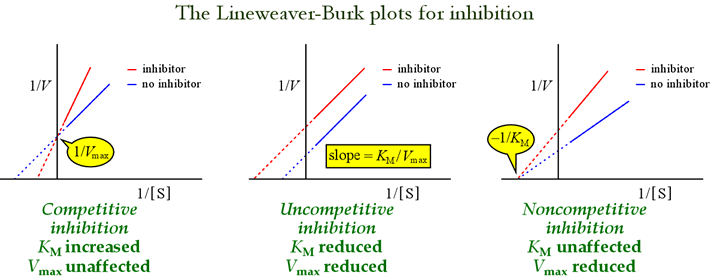
Vmax is the maximum velocity, or how fast the enzyme can go at full ‘‘speed.’’ Vmax is reached when all of the enzyme is in the enzyme–substrate complex. Km is the substrate concentration at which v = 1/2 Vmax. Km approximately describes the affinity of the substrate for the enzyme….
Tag: Biochemistry
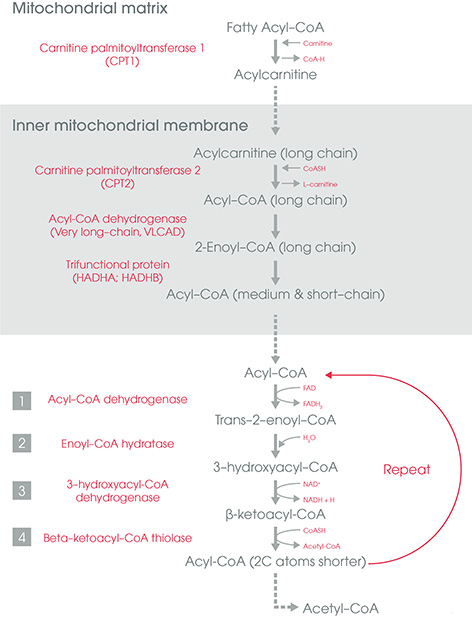
Beta-oxidation of Fatty Acids : Simplified
Fatty Acid Activation (Cytoplasm) Before undergoing oxidation, fatty acid must be activated first by conversion into Acyl-CoA by the action of Fatty Acyl-CoA synthase (thiokinase). ATP is converted to AMP (not ADP) – 2 ATP equivalent used Uses Mg2+ as cofactor, Co-ASH and ATP Sites of Beta-oxidation A. Mitochondria: Short/Medium…
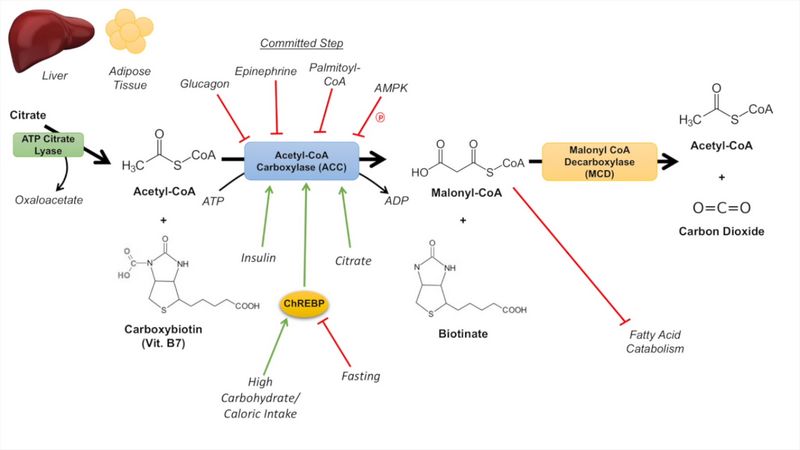
Fatty Acid Synthesis : Simplified
Enzymes: Fatty acid synthase (6 enzymes and 1 Acyl carrier protein molecule) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (rate-limiting enzyme) Starting material: For palmitate synthesis: Acetyl-CoA For odd number carbon long chain fatty acid synthesis: Propionyl-CoA 2 Carbon donor: Malonyl-CoA (donates 2 C and 1 C is thrown out as CO2) Site: Cytosol Citrate…
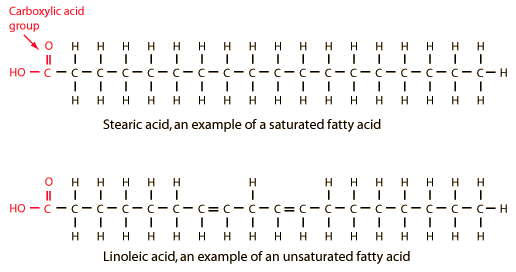
Structure of Fatty acids and Derivatives : Simplified
Structure Saturated fatty acid: Single bond (“S” for saturated and single bond) Unsaturated fatty acid: Double bond(s), i.e. “D” for Double bonds, Decreased melting temperature and Decreased atherosclerotic risk (by decreasing LDL) Trans-fatty acid: Unsaturated fatty acid which act like saturated fatty acid (hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acid) Nomencleture: C…
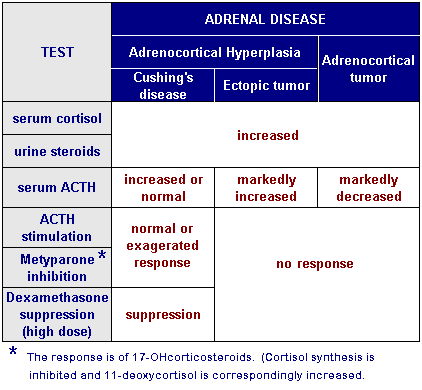
