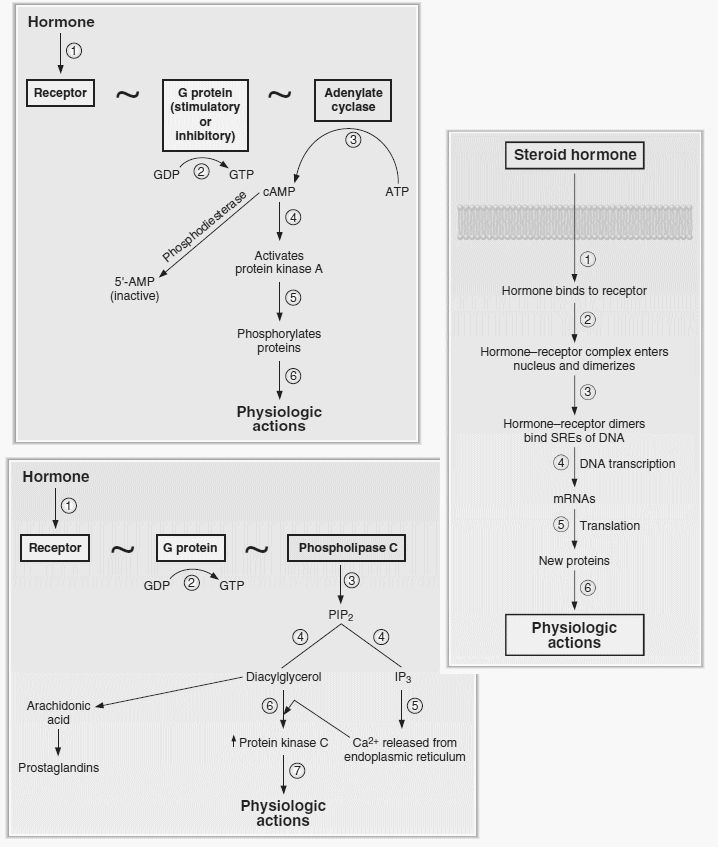
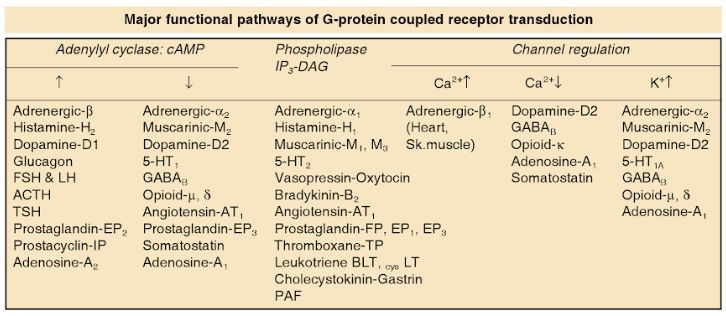
cAMP Mechanism
Mnemonic: FLAT CAMP B-HCGS
Remember “B-FLAT” mnemonic for hormones secreted by basophilic cells of the anterior pituitary. This is the same “FLAT” here.
Also CAMP matches cAMP.
Beta-HCG works by cAMP mechanism.
All 2 except Beta 1 and 5-HT1
So, this is an easy mnemonic to remember.
- FSH
- LH (+ Lipotropin)
- ACTH
- TSH
- CRH
- Aquaporin ADH (V2), Alpha 2 adrenergic (Both have 2) and Adenosine A2
- MSH and M2/M4
- PTH, Prolactin Inhibiting Factor (Dopamine), PGE2-EP2 and PGI2
- Beta adrenergics (Both 1 and 2 – Beta 1 and Beta 2)
- HCG and Histamine H2 (This is also 2)
- Calcitonin
- Glucagon and GABA-B (Assume B = 2)
- Somatostatin, Secretin and Serotonin (5HT-1 and 5-HT4)
c-GMP Mechanism
Mnemonic: Starts with “N”
- Natriuretic peptides (ANP and BNP)
- Nitric oxide (NO)
- Night vision (photic response of retinal rods)
IP3/DAG Mechanism
Mnemonic:
- Hypothalamic hormones except CRH and V2 ADH
- All 1 except Beta 1, Dopamine 1 and 5-HT1 (c-AMP mechanism)
- BCGS
- 3 P (Matches with IP3)
- GnRH
- TRH
- GHRH
- Oxytocin (produced by hypothalamus and stored in posterior pituitary)
- V1 (ADH)
- Alpha 1 adrenergic
- H1
- AT1 (Angiotensin II)
- Endothelin-1
- M1/M3/M5
- Bradykinin (B1 and B2)
- Cholecystokinin
- Gastrin and Ghrelin
- Serotonin (5-HT2)
- substance P
- PDGF
- Prostaglandins and leukotrienes (PGE2 – EP1/EP3, PGF, Thromboxane, LTB4, cysLT )
Tyrosine kinase (MAP and JAK/STAT) Mechanism
Mnemonic:
- All that have “Growth“.
- PIGLET (Remember the mnemonic PiG for anterior pitutiary hormones secreted by acidophilic cells. Both prolactin and growth hormone use tyrosine kinase receptor mechanism)
- MAP kinase pathway – Think growth factors (insulin, IGF-1, FGF, PDGF, EGF)
- Non-receptor (JAK/STAT) pathway – Others
- Growth factors (EGF, FGF, PDGF, NGF, IGF-1 and 2) and Growth hormone
- PIGLET:
- Prolactin
- Insulin
- G-CSF
- Lymphokines (IL-2, IL-6, IFN, TNF, growth factors, GM-CSF) and Leptin
- Erythropoietin
- Thrombopoietin
Hormone response elements (HRE) on DNA
Mnemonic: All lipohilic hormones – Steroids and Thyroids
- Thyroid hormone
- Cortisol
- Aldosterone
- Testosterone
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Vitamin D