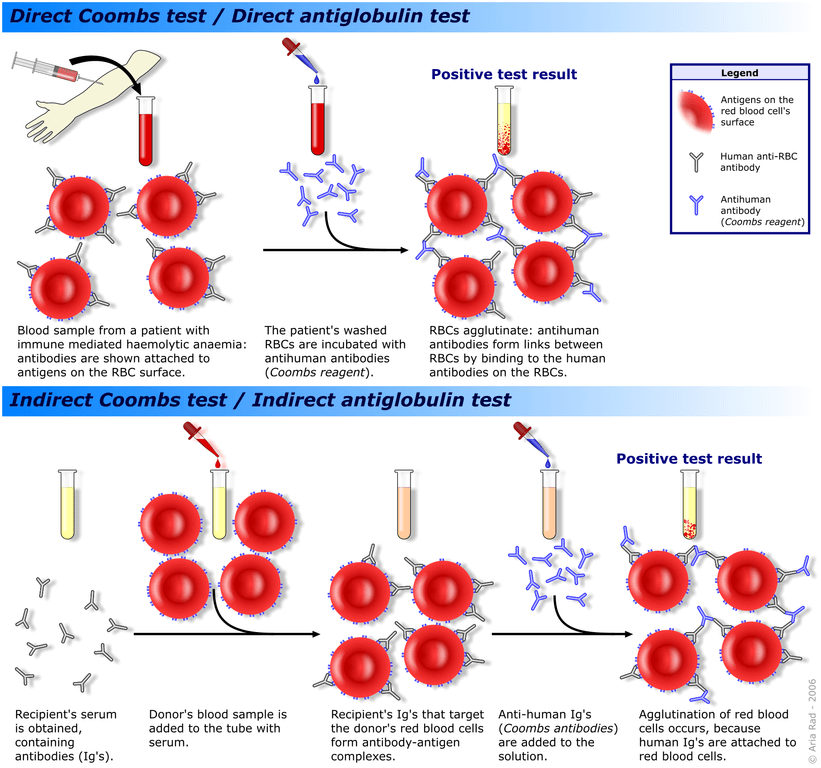
Coomb’s test : Mnemonic
Components of Coomb’s test: Mnemonic: ABCD A: Antibody (to be detected) B: Blood antigen (RBC) C: Coomb’s reagent (Anti-antibody) D: Detect agglutination Direct Coomb’s/Antiglobulin test (DAT or DCT): Mnemonic: In DAT/DCT we take A+B from patient and add C [(A+B) + C] Another Mnemonic: DCBA (Direct Coomb’s detect Blood Bound…

Protein C and S pathway – Mnemonic
Factor Va and VIIIa are different in coagulation cascade. They are the co-factors for factor Xa and IXa respectively. Another mnemonic: protein C Cuts Coagulation by Cutting Cofactors (Va and VIIIa) Protein S is cofactor for protein S. Protein C and S pathway using the mnemonic: Time To: Thrombin (factor…
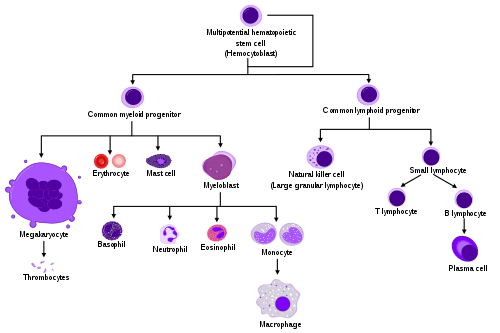
Hematopoietic growth factors list with mnemonics
a. SCF (Steel factor): Multipontent stem cells b. IL-3: Myeloid stem cells (“3” turned down looks like “m“) c. IL-7: Lymphoid stem cell (“L” turned up looks like “7“) d. GM-CSF (Granulocyte macrophage Colony stimulating factor): Myeloid lineage (Erythrocytes, Thrombocytes, Granulocytes and Monocytes) Pharmaceutical: Sargramostim e. G-CSF: Granulocytes (Neutrophil, Eosinophil,…
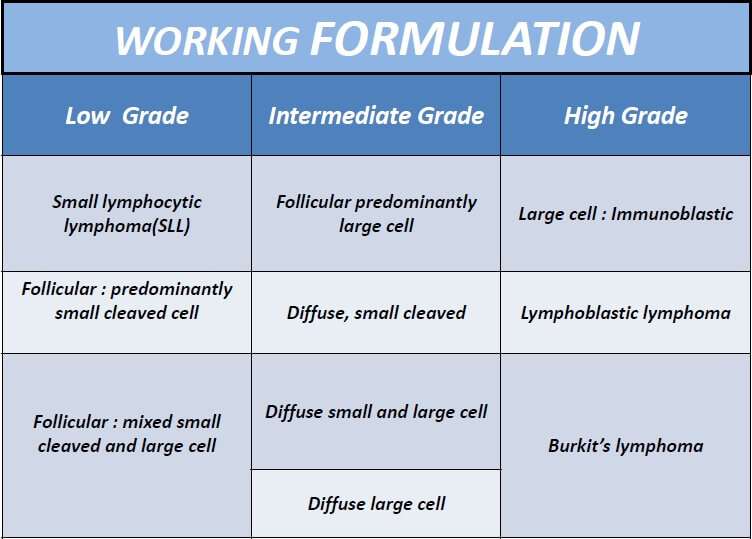
Working formulation of NHL (Mnemonic)
