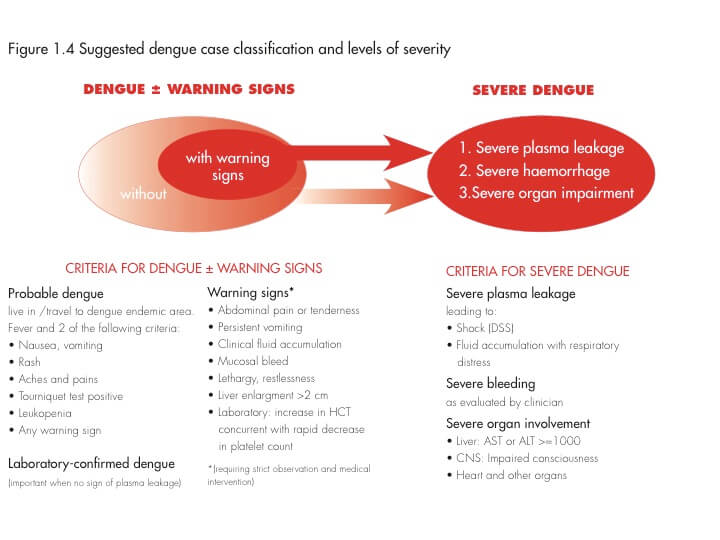
Jod = Addition in Hindi or Nepali = Iodine induced Hyperthyroidisim
ChaikOFF = Thyroid hormone synthesis is switched OFF = Iodine induced Hypothyroidisim
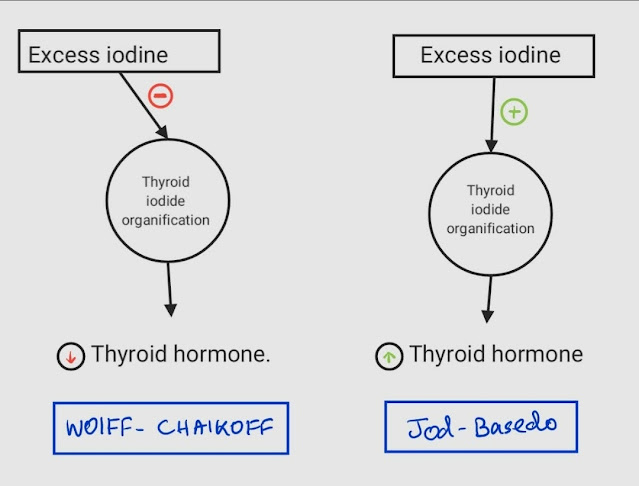
Mechanism
| Jod-Basedow | Wolff-Chaikoff | |
| Pre-requisite | Abnormal thyroid gland free from pituitary control | Thyroid gland under pituitary control |
| Conditions | Endemic goitre, Grave’s disease, Toxic multinodular goitre, Thyroid adenoma | Normal thyroid (Euthyroid), Hyperthyroid (Grave’s disease) |
| Mechanism | Excess iodine stimulates thyroid iodide organification | Excess iodine inhibits thyroid iodide organification |
| Result | Iodine induced hyperthyroidism | Iodine induced hypothyroidism a. Normal thyroid (Euthyroid): Escapes after 10 days b. Autoimmune thyroid: Persists After |