Thyroid Hormone Functions
Mnemonic: 7 X B’s
- Basal metabolic rate
- Blood sugar (increases glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis)
- Break down lipids (lipolysis)
- Bone growth (synergism with growth hormone)
- Beta-adrenergic effects
- Brain maturation
- Babies – stimulation of surfactant production
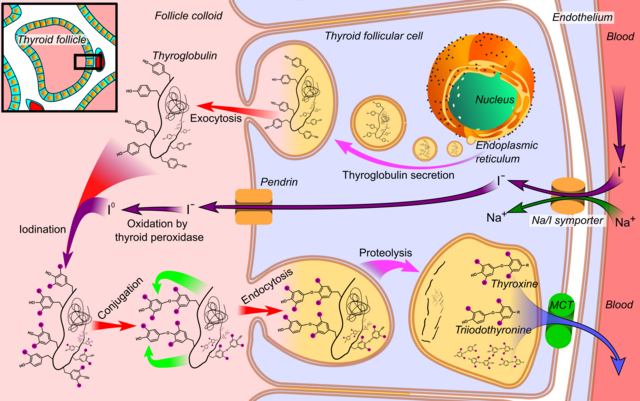
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
Mnemonic: ATE ICE
1. Active transport of iodide:
- Circulation to thyroid follicular cells: via NIS (Na-Iodide Symporter)
- Thyroid follicular cells to lumen: via Pendrin
2. Thyroglobulin (rich in Tyrosine): formed in follicular ribosomes
3. Exocytosis of thyroglobulin into follicular lumen: stored as colloid
4. Iodination: Peroxidase enzyme –
- Oxidation of Iodide (I-) to Iodine (I2)
- I2 + Tyrosine (Organification) = MIT (Monoiodotyrosine), DIT (Diiodotyrosine)
5. Coupling:
- MIT + DIT = T3
- DIT + DIT = T4
6. Endocytosis: of T3 and T4 containing colloid into follicular cells and liberation of free T3 and T4 after proteolysis (mediated by proteases). At the peripheries, T4 is de-iodinated into more active T3.
Another mnemonic: IPOCP
1. Iodide transport
2. Peroxidation
3. Organification
4. Coupling
5. Peripheral conversion
| T3 | T4 | |
|---|---|---|
| Potency | 4 times more than T4 | Less |
| Rate of secretion | Less | 10 times more than T3 |
| Onset of action | Rapid (2-3 hours) | Slow (2-3 days) |
| Half-life | 1 day | 1 week |
| Storage | Less | More (high affinity to proteins) |
| Inactivation | Rapid | Slow |
| Binding | 0.2% in unbound | 0.02% in unbound |
| Source | 20-25% by gland 75-80% by peripheral conversion | 100% by gland |
Inhibition of Thyroid Synthesis and Antithyroid Drugs
| Metabolic step | Inhibitor |
|---|---|
| Iodine transport | Inorganic anions (Perchlorate, Thiocyanate) |
| Iodination | Thionamides (PTU, Methimazole, Carbimazole), Iodides via Wolff-Chaikoff effect (Lugol’s iodone, KI) |
| Coupling | Thionamides |
| Colloid resorption | Colchicine, Li+, I- |
| Deiodination of DIT + MIT | Dinitrotyrosine |
| Hormone release | Iodine, Iodides of Na and K |
| Peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 | Dexamethasone, Beta-blockers (Propranolol), Radiocontrast dye, PTU |
| Destruction of thyroid tissue | Radioactive iodine |