Limbic system is complex both structurally and functionally. It is located on either side of the thalamus, immediately below the cerebrum and consists of both the grey mater and white mater. Let us simplify the structure of limbic system:
- Hypothalamus is central to the limbic system
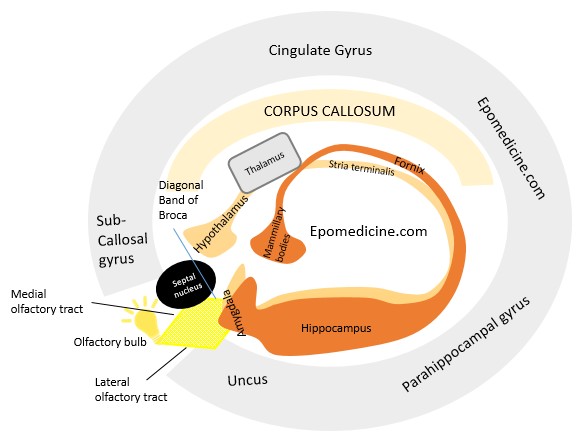
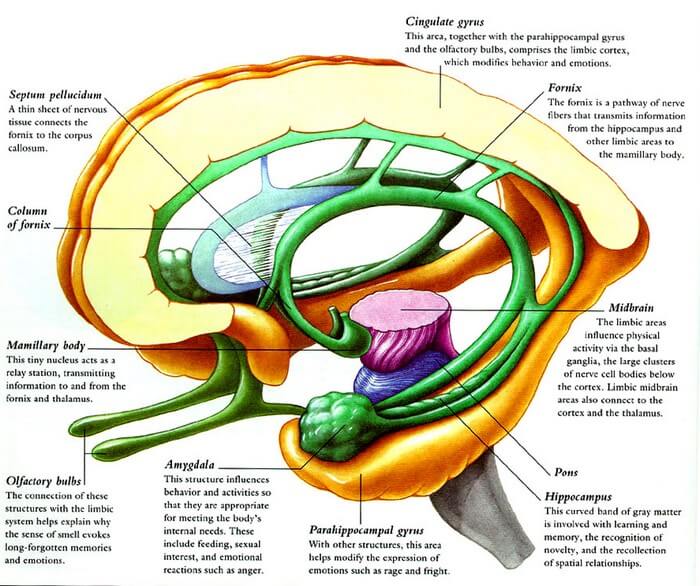
- Limbic cortex: 2 “C” shaped concentric gyri surrounding the corpus callosum.
- Limbic gyrus: Above corpus callosum
- Cingulate gyrus which is continuous anteriorly as Sub-callosal gyrus and posteriorly has para-hippocampal gyrus (overlying the hippocampus)
- Para-hippocampal gyrus contains pyriform cortex which includes entorhinal cortex and uncus.
- Intralimbic gyrus (Hippocampal formation): Below corpus callosum
- Dentate gyrus
- Hippocampus proper
- Suiculum
- Transitional (5 layered) between Entorhinal cortex (6 layered neocrotex) and Hippocampus (3 layered allocortex)
- Limbic gyrus: Above corpus callosum
- Subcortical structures:
- Amygdala
- Septal nucleus
- Anterior nucleus of thalamus
Limbic System Mnemonic
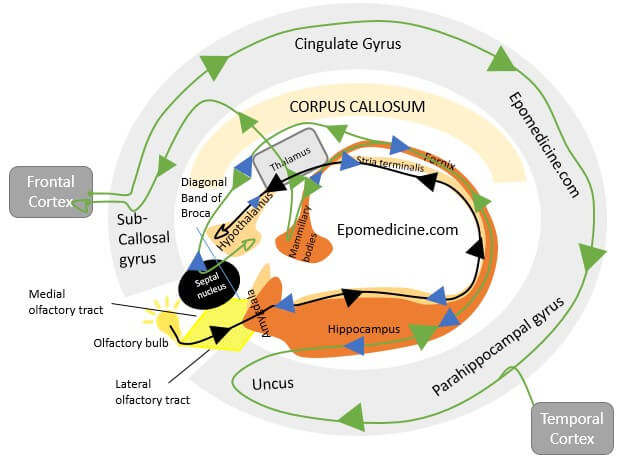
I will provide you with a visual mnemonic to help you build limbic system in your mind and also easily remember it. Try drawing it on a piece of paper without looking after going through it. This will help you to understand the orientation of the limbic system in human brain.
- Hippocampus means mythical sea monster that resembles a sea horse.
- Imagine 2 Sea horses sleeping under the light bulb under the sea (“C”).
- The sea “C” is flipped horizontally and there are 2 big “C”s surrounding 2 seahorses:
- Inner smaller “C” representing Corpus callosum.
- Outer larger “C” representing Cingulate gyrus and it’s Continuations.
- The sea horses are sleeping under the the light bulb:
- The light bulb is the olfactory bulb.
- The illumination of light bulb around the head of the seahorses form several structures:
- Illumination field: Anterior perforated substance
- Superior lateral border: Lateral olfactory tract
- Superior medial border: Medial olfactory tract
- Inferior medial border: Diagonal band of Broca
- Medial to the Medial olfactory tract and just below the limbic gyrus lies Septal nucleus.
