Cephalosporins are one of the most widely prescribed antimicrobial drugs. They can be classified into 5 to generations and the medical students often have hard time remembering the names of drugs falling into different generations as the names appear and sound similar. This is a collection of mnemonics from different sources.
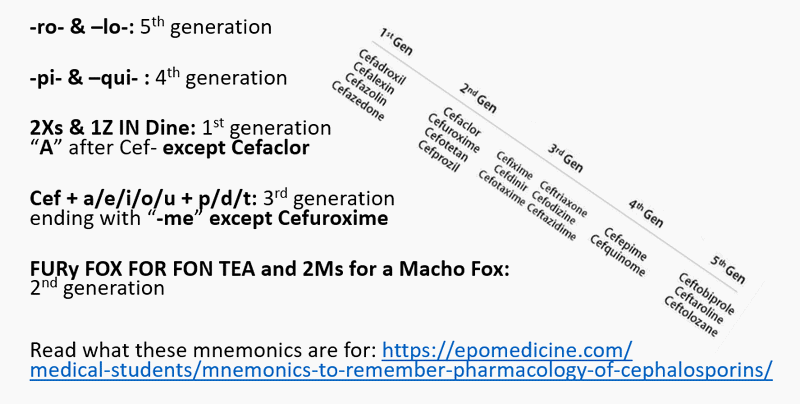
Classification of Cephalosporins
| 1st Generation | 2nd Generation | 3rd Generation | 4th Generation | 5th Generation | |||
| Oral | Parenteral | Oral | Parenteral | Oral | Parenteral | Parenteral | Parenteral |
| Ceph-a-lexin | Cef-a-zolin | Cef-a-clor (exception) | Cefuroxime | Cefixi-me | Cefotaxi-me | Cefi-pi-me | Cefta-ro-line |
| Cef-a-droxil | Cefuroxi-me axetil (exception) | Cefotetan | Cefpodoxi-me axetil | Ceftizoxi-me | Cefi-pi-rome | Ceftobip-ro-le | |
| Ceph-a-ridine | Loracarbef | Cefoxitin | Ceftibuten | Ceftriaxone | Cef-qui-nome | Cefto-lo-zane | |
| Cefprozil | Cefmetazole | Cefditoren | Ceftazidi-me | ||||
| Cefdinir | Cefoperazone | ||||||
| Moxalactam | |||||||
Mnemonic for Oral and Parenteral Cephalosporins
Parenteral:
- All 4th and 5th generation cephalosporins
- Have “t” except ceftibuten and cefditoren
- Having “z” – zone, zolin, zole
Oral: Have “OR” in the name – Cefaclor, Cefditoren, Loracarbef
Menmonic to remember classification by generation of Cephalosporins
A. 5th generation:
- With “ro” and “lo”: ceftobiprole, ceftaroline, ceftolozane
B. 4th generation:
- With “pi” and “qui”: Cefepime, Cefepirome, Cefquinome
C. 1st generation:
All cephalosporins having “A” after “Cef” are 1st generation except Cefaclor.
2 Xs and 1 Z in Dine
- 2 “X” – cefalexin, cefadroxil
- 1 “Z” – cefazolin
- 2 “IN” – cefalothin, cefaparin
- DINE – cephradine
D. 3rd generation:
Cephalosporins ending with “me” are 3rd generation except cefuroxime.
“cef” +/- (a,e,i,o,u) + p/d/t
- cefotaxime, ceftizoxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefoperazone
- cefixime, cefpodoxime, cefdinir, ceftibuten, ceftamet
E. 2nd generation:
FURy FOX FOR FON TEA and 2 Ms for a Macho fox
- ceFURoxime, ceFOXitine, ceFORanide, ceFONicid, cefoTEtan
- cefMandole, cefMetazole
- Remember one more drug: Cefaclor
Flomoxef has been classified by different authors into different generations – 2nd, 3rd and 4th generations.
Short review of pharmacology of cephalosporins
A. Class: Beta-lactams (like Penicillin)
B. Mechanism of action: Disrupt cell wall synthesis by inhibiting transpeptidase (cross-linking)
C. Pharmacokinetics:
- Most are excreted by kideny (tubular secretion).
