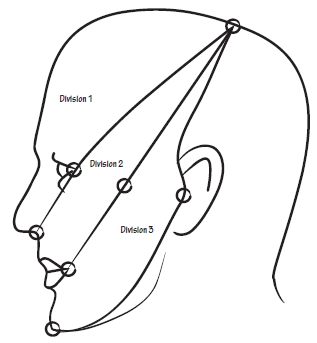
Course of Trigeminal Nerve and Trigeminothalamic Pathway Mandibular (CN V3) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Maxillary (CN V2) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Ophthalmic (CN V1) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Sensory Map Of Trigeminal Nerve on Face Area of Ophthalmic division: Line joining – Just behind the top of head Corner of eyes…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
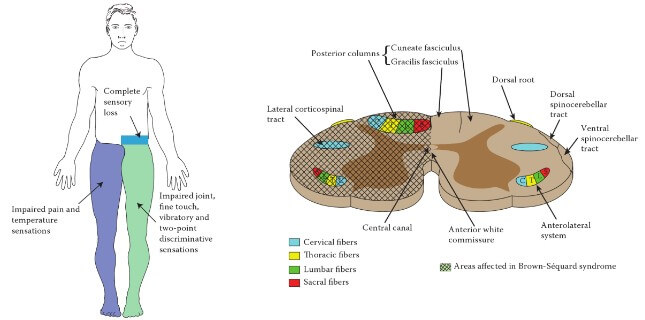
Brown-Sequard Syndrome – Anatomical Basis
Definition of Brown Sequard Syndrome Neurological syndrome resulting from spinal cord hemisection (damage to one lateral half of spinal cord). Causes of Brown Sequard Syndrome Penetrating trauma Spinal fractures Spinal dislocation Disc herniation Vasculitis Radiation induced injury Clinical Manifestations and Anatomical Basis of Brown Sequard Syndrome 1. Damage of Corticospinal…
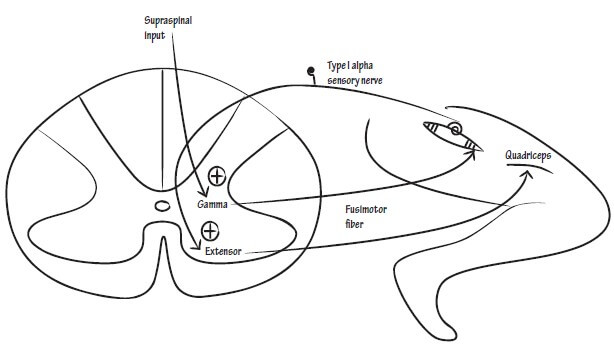
Lower Motor Neuron Lesion (LMNL) – Anatomical Basis
The anatomical basis of Upper Motor Neuron Lesion (UMNL) has already been discussed earlier. Similarly, we will explain the anatomical basis of clinical syndrome of Lower Motor Neuron Lesion (LMNL). A. Ipsilateral involvment: Lower motor neuron comprises of motor neurons in the anterior neurons and the fibers originating from them,…
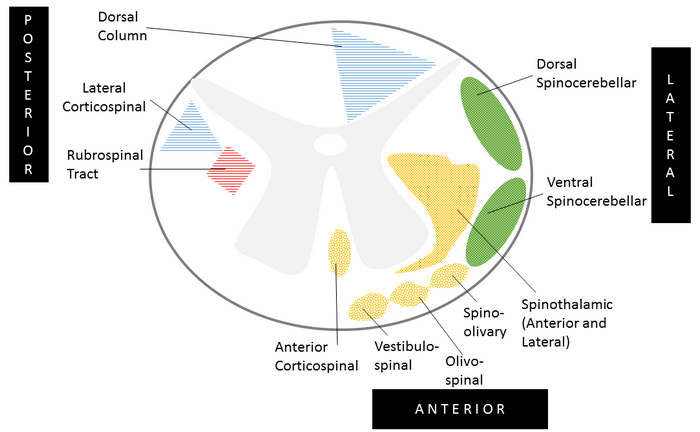
Spinal Tracts Simplified
Organization of Ascending and Descending Tracts in Spinal Cord A. 2 Posterior Tracts: The fibers of these tracts cross to the opposite side at the level of medulla: B. 2 Lateral Tracts: The fibers of these tracts remain on ipsilateral side: C. 2 Anterior Tracts: The fibers of these tracts…

Upper Motor Neuron Lesions (UMNL) – Anatomical Basis
For the purpose of remembering the clinical manifestations of upper motor neuron lesion (UMNL) and lower motor neuron lesion (LMNL), a mnemonic has already been devised and discussed here. Now, it’s time to understand the anatomical and physiological basis of these manifestations. Upper Motor Neuron Lesion (UMNL) Syndrome Acute Manifestations…
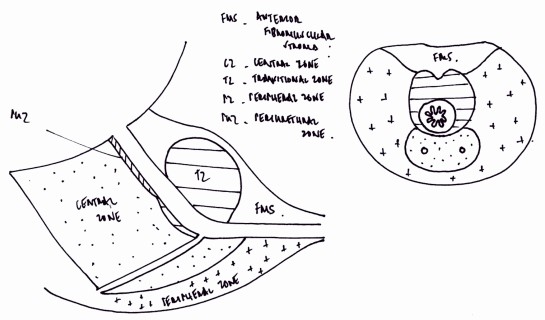
How to draw Medulla Oblongata Cross-section ?
Like in Midbrain and Pons: Corticospinal tract passes ventrally Ventricular system is located dorsally in midline Cranial nerve nuclei are located just anterior to the ventricle Medial longitudinal fasciculus is present around the center Another important thing to remember is that, the caudal medulla resembles “spinal cord“: Circular in shape…
Prostate – Applied Anatomy
Embryology and Development of Prostate Gland Time: During 3rd month of gestation Fetal testosterone is converted by 5α-reductase into 5α-Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone stimulates urogenital sinus mesenchyme, which in turn stimulates formation of prostatic buds (endodermal outhgrowths) from posterior urogenital sinus epithelium. Prostatic buds invade into urogenital sinus mesenchyme. Differentiation:…
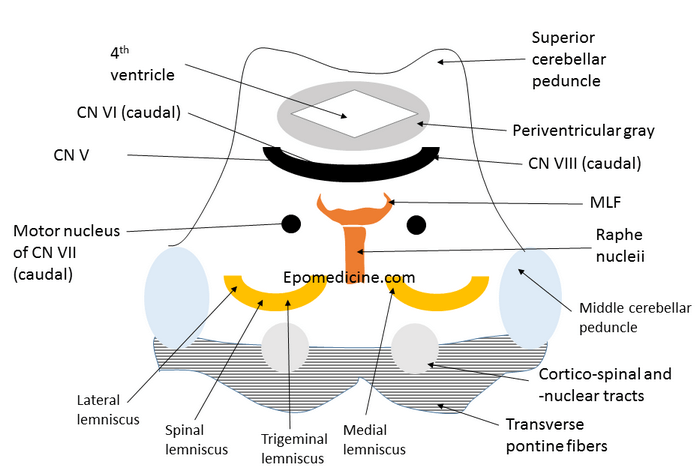
How to Draw Pons Cross-section ?
Pons in latin, refers to a “bridge”. Pons varolli is a part of brain-stem, that links thalamus with medulla oblongata. The cross-section of pons is similar to the midbrain as described earlier but few things must be kept in mind: The orientation of lemnisci in midbrain is more or less…