All follicular except large cell: Low grade All diffuse: Intermediate grade Blastic and non-cleaved: High grade
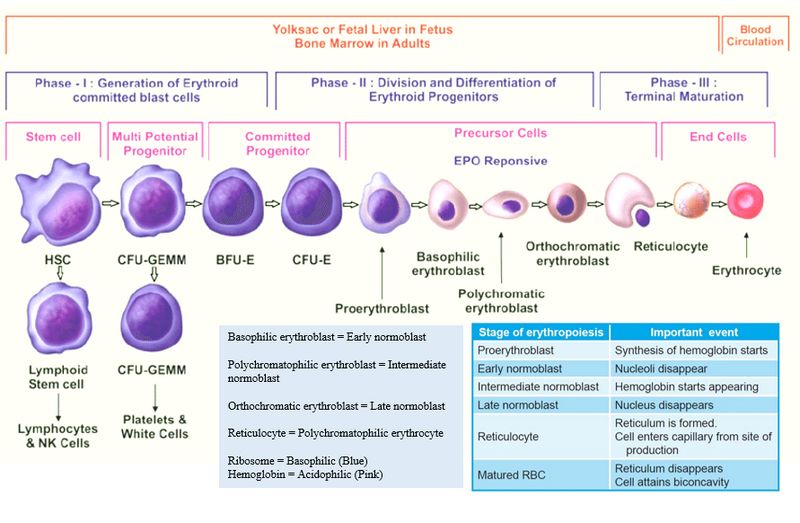
Erythropoiesis Simplified
Hemoglobin Switching mnemonics 1st to appear: Embryonic hemoglobin (Gower and Portland) Switch from fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin: “Gamma goes, Beta becomes, Alpha always” Fetal hemoglobin: α2γ2 Adult hemoglobin: α2β2 ζ chain α chain ε chain HbE Gower 1 HbE Gower 2 γ chain HbE Portland I HbF β chain HbE Portland II…
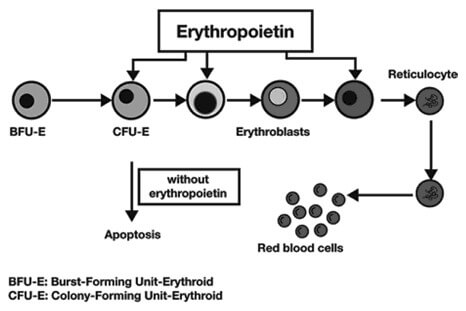
Erythropoietin (EPO) Physiology
Structure of erythropoietin (EPO) Glycoprotein hormone 165 amino acids Molecular mass – 30 kDa Site of production/synthesis of erythropoietin (EPO) Kidneys (75-90%): Peritubular interstitial cells Liver (15%; chief source in fetus and neonates): Centrilobular hepatocytes After birth, erythropoietin is not detectable until 8-12 weeks after birth leading to physiological anaemia…
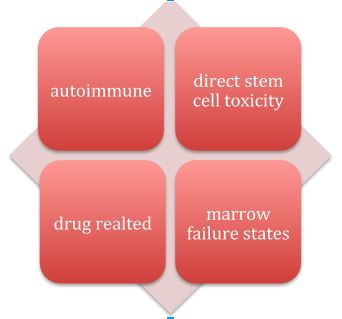
Aplastic Anemia : Review notes
Definition Failure of bone marrow to produce peripheral blood cells and its progenitors Etiology The following illustration gives a brief idea about the etiological factors of aplastic anemia Now going into each etiological factor: – Autoimmune diseases: – Either they affect all the lineages (autoimmune aplastic anemia) or a single…