- 2 “Zones” are secreted in bile: Ceftriaxone and Cefoperazone
D. Blood brain barrier (BBB) penetration:
- 1st generation: No BBB penetration
- 2nd generation: Cefuroxime has highest among 2nd generation
- 3rd generation: Except Cefoperazone and Cefixime
E. Spectrum of activity:
| Generation | Gram Negatives | Gram Positives | β-Lactamase Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | + | +++ | +/- |
| 2nd | ++ | ++ | + |
| 3rd | +++ | + | ++ |
| 4th | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| 5th | +++ | +++ | ++++ |
- 1st generation: Mainly Gram+
Gram – (PEcK): Proteus, E.Coli, Klebsiella
- 2nd generation: Gram- > Gram+
HEN PEcKS: Haemophilus influenzae, Enterobacter, Neissera, Proteus, E. Coli, Klebsiella, Serratia
- 3rd generation: Gram – >> Gram +
Ceftriaxone: Meningitis, Gonorrhea
Ceftazidime and Cefoperazone: Pseudomonas
Used to treat meningitis and sepsis (can cross Blood Brain Barrier) - 4th generation: Pseudomonas
- 5th generation: MRSA
Activity against Bacteroides:
- 2nd generation: Cefoxitin, Cefotetan and Cefmetazole
- 3rd generation: Ceftizoxime (maximum)
Activity agaisnt pseudomonas:
- Ceftazidime (maximum)
- Ceftazolone
- Cefoperazone
Cephalosporins don’t have activity against: “LAME”
- Listeria
- Atypicals (including Mycoplasma and Chlamydia)
- MRSA (Except 5th generation)
- Enterococci
F. Drug of choice:
- Surgical prophylaxis: Cefazolin
- Melioidiosis (Burkholderia psudomalleri): Ceftazidime
- Gonorrhea, salmonellosis (including typhoid), E. coli sepsis, Proteus, Serratia, Haemophilus and empirical therapy for bacterial
meningitis: Ceftriaxone - Pseudomonal CNS infection: Ceftazidime or Cefepime or Meropenem (For GU and GI infections – Fluoroquinolones and Aminoglycosides)
- Bacteroides: Metronidazole (Cefoxitin is an alternative along with clindamycin and chloramphenicol)
G. Adverse effects:
- Drugs with methylthiotetrazole group: Cefamandole, Cefoperazone, Cefotetan, Moxalactam
- Acts like oral anticoagulant (Vit. K antagonist): Bleeding (hypoporthrombinemia)
- Disulfiram like reaction
- Biliary sludging:
- Ceftriaxone
- Cefotaxime
- Taste disutrbance: Ceftobiprole
- Non-bloody red stools: Cefdinir
- Nephrotoxicity:
- Cephaloridine (highest nephrotoxicity)
- Cephalothin
- Neutropenia: Ceftazidime
- Thrombophlebitis (Parenteral)
- Diarrhea
- Anaphylaxis
Mnemonic: “DDT HAPeNS”
D – diarrhea
D – disulfiram like reaction
T – thrombophlebitis
H – hypoprothrombinemia
A – allergy (hypersensitivity)
P – pain (severe with i.m.)
N – nephrotoxicity
S – super infections with fungi
H. Summary mnemonics for generation of cephalosporins:
- First Generation = “FA/PHA”
- Second Generation = “Everything Else”
- Third Generation = “ONE/TEN/IME”
- Fourth Generation = “PI” and “QUI”
- Fifth Generation = “ROL”

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.


I love you. Thank you so much
Great job 🙂
Thankyou
Thank you sooo much… It saved my time and helped me to quickly learn them without mess… Thanks… 🙂
what a nice job.keep it coming
Your absolutely amazing!!!
Thank you !
Jazak Allah khair
Thank you !
Quite helpful…. thanqq so much..
I was totally cef cef before reading this 😀
Interesting medical discussion guys.
So damn helpful. God bless you.
Thanks
U are a genious ….thank you so much…
Nice job………..:)
It is important for medical student and physcian. Thanks
It is a nice mnemonic ever! Now I memorize simply. THANK YOU!
Tq u so much
Thank you so much!!!
Still hard for me to remember all, tried my best but only 1st and 2nd generation stick in my mind…all in all thanks for your help …
Very nice mnemonics & saved my time.. Thank you so much..!!
You helped me learn cephalosporins better than EVER !!!!!
Thank you so much ..
God bless the womb that be-got you
its still hard for me to remember the 3rd generation cephalosporins …can someone help me
Nice mnemonics. Very good revision of topic. Thank you.
Thanks a lot. 🙂
Thank you. Just a note in terms of third gen mnemonic. It says all drugs ending in -me are third generation except cefuroxime. I just wanted to add cefepime to that except also, which is fourth gen
Thanks you. ..
it was very helpful
IWAS VERY HAPPY ,THANKYU SO MACH
thank you so much it was really helpful..
(Pakistan)
Thnk u soo much …as it bcm vry diff 2 remember dis classification as dey all r hmshkl😃
This was so very useful. Thank you.
TYSM THIS IS VERY HELPFUL
ADD 4TH,5TH GEN TOO
tysm