Understanding Dexamethasone Suppression Test
The Dexamethasone Suppression Test (DST) is based on the principle of negative feedback exerted by steroids on pituitary gland’s ACTH secretion. Negative feedback with exogenous steroid works if the cause is excessive ACTH secretion from pituitary: 1. Cushing’s disease (pituitary ACTH dependent Cushing’s syndrome): Excessive ACTH secretion by pituitary adenoma…
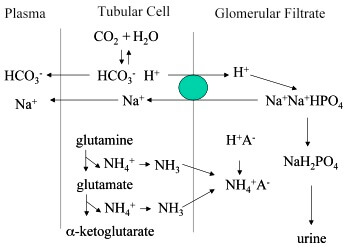
Most Important Urinary Buffer: Phosphate or Ammonia?
There are multiple choice questions (mcq) which asks: What is the most important urinary buffer? And the choices include both the phosphate and ammonia. Different textbooks on physiology and biochemistry have different opinions. Some say that the most important is Phosphate and the others say Ammonia is more important. So,…
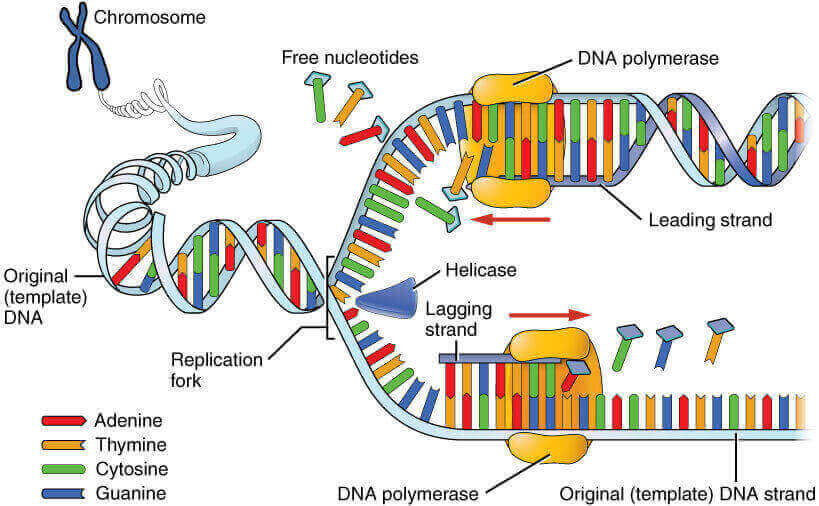
DNA Replication Explained With Zipper Model
Imagine DNA as a zipper Prokaryotic DNA as a zipper with single slider (single origin of replication) and Eukaryotic DNA as a zipper with two sliders (multiple origin of replication). Zipper teeth: Purines and pyrimidine bases Complementary teeth pair: Complementary base pairs attached by hydrogen bonds Top stops: Origin of…
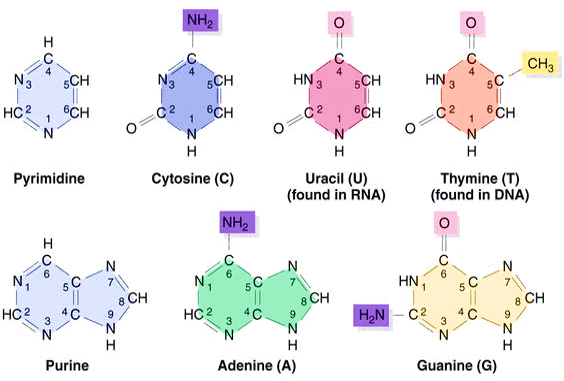
Purine and Pyrimidines : Structure, Synthesis and Metabolism
Purines and Pyrimidines Bases Purines = 2 rings Adenine Guanine Hypoxanthine (Deaminated Adenine) Adenine to Hypoxanthine deamination is mediated by Adenosine deaminase which is decreased in Autosomal recessive SCID. Accumulated dATP inhibit ribonucleotide reductase leading to deficient synthesis of other deoxyribonulceotide precursors for DNA synthesis. Xanthine (Deaminated Guanine) Mnemonics: Pure…