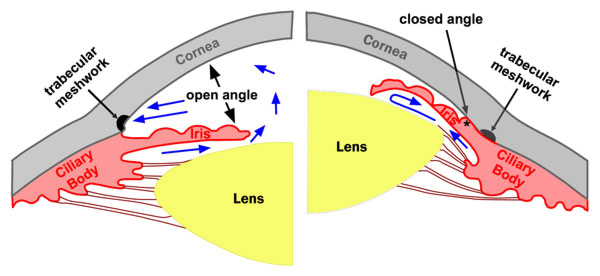
Definition: Glaucoma is a group of disorders characterized by a progressive optic neuropathy resulting in a characterstic appearance of the optic disc and a specific pattern of irreversible visual field defects that are associated frequently but not invariably with raised intraocular pressure (IOP). It is one of the commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world. Open-angle…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
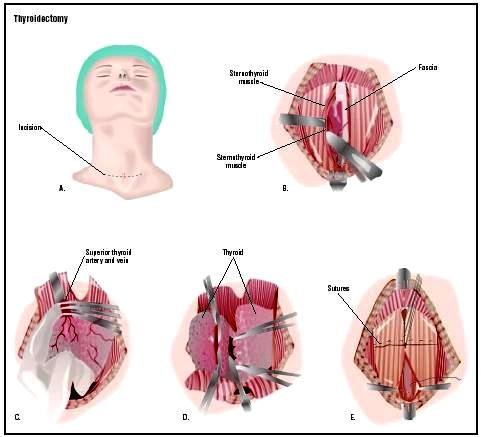
Thyroidectomy Basics
Synonyms: Thyroid resection surgery, Thyroid removal surge Definition: Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. A “thyroidectomy” should not be confused with a “thyroidotomy” (“thyrotomy”), which is a cutting into the thyroid, to get access for a median laryngotomy, or to perform a biopsy. Indications: Proven neoplasm…

Applied Anatomy of Submandibular Salivary Gland
Synonyms: Submaxillary gland (SMG), Mandibular gland Definition: Submandibular glands are one of the major salivary glands comprised of mixed serous and mucous acini and located below the lower border of the body of mandible. It is the second largest salivary gland and produces approximately 70% of the saliva. Location: Submandibular triangle…
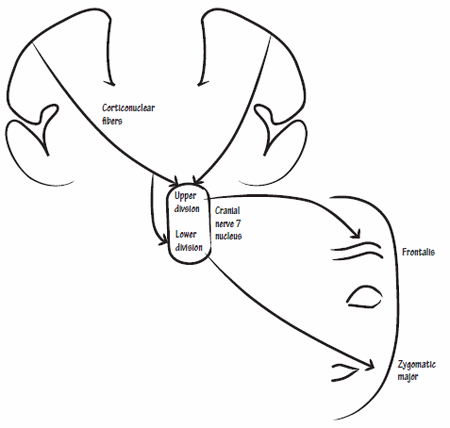
Facial Nerve Anatomy
SYNONYMS: Cranial nerve seven (VII), Nervus facialis Supranuclear pathways 1. Somatomotor cortex: controlling motor component of facial nerve lies in precentral gyrus (Broadmann area 4,6,8) 2. Volitional component: Corticonuclear tracts descend and cross to supply both ipsilateral and contralateral facial (mainly to the contralateral side) nucleus i.e. frontal branch components…
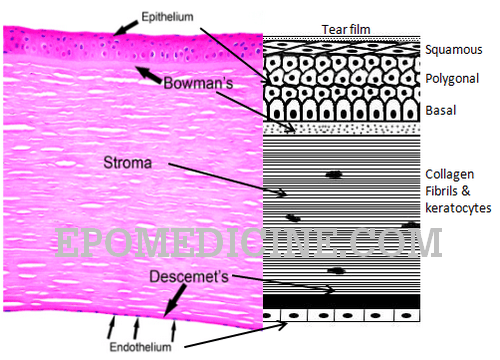
Histology of Cornea and Corneal Dystrophies
Prefix: kerat- Definition: The cornea is a transparent, avascular, watch-glass like structure which forms anterior one-sixth of the outer fibrous coat of the eyeball and covers iris, pupil and anterior chamber. Histology: It consists of 5 distinct layers which can be remembered using the mnemonic “ABCDE“:
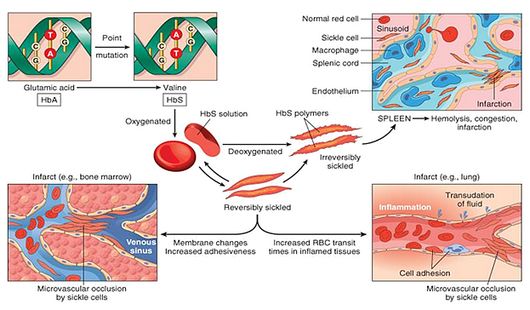
Salmonella Osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary disorder of hemoglobin synthesis caused by a mutation in the globin gene that changes the sixth amino acid from glutamic acid to valine resulting in abnormal sickling (rigid, inflexibled and sickle-shaped) of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) under low oxygen conditions. Sickle cell anemia…
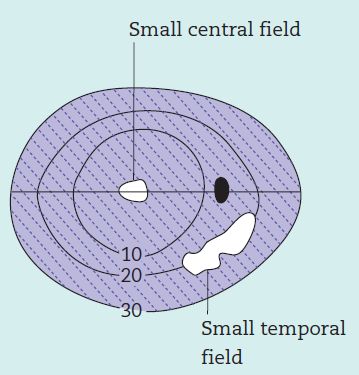
Understanding visual field defects in Glaucoma (Perimetry)
Introduction Field of vision or Visual field is defined as the area that is perceived while fixating one central target. According to traquair’s analogy, visual field is “an island of vision surrounded by a sea of darkness”. It is a 3D hill – peak being fovea and at ground level,…
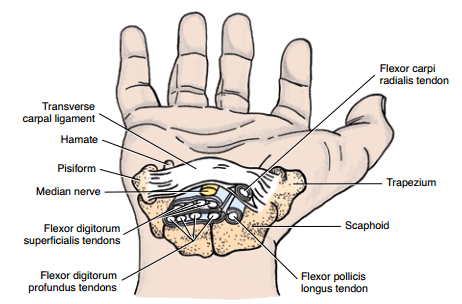
Carpal Tunnel Anatomy
Synonyms: Carpal canal Definition of Carpal Tunnel Carpal tunnel is an osseofibrous space on the palmar aspect of wrist extending from distal volar wrist crease to the mid-palm, which serves as a passageway to the palm for flexor tendons and the median nerve. Boundaries of Carpal Tunnel A. Roof: Flexor…