1. Division of Airway:
- Extrathoracic (Upper) airway: Nose to Upper trachea
- Intrathoracic (Lower) airway: Lower trachea to Alveoli and lungs
Note: Vocal fold is also regarded as the demarcating line between upper and lower respiratory tract
2. Angle of Louis: Junction of body of sternum to manubrium (2nd costal cartilage anteriorly and T4/5 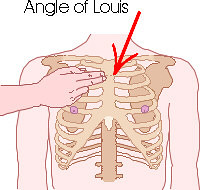
- 2nd rib joins manubrium (Start counting ribs)
- Bifurcation of trachea
- Beginning and end of arch of aorta
- Division of pulmonary trunk
- Division of mediastinum into superior and inferior
- Thoracic duct crosses from left to right
3. Bronchi and bronchioles: About 25 divisions of which last 16 are bronchioles (no cartilage, less goblet cells and less musculature)
4. Lungs and pleura:
a. Base
At Mid-clavicular line (Midpoint between tip of acromion and suprasternal notch)
- Lungs: 6th rib
- Pleura: 8th rib
At Mid-axillary line (Midpoint between anterior and posterior axillary line)
- Lungs: 8th rib
- Pleura: 10th rib
At Vertebral line (Vertical line over spinous process midline)
- Lungs: 10th rib
- Pleura: 12th rib
b. Apex: 1 inch above the clavicle in midclavicular line
c. Medial border: Touches parasternal line at Angle of Louis
- Right lung: Passes vertically downwards to reach base
- Left lung: Follows outer margin of heart to reach base
d. Interlobar fissures:
- Oblique/Major fissure: 6th rib in MCL – 5th rib MAL – medial border of scapula with hyperabducted arm – T2 spine
- Horizontal/Minor fissure (Only on right): Sternum at level of 4th costal cartilage – first line of oblique fissure
Anteriorly: Most upper lobe and whole middle lobe; Posteriorly: Most lower lobe
5. Ribs: 1-7 attach to sternum by cartilage; 8-10 attach to eachother by cartilage; 11-12 floating ribs
6. Topographical division of chest:
a. Anteriorly:
- Supraclavicular region
- Infraclavicular region
- Mammary region: Upper border of 3rd rib to Upper border of 6th rib (sternum to anterior axillary fold)
- Infra-mammary region: Upper margin of 6th rib to lower margin of thorax
b. Laterally: between axillary folds
- Axillary region: Upto upper margin of 6th rib
- Infra-axillary region: Upper margin of 6th rib to lower edge of thorax
c. Posteriorly:
- Suprascapular: Above spine of scapula
- Scapular: Body of scapula below spine
- Infrascapular: Below angle of scapula (7th rib)
- Interscapular: Between posterior edge of scapula
PHYSIOLOGY
a. Inspiration:
- Primary muscle: Diaphragm (Phrenic nerve – C3,4,5), External intercostal
- Accessory muscle: Scalene, Sternocleidomastoid, Alae nasi, Serratus anterior, Others
- Lift and expand chest wall up creating more negative intrathoracic pressure and thus more air enters lung
b. Expiration:
- Primarily: Elastic recoil
- Secondarily: Internal intercostal, Anterior abdominal wall muscles
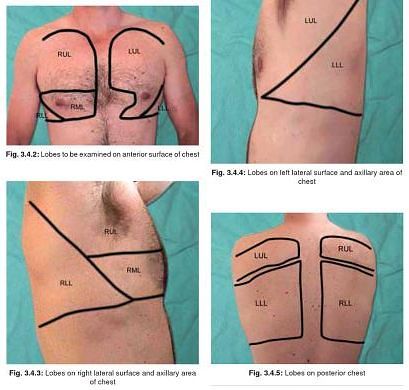
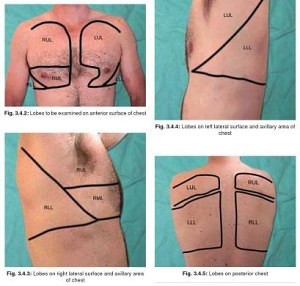
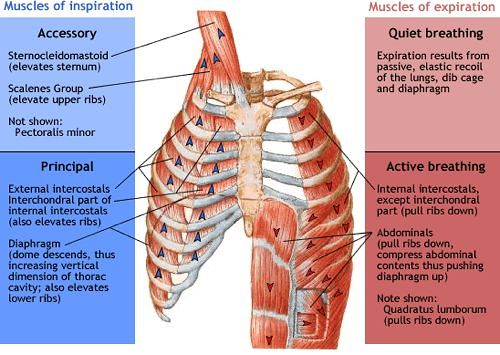
Very clearly explained