- Now the 2 sleeping sea horses:
- Outer sea horse:
- Body = Hippocampus
- Tail = Fornix
- Tail fin = Mammillary body
- Inner sea horse:
- Body and tail = Stria terminalis
- Tail fin = Hypothalamus
- Head of both sea horses = Amygdala
- Outer sea horse:
- Thalamus lies above hypothalamus.
- Dorsomedial nucleus: Connected to amygdala
- Anterior nucleus: Connected to mammillary bodies
We have skipped unnecessary structures in this diagram. Now, we will discuss the pathways of limbic system in concise, eliminating unnecessary details.
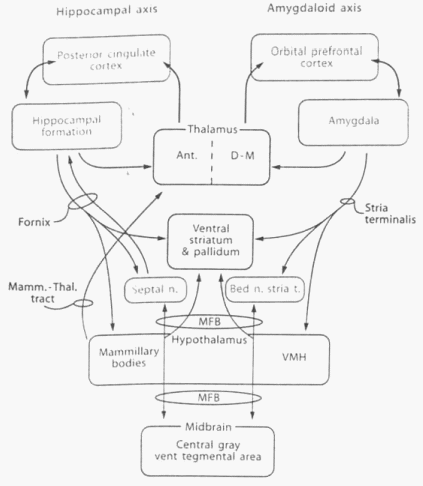
Limbic Connections
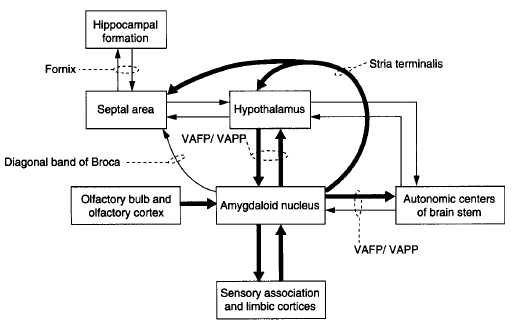
Most conspicuous are the reciprocal connections with hypothalamus.
Hypothalamus and Mammillary bodies:
- communicate with Hippocampus and Septum via Fornix.
- communicate with Amygdala via Stria terminalis and Amygdalofugal fibers.
- communicate with frontobasal parts of Olfactory brain via Medial forebrain bundle.
Limbic system communicates with neocortex by the way of Frontal and Temporal regions.
- Temporal brain: mediates primarily information from visual, auditory and somatosensory cortices to Amygdala and Hippocampus.
- Frontal brain: only neocortical region with direct neuronal connections to hypothalamus.
INTERNAL CIRCUITS
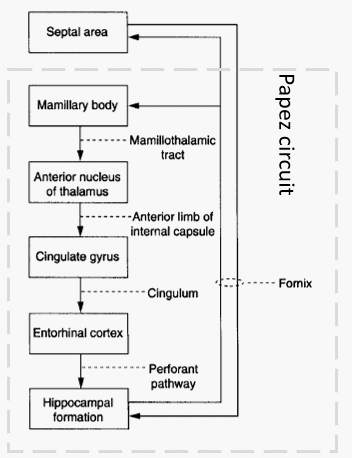
| Hippocampal axis | Amygdaloid axis | |
| Sense | Extroceptive | Introceptive |
| Function | Congitive process – learning and memory | Generation of emotion and motivational states |
| Afferent | Receives information from cortical sensory organs | Receives information from cortical sensory organs and internal organs |
| Thalamic connection | Anterior thalamus | Dorsomedial thalamus |
Functions of Limbic System and Structures
Olfaction:
- Amygdala plays role in emotional response to smell.
- Entorhinal cortex (parahippocampal gyrus) plays role in olfactory memory.
Hypothalamic nuclei and their function
Lesions of Limbic System
Bilateral lesion of Cingulate gyrus – Abulia
- Loss of initiative and inhibition and dulling of emotions.
- Memory is unaffected.
Bilateral lesion of Amygdala – Kluver Bucy Syndrome
- Hyperorality
- Visual, tactile and auditory agnosia
- Placidity
- Intense desire to explore immediate environment (hypermetamorphosis)
- Hypersexuality
More details about Kluver Bucy Syndrome.
Hippocampus
- Most epileptogenic part
- Bilateral lesion of hippocampus – Amnestic (Confabulatory) syndrome
- Anterograde amnesia (unable to learn and retain new information)
- Intellect unaffected
- Procedural memory unaffected
Fornix
Bilateral lesion of fornix leads to acute amnestic syndrome i.e. inability to consolidate short-term memory to long-term memory.
Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
Cause: Thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency
The involved structures are:
- Mammillary bodies
- Dorsomedial thalamus
- Periaqueductal grey
- Pontine tegmentum
Clinical manifestations:
- Ocular disturbances and nystagmus
- Gait ataxia
- Mental dysfunction
Sommer’s sector
- Junction of Hippocampal area CA1 (Cornu Ammonis 1) and Subiculum
- Very sensitive to ischemia

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.

Hello all at epomedicine,
I am currently writing a paper on the limbic motor system in horses and requesting permission to use one of your illustrations.
Kind regards
Dr David Fairclough (osteopath).
I find the image showing connectivity to be very clear and useful. I would like permission to use it for a neuroscience and clinical reasoning class I teach to occupational therapists. Thank your for your consideration.