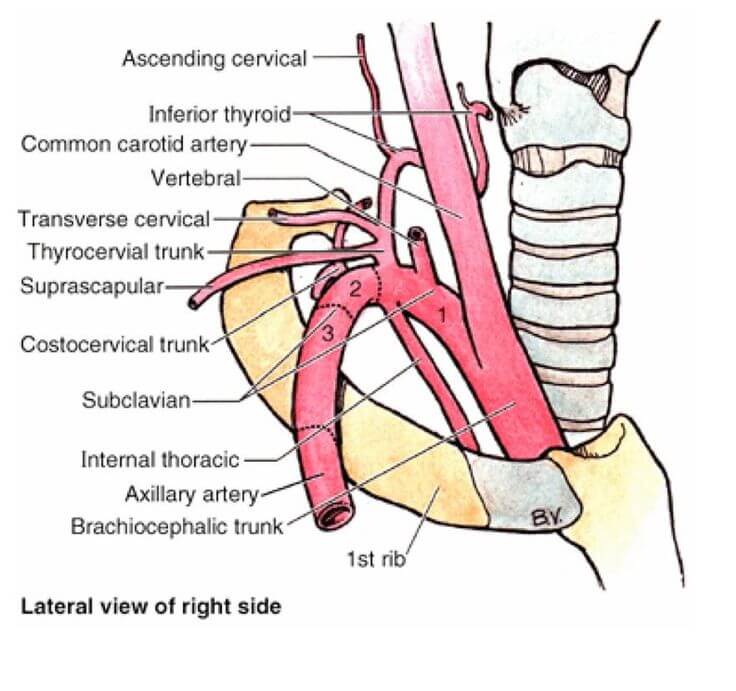
Origin of Subclavian artery:
- Left: Arch of aorta
- Right: Brachiocephalic artery
Extent of Subclavian artery: Arises posterior to sternoclavicular joint and ends at outer border of 1st rib by becoming acillary artery.
Divisions of Subclavian artery: 3 parts in relation to Scalenus anterior muscle
- 1st part (medial to muscle)
- 2nd part (posterior to muscle)
- 3rd part (lateral to muscle)
Branches of Subclavian artery:
Remember Vitamin C and D
Mnemonic: VIT(sit) C(sid) and D
- Orange (VIT – from 1st part)
- Green (C – from 2nd part)
- Blue (D – from 3rd part)
- Vertebral artery
- Internal thoracic artery
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Suprascapular artery
- Inferior thyroid artery (Thyro-)
- Transverse cervical artery (Cervical)
- Costocervical trunk
- Superior intercostal (Costo-)
- Deep cervical (Cervical)
- Dorsal scapular artery

Well done
Very useful